The calculation of cooling results for each element in the model is influenced by the surrounding elements.
In Surrounding elements in geometry influence, the orange colored elements are explicitly used when calculating results for the yellow colored element in the center, and the remaining model elements are lumped into a single bulk term.

Surrounding elements in geometry influence
.a Automatic, b Ideal
Geometry influence determines which surrounding elements are used for each element. As the number of surrounding elements explicitly used increases, both accuracy and hardware requirements increase. Cool provides the following three methods for calculating geometry influence.
Automatic
In the Automatic method, the software calculates the minimum number of surrounding elements required to produce accurate results for each element. The number of surrounding elements used will vary from element to element.
Each model will have a given ratio of the total number of part elements to the total number of cooling channel elements. The Automatic method aims to ensure that, for every element, the number of surrounding part elements and the number of neighboring cooling channel elements used in the geometry influence calculation are in the same ratio as the overall part-element-to-cooling-channel-element ratio for the model.
Ideal
In the Ideal method, the geometry influence calculation for each element takes into account all other elements in the model. This method will produce the most accurate results but will require considerable disk space, and computing time. In models with a high number of elements, the Ideal method may become impractical due to hardware limitations, in particular available disk space.
Parameter
This method allows you to specify a geometry influence parameter (GIP) number, which is used to determine the number of surrounding elements to use in the geometry influence calculations. Geometry influence parameter illustrates how this parameter is used.
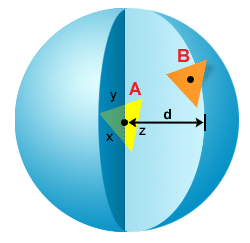
Geometry influence parameter
In this case, if you take the average length of element A ((x+y+z)/3) and multiply it by the GIP number you will get the distance d. All elements with a centroid within this distance from the centroid of element A will be included in the calculation. Therefore, to include element B in the results calculation for element A:
Recommended usage
It is recommended that you use the default Automatic method unless you encounter problems. The Automatic option is approximately equal to a GIP value of 10. For large models, it is possible to reduce the hard disc requirements for analysis by selecting a GIP value in the range 6–10. You can also set a high GIP value (20–30) if you are having problems with the Ideal method.