In this step, the Helius PFA state variable outputs are viewed and discussed.
Helius PFA generates several state variable outputs. In this step, a key variable (SV2) is viewed and discussed. SV2 is the state variable that tracks fiber and matrix failure within an element.
To view the composite results in Patran for large models that use solid composite elements, you must open Patran using a special environment variable.
- Type the following in the command prompt to open Patran after the analysis has completed:
>>SET DRANAS_NAST_MEM=2048MB >>C:\MSC.SOFTWARE\PATRAN_x64\20130\bin\patran.exe -skin
The second line provides the path to the patran.exe file. To determine this path on your machine, right click the Patran 2013 desktop icon and click Properties. - Click File > New and navigate to the directory containing the results. Name the database file Tutorial_3_Nastran_Results.db and click OK.
- Click File > Import and specify the Source as MSC.Nastran Input.
- Navigate to the location of the bulk data file. Click Apply.
- From the Analysis form, set the Action to Access Results and set the Object to Attach Output2.
- Click Select Results File and navigate to the location of the .op2 file. Click OK.
- Click Apply.
- Click the Fringe button on the Results tab.
- Choose the SC1:Step 1, At1:Time = 1 subcase from the Select Result Cases list.
- Select SV3, NonLinear Output from the Select Fringe Result window and click Apply.
SV3 represents the matrix failure index. This variable indicates how close the matrix is to failure, which occurs when SV3 is greater than or equal to 1.
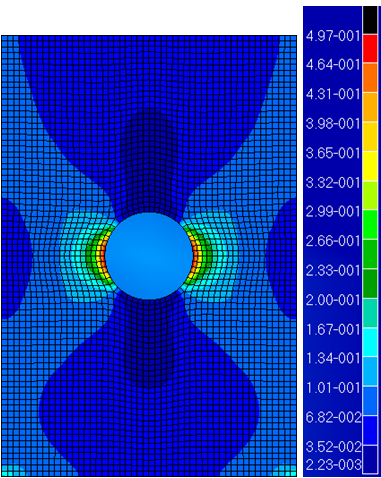
The default ply for the contour plot shown above is Ply 8 and the maximum SV3 value is 0.497. This means that in Ply 8, the matrix failure index is less than 1 and no failure has been detected.
Create an envelope plot to view the maximum matrix failure index in all of the plies. Envelope plots display the maximum or minimum integration point value across all of the section points in each element.
- To create an envelope plot, click the Layer button on the Results form and highlight all 8 layers.
- Select Maximum from the menu and click OK. Click Apply on the Results form.
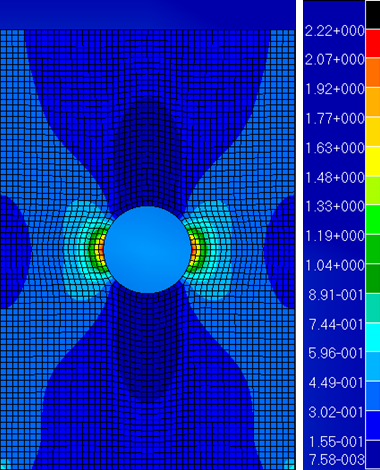 The maximum matrix failure index is 2.22, which indicates that matrix failure is predicted to occur in one or more of the plies.
The maximum matrix failure index is 2.22, which indicates that matrix failure is predicted to occur in one or more of the plies. - The step in which matrix failure first occurs can be determined by viewing results from intermediate load steps.
- Starting at Time = 0.05, progress through the steps while watching the viewport to determine when matrix failure is detected (when the maximum SV3 value is 1 or greater). Matrix failure occurs between step time 0.65 and 0.7.
- To determine which plies have matrix failure, click Position on the Results form and view the failure distribution in each ply. Note that plies with the same orientation have identical failure index distributions since the laminate is symmetric. For example, Ply 2 and Ply 7 have the same failure index distribution.
All plies except plies 1 and 8 have matrix failure. Matrix failure is not predicted in plies 1 and 8 since these plies have their fibers oriented in the loading direction. The stiff fibers restrict the strains in plies 1 and 8 from reaching critical levels.
- Switch back to the envelope plot and plot the last frame (time = 1.0).
- Select SV4, Nonlinear Output from the Select Fringe Result window. SV4 represents the fiber failure index and is an indication of how close the fiber is to failure. Fiber failure occurs when the value of SV4 is greater than or equal to 1. The plot should be similar to that shown below.
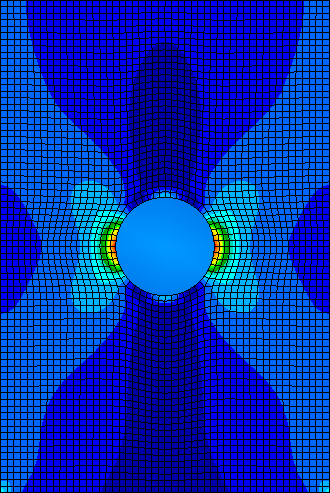
Since the maximum value of SV4 in all plies is less than 1 (max = 0.61), fiber failure is not predicted.