The Ray-Traced Shadow Parameters rollout appears when you have chosen raytracing as the shadow-generation technique for a light. You select this in the General Parameters rollout.
Both the scanline renderer and the mental ray renderer support Ray-Traced shadows.
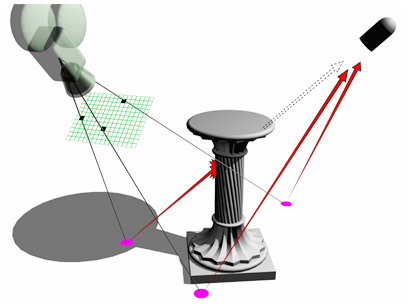
Ray-traced shadows
Interface
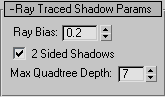
- Ray Bias
-
Shadow bias moves the shadow toward or away from the shadow-casting object (or objects).
If the Bias value is too low, shadows can "leak" through places they shouldn't, producing moire patterns or making out-of-place dark areas on meshes. If Bias is too high, shadows can "detach" from an object. If the Bias value is too extreme in either direction, shadows might not be rendered at all.
- 2-Sided Shadows
-
When on, backfaces are not ignored when calculating shadows. Objects seen from the inside are not lit by lights from the outside. This costs a bit more render time. When off, backfaces are ignored. Rendering is quicker, but outside lights illuminate object interiors. Default=on.
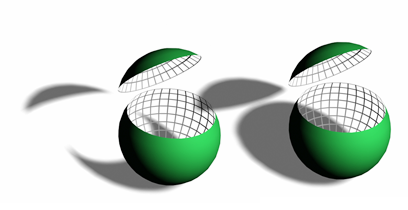
The faces inside the sliced sphere do not cast shadows if 2-Sided Shadows is not selected.
Note: The mental ray renderer disregards this setting, and always renders 2-sided shadows. - Max Quadtree Depth
-
Adjusts the depth of the quadtree used by the ray-tracer. Greater quadtree depth values can improve ray-tracing time at the cost of memory use. However, there is a depth value where the performance improvement is offset by the time it takes to generate the quadtree itself. This depends on the geometry of the scene. Default=7.
Tip: An Omni light can generate up to six quadtrees, so it generates ray-traced shadows more slowly than spotlights. Avoid using ray-traced shadows with omni lights unless your scene requires this.