Some models and animated motions don't fit neatly into a Child->Parent or Parent->Child precedence. In such situations you can manually assign precedence values to any object in the IK chain on a joint-by-joint basis.
For example:
- Animating models with a combination of light, flexible joints and heavy, resisting joints. Imagine a model of heavy iron balls linked together with lengths of chain. Setting the precedence values of the chains higher than the precedence values of the iron balls simulates the balls' inertial resistance to motion.
- Animating a motion where certain joints must move before other joints. Imagine a golfer's arm where the elbow should remain locked while swinging a golf club. You could accomplish this by setting the precedence of the elbow lower than the precedence of the wrist and shoulder.
High precedence values are calculated before low precedence values. Precedence values that are equal are calculated in Child->Parent order.
The precedence calculations only consider the relative IK values. This means that an IK chain of three objects with precedence values of 0, 30, and 200 would have the same solution if the precedence were changed to 1, 2, and 3.
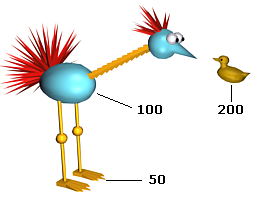
The figures show precedence values that were assigned manually: the chain for the structure uses the body as the root object and the duck as the end effector.
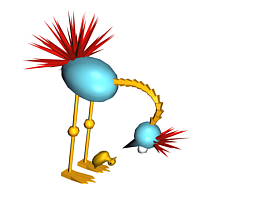
The figures show precedence values that were assigned manually: the chain for the structure uses the body as the root object and the duck as the end effector.