The Gravity space warp simulates the effect of natural gravity on particles generated by a particle system. Gravity is directional. Particles moving in the direction of the gravity arrow accelerate. Particles moving against the arrow decelerate.
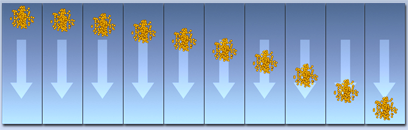
Particles falling because of gravity
In the case of spherical gravity, motion is toward the icon.
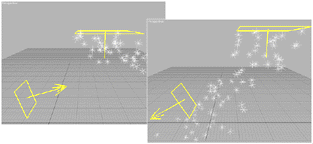
Gravity effect on snow
Procedures
To create gravity:
- On the
 Create panel, click
Create panel, click  (Space Warps). Choose Forces from the list, then on the Object Type rollout, click Gravity.
(Space Warps). Choose Forces from the list, then on the Object Type rollout, click Gravity. - Drag in a viewport.
The Gravity icon appears. For planar gravity (the default), the icon is a wireframe square with a direction arrow on one side. For spherical gravity, the icon is a wireframe sphere.
The initial direction of planar gravity is along the negative Z axis of the construction grid that is active in the viewport where you drag. You can rotate the gravity object to change the direction.
Interface
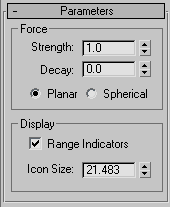
Force group
- Strength
-
Increasing Strength increases the effect of gravity; that is, how objects move in relation to the Gravity icon's direction arrow. Strength less than 0.0 creates negative gravity, which repels particles moving in the same direction and attracts particles moving in the opposite direction. When Strength is set to 0.0, the Gravity space warp has no effect.
- Decay
-
When Decay is set to 0.0, the Gravity space warp has the same strength throughout world space. Increasing the Decay value causes gravity strength to diminish as distance increases from the position of the gravity warp object. Default=0.0.
- Planar Gravity effect is perpendicular to the plane of the Gravity warp object throughout the scene.
- Spherical Gravity effect is spherical, centered on the Gravity warp object. This choice is effective for creating water fountain or planetary effects.
Display group
- Range Indicators
-
When on, and when the Decay value is greater than 0.0, icons in the viewports indicate the range at which the force of gravity is half the maximum value. For the Planar option, the indicators are two planes; for use the Spherical option, the indicator is a double-hooped sphere.
- Icon Size
-
Size of the Gravity warp object icon, in active units. You set the initial size when you drag to create the Gravity object. This value does not change the gravity effect.