Linear steady-state heat transfer occurs when the conductivity of the material is not dependent on temperature and when radiation is not applied. Either of these effects makes the problem nonlinear (iterative). Refer to the page, Nonlinear Steady-state Heat Transfer Analysis, for details.
Specifically the following loads can be included in a linear analysis:
Conduction
![]()
where
- q = heat flow
- k = thermal conductivity (a constant) entered as a material property. Isotropic materials fall under this category.
- A = cross section area of an element face
-
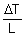 = the temperature gradient in the direction normal to the area, A
= the temperature gradient in the direction normal to the area, A
Convection
![]()
where
- h = convective heat-transfer coefficient (constant) entered by the user.
- A = area of the element subject to convection
- X = Convection multiplier entered on the Analysis Parameters screen.
- ΔT = T s -T ∞
- T s = surface temperature of the element (calculated)
- T ∞ = temperature of the fluid (assumed to be constant) and entered by the user.
Internal Heat Generation
q = (q per unit volume)(X)(volume)
where
- q per unit volume = the amount of heat generated internal to the element per unit volume, entered by the user.
- X= the Heat generation multiplier entered on the Analysis Parameters screen.
- volume = the volume of the element (calculated)
Applied Temperature
q = stiffness(ΔT)
where
- stiffness = equivalent of convection coefficient times the area (hA), entered by the user.
- ΔT = Tn-XT ∞
- T n = temperature of the node (calculated)
- X= Boundary temperature multiplier entered on the Analysis Parameters screen.
- T ∞ = Magnitude of the temperature entered by the user.
Heat Flux
q = (heat flux)AX
where
- heat flux = the amount of heat flux (heat per unit area) applied to a surface, entered by the user.
- A = surface area of the face
- X= the Convection multiplier entered on the Analysis Parameters screen.