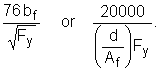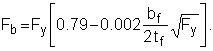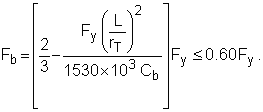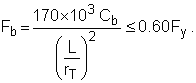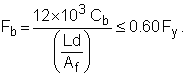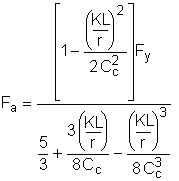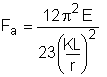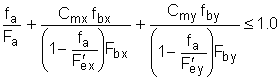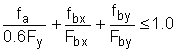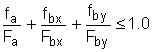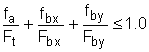X: Strong axis
Y: Weak axis
Z: Primary axis
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| α | Rotation angle for principal axes of angle section |
| A | Cross-sectional area |
|
A f |
Area of compression flange. |
|
A s |
Shear area for tubular member - pipe |
|
A sx |
X shear area of prismatic member |
|
A sy |
Y shear area of prismatic member |
|
b |
Width of member (b ≤ d) |
| b 0 |
Distance from neutral axis to edge of web:
|
|
b e |
Effective width of structural tubing member |
|
b f |
Width of flange. |
|
C b |
Bending coefficient dependent upon moment gradient (section F). |
|
C c |
Column slenderness ratio separating elastic and inelastic buckling (section E). |
| C mx , C mx |
Coefficient applied to bending term in interaction equation (section H). |
|
d |
Depth of member (d ≥ b) |
|
E |
Modulus of elasticity |
|
E 0 |
Distance of the shear center from center line of web for channel: E 0 = e 0 + t w /2 |
|
F a |
Maximum allowable compressive stress |
|
F b |
Maximum allowable bending stress |
|
F bx |
Maximum allowable strong axis bending stress |
|
F by |
Maximum allowable weak axis bending stress |
|
F ex , F ey |
Euler stress for a prismatic member divided by factor of safety. |
|
F t |
Maximum allowable tensile stress |
|
F y |
Yield stress |
|
F n |
Maximum allowable shear stress |
|
f a |
Computed axial stress (either tension or compression, both taken as positive) |
|
f b |
Computed bending stress (taken as a positive quantity) |
|
f bx |
Computed strong axis bending stress |
|
f by |
Computed weak axis bending stress |
|
f νx |
Computed shear stress in X direction |
| f νy |
Computed shear stress in Y direction |
|
h |
Clear distance between flanges in I-shaped members: h = d 2t f |
|
I x , I y |
Moments of inertia about principal axes |
|
I u , I v |
Moments of inertia about principal axes of angle section member |
|
K |
Effective length factor for prismatic member |
|
L |
Distance between cross sections braced against twist or lateral displacement of the compression flange. |
|
L b |
Laterally unsupported length of the compression flange. |
|
L c |
Maximum unbraced length of the compression flange. |
|
L x L y |
L in X and Y directions |
|
M 1 , M 2 |
Smaller and larger moment at end of unbraced length, respectively. |
|
P |
Axial force load |
| r |
Governing radius of gyration |
|
r T |
Radius of gyration of a section comprising the compression flange plus 1/3 of the compression web area, taken about an axis in the plane of the web |
|
r x , r y |
Radius of gyration about principal axes. |
|
t |
Thickness |
|
t f |
Thickness of flange |
|
U, V |
Principal axes of angle section member |
|
u, v |
Distances from principal axes |
| x, y |
Offsets of centroid of angle section |
Allowable Stresses
X is the strong axis, and Y is the weak axis for all I-shaped and members and channels. Tees can have either axis as their strong axis.
1. Strong Axis Bending Stress
- Members loaded along their weak axis, Y (bent about their strong axis, X).
- This maximum allowable strong axis bending stress is referred to as F b in this section.
- Two categories are considered:
- I-shaped members, tees and channels
- Pipes and structural tubing, including square and rectangular ducts and pipes
1.A. Members with compact sections
- Includes tees with compact flanges.
- Tees loaded along then X-axis are not considered, in this code check.
- Applicable to all I-shaped and members and channels, and tees with I xx > I yy . Tees with I xx ≤ I yy are not considered in code check.
Category I. I-shaped members, tees and channels Section F1.1
The allowable bending stress is
|
F b = 0.66 F y |
(F1-1) |
with the constraint that L b ≤ L c , which is given by the smaller of:
|
|
(F1-2) |
-
F b = 0.66 F y
(F3-1) - subject to the following conditions:
- Rectangular members cannot have a depth greater than 6 times the width.
- L b ≤ L c , where L c is given by
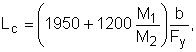
(F3-2)
Category II. Pipes and structural tubing Section F3.1
The allowable bending stress is
except, that L c need not be less than 1200 (b/F y ), M 1 is the smaller and M 2 is the largest bending moments about the ends of the unbraced length, taken about the strong axis.
1.B. Members with noncompact sections
- Must satisfy constraint, L b ≤ L c (F1-2) or (F3-2), including that rectangular members cannot have a depth greater than 6 times the width.
- Includes tees with noncompact flanges.
- Tees loaded along the X-axis are not considered.
Category I. I-shaped members, tees and channels Section F1.2
|
|
(F1-3) |
Category II. Pipes and structural tubing Section F3.2
|
F b = 0.60 F y |
(F3-3) |
1.C. Members with compact or noncompact sections with L b > L c
- The section is only applicable to Category I. I-shaped members, tees and channels.
If member is in tension,
|
F b = 0.60 F y |
(F1-5) |
If member is in compression, the allowable bending stress is determined as the larger value from equations (F1-6) or (F1-7) and (F1-8), with the exceptions:
- Only equation (F1-8) is used for channels.
- None of these equations apply to tees in compression, thus such tees are not considered.
When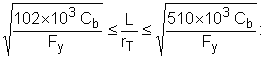
|
|
(F1-6) |
When 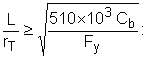
|
|
(F1-7) |
For any value of L/r T :
|
|
(F1-8) |
C b is conservatively taken as unity (1.0) in equations (F1-6), (F1-7) and (F1-8).
2. Weak Axis Bending Stress
- The section is only applicable to Category I. I-shaped members, tees, channels and solid bars (prismatic members).
- Category II. Structural tubing in this category use same value of F b found for their strong axis for their weak axis.
- Members loaded along their strong axis, X (bent about their weak axis, Y).
- This weak allowable strong axis bending stress is referred to as F by , yet in this section it is labeled as F b .
- Applicable to all I-shaped members; all others are not considered.
-
F b = 0.75 F y
(F2-1)
2.A. Members with compact sections: Section F2.1
-
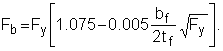
(F2-3)
2.B. Members with noncompact sections: Section F2.2
3. Tensile Stress
|
F t = 0.60 F y |
Section D1 |
4. Compressive Stress
Section E2
![]()
|
|
(E2-1) |
where KL/r is the largest of KL
x
/r
x
and KL
y
/r
y
, which are equal for pipes and squares, and 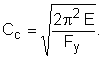
![]()
|
|
(E2-2) |
5. Combined Stress
Chapter H
5.A. Axial compression and bending
The following requirements must be satisfied for members experiencing both axial compression and bending:
|
|
(H1-1) |
|
|
(H1-2) |
When f a /F a ≤ 0.15, Equation (H1-3) is used in lieu of Equations (H1-1) and (H1-2).
|
|
(H1-3) |
The coefficients, also known as the Euler stress divided by safety factor, F ex and F ey are given by the following:
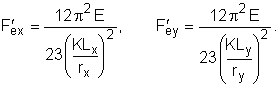
The coefficients C mx and C my have a default value of 0.85.
5.B. Axial tension and bending
The following requirements must be satisfied for members experiencing both axial tension and bending:
|
|
(H2-1) |