Transform Attributes
See General attributes.
Skeleton Info
- Start Joint
-
Displays the name of the start joint IK handle’s joint chain. You can click the > icon button to open the Attribute Editor for the start joint.
- End Effector
-
Displays the name of the IK handle’s end effector. You can click on the > icon button to open the Attribute Editor for the end effector.
IK Handle Attributes
- Snap Enable
-
When this attribute is on, the current IK handle will snap back to the position of its end joint. Default is on.
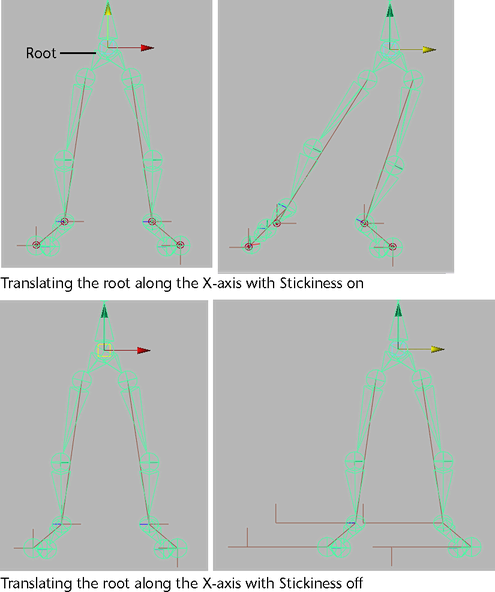
- Stickiness
-
When this attribute is on and the current IK handle has no keyframes, the current IK handle will stick to its current position when you pose the skeleton with another IK handle or by translating, rotating, or scaling the joints directly. When this attribute is on and there are keyframes on the current handle, Stickiness is ignored. Default is off.
You can use Stickiness when posing a joint chain with an IK handle to prevent unwanted joint chain movement. For example, you can turn on Stickiness for the IK handles of a model’s legs if you want the feet to stay firmly planted on the floor while you move and pose the hips of the model.
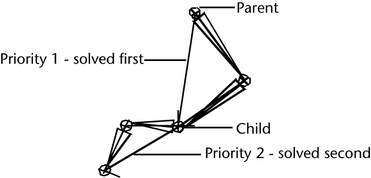
- Priority
-
Specifies the priority of the current IK handle. Priority is useful only when a joint chain has more than one IK handle. The purpose of Priority is to ensure that the IK handles of a joint chain solve in the correct order so that they properly produce the desired animation.
When you set Priority for the IK handles of a joint chain, Maya calculates the priority for each handle based on its position in the hierarchy. The IK handle with a Priority of 1 has first priority, and will rotate the joints first. An IK handle with a Priority of 2 has second priority, and will rotate the joints next, and so on. Default is 1.
- Weight
-
Sets the weight value for the current IK handle.
The weight value, in conjunction with the current distance between the IK handle’s end effector and its goal, serve to prioritize the solutions of the current IK chain and those of its other IK handles that have the same Priority settings. See Priority.
When the end effector of two or more IK handles with the same Priority cannot reach their goals simultaneously, the IK handle whose end effectors are furthest from their goals and whose weights are greatest are solved first.
Not available for Single-Chain Solver, Rotate-Plane Solver, or ik2Bsolver handles.
- POWeight
-
Specifies whether the current IK handle’s end effector favors reaching its goal’s orientation or position.
When this attribute is set to 1, the end effector tries to reach the IK handle’s position. When this attribute is set to 0, the end effector only tries to reach the IK handle’s orientation. A value of 0.5 specifies that the end effector equally favors reaching both the position and orientation as closely as possible. Default is 1.000.
Not available for the ik2Bsolver or Rotate-Plane Solver handles.
IK Solver Attributes
- Ik Blend
-
An Ik Blend value of 0.000 sets the animation mode to pure FK, and an Ik Blend value of 1.000 sets the animation mode to pure IK. When the Ik Blend value is a number between 0.000 and 1.000, then the animation on the current skeleton is blended IK and FK. See IK/FK blending.
Note:In addition to blending IK and FK animation over multiple frames, a blend can occur over a single frame. Blending over a single frame instantly switches IK to FK or FK to IK.
- Ik Fk Control
-
Lets you manipulate and key the joints of a joint chain that has an animated IK handle. In addition to being located in the local IK Handle Attributes, Ik Fk Control is also present in the global skeleton settings (Skeleton > Enable IK/FK Control).
Note: The Ik Fk Control attribute turns off global and local IK Handle Snap. - IK Solver
-
Specifies the type of solver for the IK handle. See IK solvers. The default options are the following:
- Single-Chain
-
Select the Single-Chain Solver for an IK single chain handle.
- Rotate-Plane
-
Select the Rotate-Plane Solver for an IK rotate plane handle.
- Pole Vector
-
Specifies the position of the pole vector’s end point.
Pole vector is only applicable for IK handles that use the rotate plane solver (IK Solver is set to Rotate-Plane Solver). See Rotate Plane solver.
- Twist
-
Not available for single chain IK handles.
Twists the joint chain from the end joint by the specified amount.