The nominal stress, SN, approach to calculating life requires minimal input to describe the material fatigue characteristics. The SN curve is generated from the material tensile strength and your input for material endurance limit.
The SN curve in the Fatigue Wizard is constructed as a straight line, on a log-log plot, from a point equating to 90% of the tensile strength at 1000 cycles, passing through the defined endurance limit at (typically) 1E7 cycles.

Life calculation is then performed as a simple linear interpolation between these points.
Mean Stress Correction
Most SN test data is generated under conditions of fully reversed loading, that is, with a mean stress of zero. The mean stress in a cycle can affect the component life. Therefore, several methods of accounting for the effect of mean stress are proposed for the SN-based fatigue-life relationship. The Fatigue Wizard utilizes two methods to calculate an equivalent (zero mean) stress; the Gerber correction and the Goodman correction. Compressive mean stress is ignored.
Gerber Correction
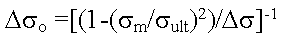
Goodman Correction
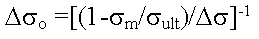
Where

Graphical example

From FEA, for a given node, it is possible to calculate a mean stress (Sm) and an amplitude stress (SA) .
If the FEA stress falls within the  . zone (Goodman) or
. zone (Goodman) or  .+
.+  . zone (Gerber) the nodal stress is acceptable.
. zone (Gerber) the nodal stress is acceptable.
The software performs this calculation for all nodes in the model.