The following equation describes the non-Newtonian Power Law property variation:
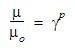
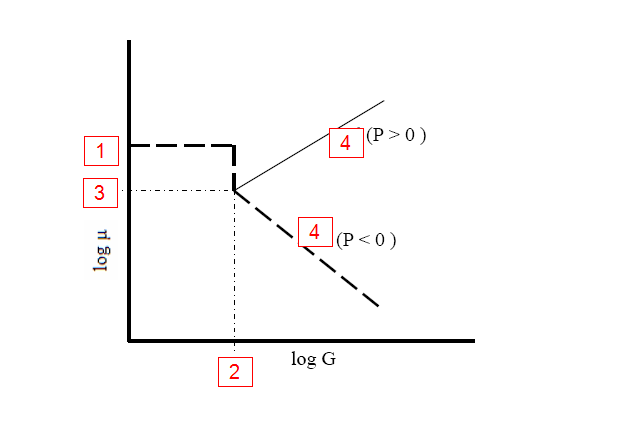
1. Cutoff Viscosity: This is the viscosity of the fluid as a Newtonian fluid.
2. Cutoff Strain Rate: The strain rate at which the fluid becomes Non-Newtonian.
3. Viscosity Coefficient: The viscosity of the fluid when the fluid becomes Non-Newtonian.
4. Power Law Exponent: Determines whether the fluid is shear thickening (P > 0) or shear thinning (P < 0). A Power Law Exponent of 0 is a Newtonian fluid. (The power law exponent is related to the power law index as p = n-1.)
If a viscosity cutoff is not applicable:
- Enter values for the Viscosity Coefficient and the Power Law Exponent
- Leave the Cutoff Strain Rate at the default.
- Make the Cutoff Viscosity = the Viscosity Coefficient.
Example:
- A non-Newtonian fluid has a viscosity = 0.0033 Pa-s.
- The Power Law index is known to be 0.62.
- This fluid does not have a cutoff viscosity, meaning that it behaves as a non-Newtonian fluid through its range of properties.
The material is defined by specifying the following properties:
| Cutoff Viscosity = 0.0033 Pa-s |
| Cutoff Strain Rate = 0 |
| Viscosity Coefficient = 0.0033 Pa-s |
| Power Law Exponent = -0.38 (= 0.62-1) |
To model a constant viscosity that starts to vary at a given strain rate:
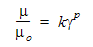
- Enter this viscosity as the Cutoff Viscosity
- Enter the strain rate in the Cutoff Strain Rate
- Enter the constant k in the Viscosity Coefficient field.