The electrostatic analysis system is used in the design and analysis of a structure with focus on the electrical conduction of the structure and insulation properties. It is intended to be used when electric currents or electric fields are an issue in the design of a product (for example, fuses, transmission lines, insulators).
This system provides a means of creating the models (or editing existing designs), defining electric elements, boundary conditions and properties, processing the model with these factors, and observing views of the structure to see the current or field results.
Governing Equations for Electrostatic Analyses
The governing partial differential equation (PDE) is the Poisson equation. This PDE is valid for both dielectric material (Electrostatic Field Strength and Voltage) and resistive material (Electrostatic Current and Voltage) analysis. The strong form of the problem is defined in the following section:

When performing an Electrostatic Current and Voltage analysis, h represents the current flux normal to a surface. The current at a point is defined as:
When performing an Electrostatic Field Strength and Voltage analysis, h represents the displacement flux normal to a surface. The displacement field at a point is defined as:
The electric field at a point is defined as:
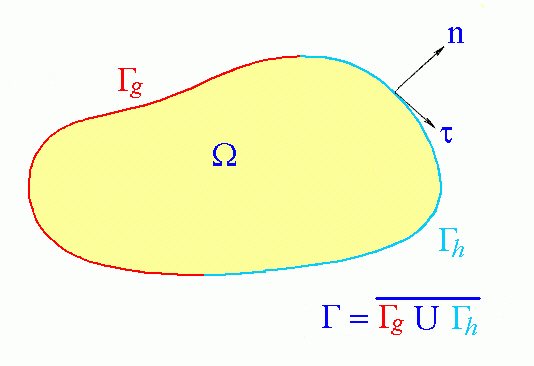
Figure 1: The Computational Domain