Materials in Autodesk products represent actual materials such as concrete, wood, and glass. These materials can be applied to parts of a design to give the objects a realistic appearance and behavior. In some design contexts, the appearance of an object is most important, so the materials have detailed appearance properties such as reflectivity and surface texture. In other contexts, the physical properties of a material such as yield strength and thermal conductivity are more important, as the materials must support engineering analysis.
The following figure shows some of the appearance properties for a Bronze, Soft Tin material, as displayed in the Material Browser.
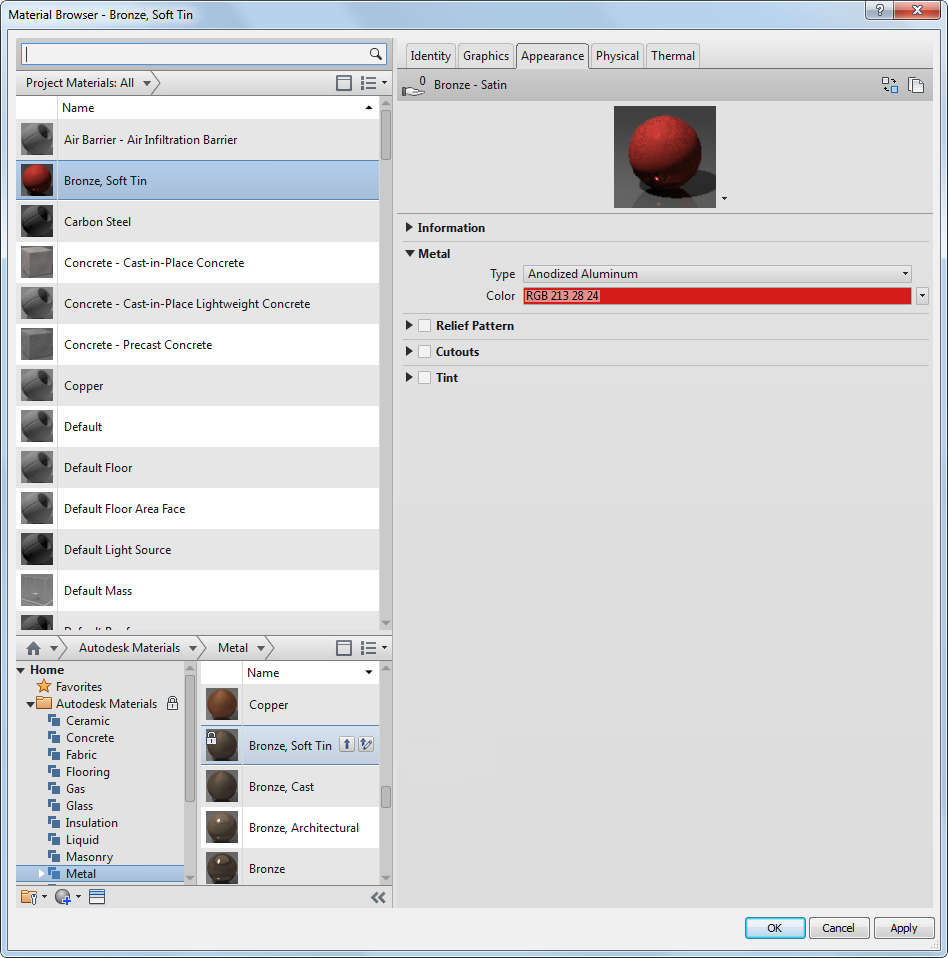
The Material Browser
The appearance properties are grouped in one "asset" of the material, and are managed on the Appearance tab. Other assets associated with the material are managed on the corresponding tab. Each asset can be changed independently when you edit a material that exists in a project. For example, if you want the bronze material to have a red color, you can replace the appearance asset with Anodized Aluminum, an asset with different appearance properties. For more information on assets, see About Material Properties and Assets.
The Material Browser dialog is used to find and manage materials. Common tasks include:
- Adding materials to the current project.
- Placing materials in a collection, known as a material library, for ease of access.
- Editing a material that is in the current project.
- Adding an asset to a material.