You will create the base layer of the composite map by choosing a bitmap of a steel shutter, then assigning its diffuse, or color, values to an Arch & Design material. You will then add two more image layers, using alpha values to define how each is superimposed over the base layer.
Set up the lesson:
- On the Quick Access toolbar, click
 (Open File), navigate to
\scenes\materials_and_mapping\composite_mapping\
and open
composite_start.max.
Note: If a dialog asks whether you want to use the scene’s Gamma And LUT settings, accept the scene Gamma settings, and click OK. If a dialog asks whether to use the scene’s units, accept the scene units, and click OK.
(Open File), navigate to
\scenes\materials_and_mapping\composite_mapping\
and open
composite_start.max.
Note: If a dialog asks whether you want to use the scene’s Gamma And LUT settings, accept the scene Gamma settings, and click OK. If a dialog asks whether to use the scene’s units, accept the scene units, and click OK.The scene consists of a pawnshop located in a rough part of town. The storefront is missing one important element: a steel shutter that protects a plate-glass window. Your task is to create a convincing composite map of the shutter.
- From the main menu, chose Customize
 Preferences
Preferences  General panel
General panel  Texture Coordinates group and turn off Use Real-World Texture Coordinates, if it is not already off. Click OK.
Texture Coordinates group and turn off Use Real-World Texture Coordinates, if it is not already off. Click OK. 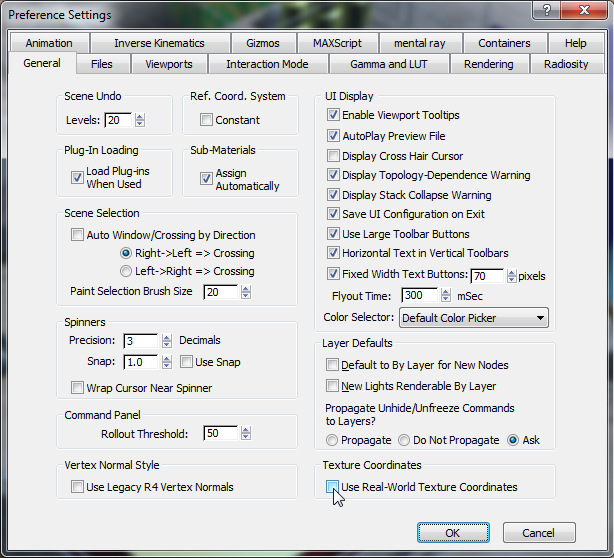
Create a base layer and color correct it:
- Open the
 Slate Material Editor.
Slate Material Editor. - In the Material/Map Browser panel on the left, locate the Sample Slots group.
The first sample slot contains an Arch & Design material called Shop-Door. This material has already been applied to the roll-up shutter object (door-sec).
- Drag the Shop-Door material from the Browser into the active View. In the Copy/Instance map dialog, make sure Instance is chosen, then click OK.
- On the Slate Material Editor toolbar, click
 (Show Shaded Material In Viewport) so that later you will be able to view the Composite map in the viewports. (If you use a legacy viewport driver, this button's tooltip reads, "Show Standard Map In Viewport.")
(Show Shaded Material In Viewport) so that later you will be able to view the Composite map in the viewports. (If you use a legacy viewport driver, this button's tooltip reads, "Show Standard Map In Viewport.") Now you will add a composite map to the material’s diffuse color component.
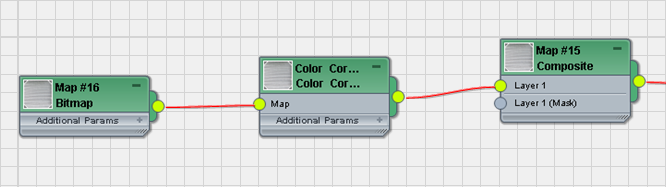
- Drag a Composite map from the Browser into the active View (in the default groups, Composite is a Standard map), then wire the Composite map node to the Diffuse Color component of the Shop-Door material.
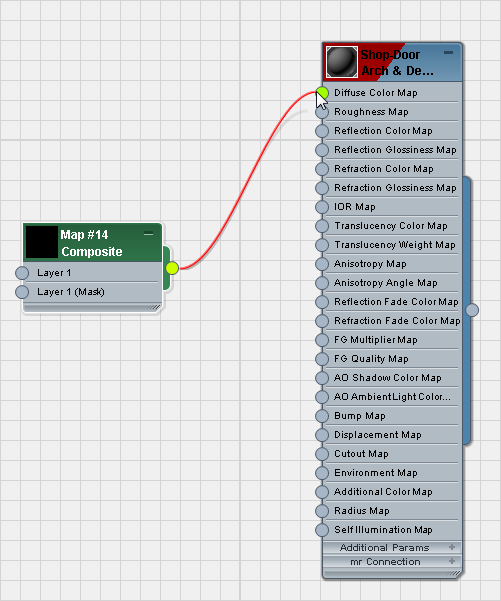
- Double-click the Composite map node to see its parameters.
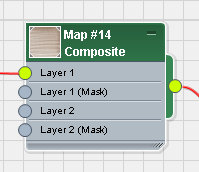
Initially, the Composite map contains a single layer.
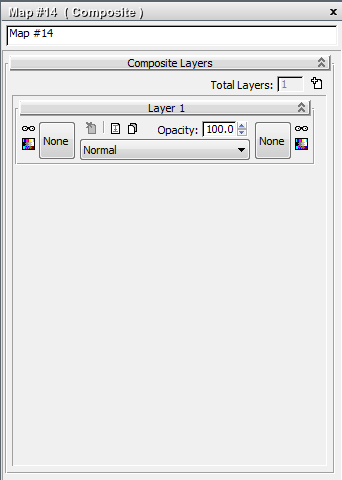
Specify the first layer of the Composite map:
- Drag a Bitmap from the Browser into the active View.
3ds Max opens a file dialog.
On the file dialog, choose shutters.jpg, and then click Open.
- Wire the new Bitmap node to the Layer 1 component of the Composite map.
On the Layers 1 rollout for the Composite map, the Texture button now shows the shutters.jpg texture. This texture will be the base layer of the Composite map.
- Right-click the title bar of the Shop Door material node, and choose Open Preview Window.
The preview helps you monitor the appearance of the map as you add more layers and make further adjustments.
Note: A preview window takes more time to render than the small preview in the title bar of the material node. - Right-click the title bar of the Shop Door material node, and choose Preview Object Type
 Box.
Box. 
3ds Max changes the sample sphere to a cube, which is a better preview of the shutter geometry.
- Drag a corner of the preview window to make it larger.
- Move this preview so you can see all of the Shop Door node and the controls in the Parameter Editor.
Add a rust tone to the first layer:
- On the Layer 1 rollout, click
 (Color Correct This Texture). This button is at the left of the rollout.
(Color Correct This Texture). This button is at the left of the rollout. 3ds Max displays Color-Correction controls in the Parameter Editor, and it inserts a Color Correction map node between the Bitmap and the Composite map.
 Tip: In the active View, press L to rearrange the layout and see this node more clearly. Use other navigation tools to move among nodes in the View.
Tip: In the active View, press L to rearrange the layout and see this node more clearly. Use other navigation tools to move among nodes in the View. - On the Color rollout, click the Hue Tint color swatch.
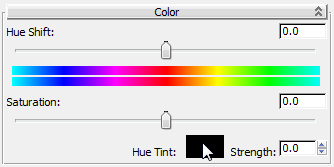
3ds Max opens a Color Selector.
- Enter the following values in the RGB fields:
- R = 0.25
- G = 0.15
- B = 0.075

Click OK to close the Color Selector.
- On the Color rollout, drag the Saturation slider to 100.0, then in the Strength field, enter 100.0.
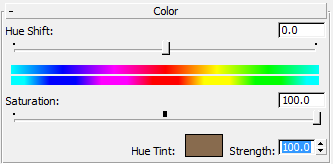
- On the Color Correction map's Lightness rollout, change the Contrast value to 32.0.
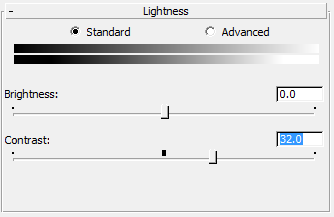
Now the Shop Door material shows a brownish tint.
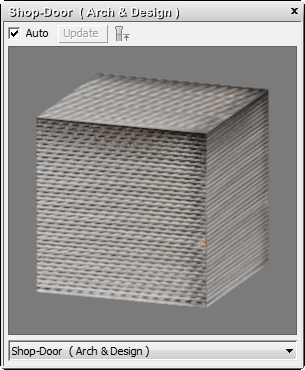
The shutter door material is uniformly gray in color. Let’s add a little rust to give the shutter a more run-down appearance.
Use alpha values to add a layer of graffiti:
- Double-click the Composite map node to see its parameters again.
- At the top of the Composite Layers rollout, click
 (Add A New Layer).
(Add A New Layer). 3ds Max adds a new Layer rollout to the display of the Composite map parameters.
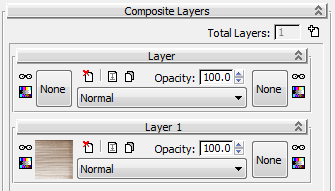
Also, in the active View, the Composite map node now shows a new Layer 2 component.
- Drag a Bitmap from the Browser to the active View, just below the Bitmap node for Layer 1.
3ds Max opens a file dialog.
On the file dialog, make sure Files Of Type is set to All Formats, choose graffiti.png, and then click View.
3ds Max opens a file viewer that shows the graffiti.png texture.
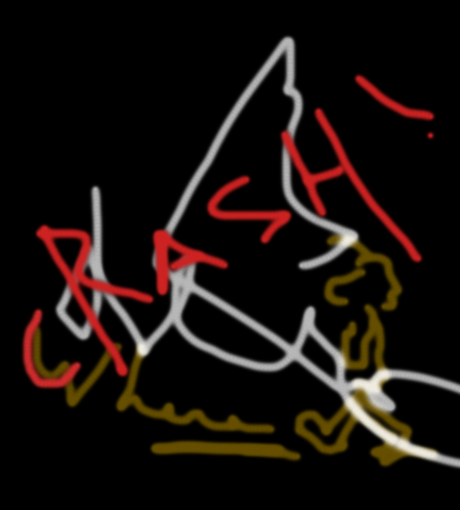

Graffiti bitmap used as the second layer in the composite map
In addition to red, green, and blue (RGB) information, the bitmap includes alpha channel information in its .png file format. This channel provides the level of opacity needed to superimpose the graffiti image over the base image.
- On the file viewer toolbar, click
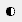 (Display Alpha Channel).
(Display Alpha Channel). The viewer displays a black-and-white version of the image, showing the file’s alpha information.
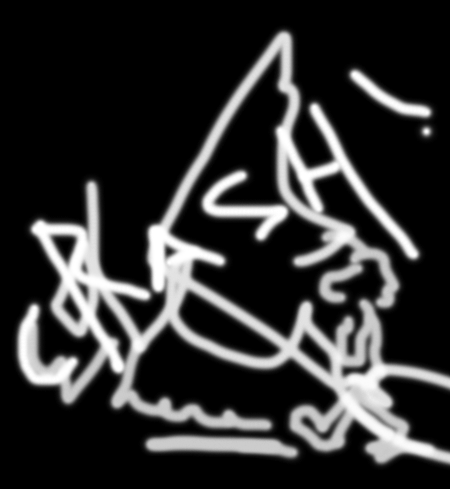

Alpha channel of the graffiti bitmap
Black regions of the bitmap will be completely transparent in the composite map. White regions, representing the graffiti strokes, will be completely opaque and fully visible in the composite map. Gray regions will be semi-transparent and provide partial visibility, giving a blurred edge to the graffiti.
Note: Other bitmap formats that can contain alpha channel information include .tif, .tga, and .exr. -
 Close the
graffiti.png
viewer, then on the file dialog, click Open.
Close the
graffiti.png
viewer, then on the file dialog, click Open. 3ds Max adds the Bitmap node to the active View.
- Wire the new graffiti Bitmap to the Layer 2 component of the Composite map.
The Layer 2 rollout now shows the graffiti.png texture, and the material preview shows the composited graffiti.

Composite map with the graffiti layer composited on the shutter layer
Next, you will add a second layer to your composite map, one that contains the bold strokes of a graffiti artist (or more than one).
Adjust the alpha and color levels:
- On the Layer 2 rollout, change the value of Opacity 90.0, then press
 .
. 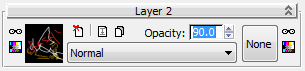
This slightly increases the overall transparency of Layer 2, so that a small portion of Layer 1 is visible beneath it. The result is a more convincing blending of the graffiti onto the shutter surface.
The graffiti layer still needs to stand out a little more: You will use the color correction tools to achieve this effect.
- Drag a Color Correction map from the Browser to the active View, and drop it on the wire between the Bitmap and the Composite map, when the cursor shows you can insert a map.

3ds Max inserts a Color Correction node between the graffiti bitmap and the Composite map. This is another way to add a Color Correction map.
- Double-click the new Color Correction node so you can see its parameters.
- On the Lightness rollout, drag the Brightness slider to the right until the Brightness field shows a value of about 15.0.
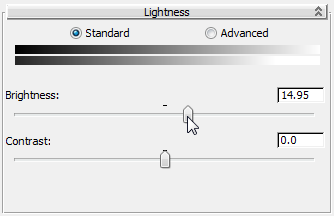
The graffiti colors are now brighter. On the other hand, the change in Brightness affects the semitransparent portion of the alpha channel as well, creating a halo effect around the graffiti strokes, which we don’t want.

Halo surrounding graffiti strokes
You will correct this problem by increasing the contrast level.
- Drag the Contrast slider to the right until the box displays a value of about 25.0.
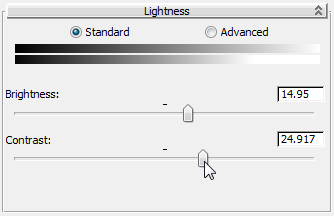
Now the graffiti looks more like it is painted on the door.
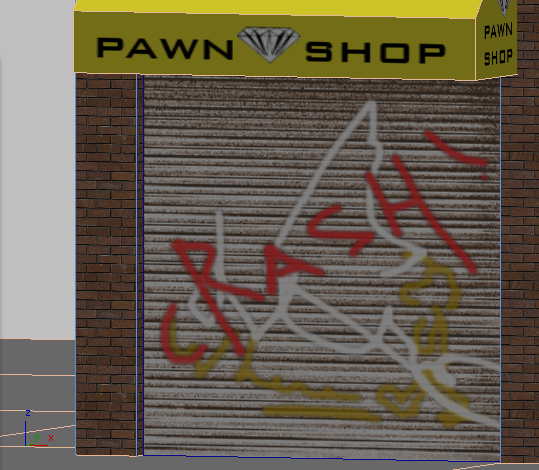

If you look at the Shop Door material in a viewport (you will have to move or minimize the Slate Material Editor), you can see that the default values for compositing graffiti.png make the graffiti appear to float above the corrugated texture of the door.

You will fix this by adjusting some of the alpha settings for this layer.
Use a mask to add a sticker:
- Double-click the Composite map node to see its parameters once more.
- At the top of the Composite Layers rollout, click
 (Add A New Layer).
(Add A New Layer). 3ds Max adds a new Layer rollout to the Composite map parameters, and a new Layer 3 component to the Composite map node in the active View.
- Drag a Bitmap from the Browser to the active View.
3ds Max opens a file dialog.
On the file dialog, choose c-sign.jpg, and then click Open.
- Wire the new Bitmap node to the Layer 3 component of the Composite map.
3ds Max displays the new Bitmap on the Layer 3 rollout and in the preview window.

The c-sign bitmap applied as a top layer in the composite map
Bitmaps saved in .jpg format have no alpha channel information. By applying the c-sign.jpg image directly as a top layer, you have completely obscured all layers beneath it. You can correct this by adding a mask. (You could easily create your mask in a paint program, but a mask image has already been prepared for you.)
- Drag a another Bitmap from the Browser to the active View.
3ds Max opens a file dialog.
On the file dialog, choose c-sign-msk.jpg, and then click Open.
- Wire the new mask Bitmap node to the Layer 3 (Mask) component of the Composite map.

The mask is a black-and-white image that acts as a “custom” alpha channel to the color map.. Black areas of the mask allow the underlying layers to show through, white areas are opaque, and gray areas are partially transparent.
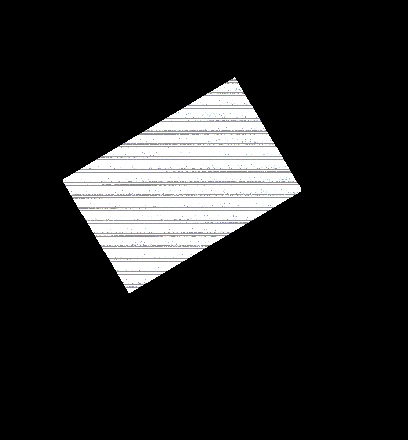
Bitmap used to create a cutout of the poster for layer 3
Now on the Layer 3 rollout, the texture with the sticker appears at the left, and the mask bitmap appears at the right.
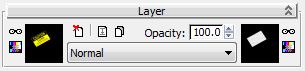
In the preview, the “CAUTION” sticker appears by itself, with the rest of the door now visible.

Layer 3 with the mask applied
One small problem remains. You want the graffiti to cover the sticker, not the other way around.
- Drag the label of the Layer 2 rollout to a point just above the new Layer 3 rollout. Release the mouse when 3ds Max displays a blue line just above the Layer 3 rollout label.
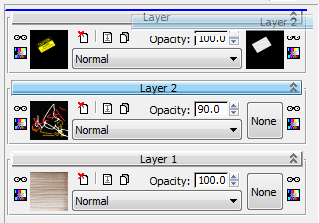
3ds Max reorders and renumbers the layers accordingly. (Layer 3 becomes Layer 2, and vice versa.)
Now the graffiti appears on top of the sticker about closure.
 Note: In the active View, 3ds Max rewires the nodes to reflect the change in the order of the layers, so you might want to press L in the active View to update the layout of the nodes.
Note: In the active View, 3ds Max rewires the nodes to reflect the change in the order of the layers, so you might want to press L in the active View to update the layout of the nodes.
Now you will add a third layer to your composite map, one that features a sticker.
Save your work:
- Save the scene as my_shop_door_3layers.max.