
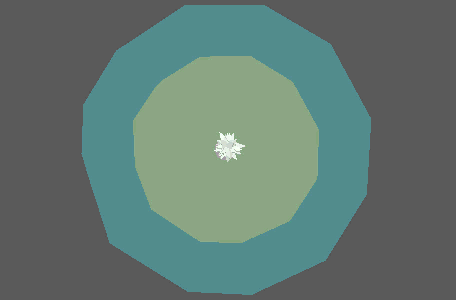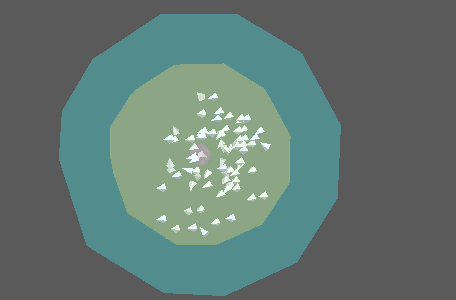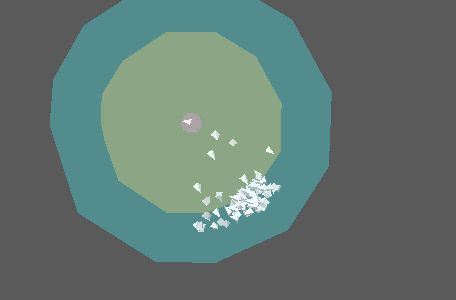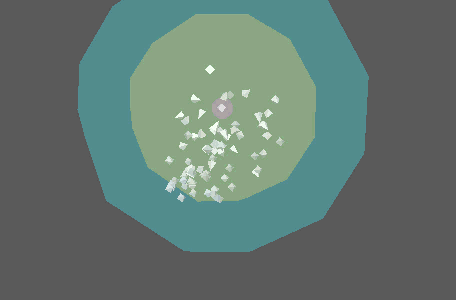
This is a multi-threaded simulation node that approximates flocking and swarming behavior by attaching objects to a number of points. It is highly recommended that you add a
Noise node to your MASH network in conjunction with this, as
Flight relies on one existing to achieve accurate simulated behavior.
Note: As a simulation node, Flight requires that
Playback Speed be set to
Play every frame. Start and end frames should also be whole numbers. Objects will face down in the Z-axis if you add an orient node.
Main Controls
- Separation Strength
- Sets how determined points are to separate from other points within their Separation Zone.
- Alignment Strength
- Sets how determined points are to travel in the same direction as other points within their Alignment Zone.
- Cohesion Strength
- Sets how determined points are to stay together.
- Search Distance
- Determines how far a point can see other points.
- Number of Companions
- How many of a point's closest neighbors to compare to when making behavior calculations such as cohesion, alignment, etc.
- Field of Vision
- The angle (in degrees) that a point can see other points.
- Alignment Zone
- The area surrounding each point at which it will try to align itself with other points within the same area according to the Alignment Strength.
- Separation Zone
- The area surrounding each point at which it will try to separate itself from other points within the same area according to the Separation Strength.
Speed and Mass
- Minimum Speed, Maximum Speed
- Controls the speed of the points.
- Steering Force
- Controls the force with which points can change direction. Lower values result in agile darting movements while higher values result in overshooting swoops.
- Mass
- Controls the mass of each point. Can be used to exaggerate calculations based on it.
- Mass Variance
- Applies a randomizer to the Mass.
Gravitate and Inertia
This determines the overall spacial bounds of the flight simulation.
- Gravitate Strength
- Determines how much influence the Type of Gravitation has on the points. Higher values result in tighter formations.
- Gravitate Distance
- Determines the distance that points are allowed to wander based on the Type of Gravitation. Lower values result in tighter formations.
- Type of Gravitation
- Determines the area around which points will gravitate. Location specifies a specific location (designated as a float box) within the scene while Group Centre uses the center of all the points.
- Given Location
- The center of gravity when Type of Gravitation is set to Location.
- Inertia
- Applies a constant force to all points.
- Gravitation Object
- Specifies a connected locator to represent the center of gravity when Type of Gravitation is set to Location.
Attractor Controls
This allows you to assign an object in the scene as an attractor, which the MASH network will head towards.
- Attraction Strength
- A multiplier for the attraction vector, which determines how hard points will head toward attractors.
- Attractor Search Distance
- The radius surrounding each point that attractors can be seen.
- Arrival Threshold
- Determines the distance between points at which they come to a standstill.
- Arrival Variance
- A randomizer applied tot he Arrival Threshold per point.
- Arrival Dampening
- Sets an additional dampening area at which objects will slow as they arrive at the attractor.
Obstacle Controls
This allows you to assign objects in the scene as obstacles, which points will try to avoid.
- Avoidance Type
- Determines the behavior that points will exhibit to avoid obstacles.
- Obstacle Strength
- A multiplier for the avoidance vector, which determines how hard points will try to avoid obstacles.
- Obstacle Search Distance
- The radius surrounding each point that obstacles can be seen.
- Connect Obstacle
- Connect an object to be used as an obstacle. You can use either Create Obstacle Locator to create a locator representing the obstacle, or Connect Obstacle Mesh to use a specific object in the scene.
Predator / Prey Controls
This allows you to designate certain points as predators and others as prey. Predators pursue prey, while prey actively avoids predators.
- Predator Strength
- A multiplier for the predator vector, which determines how hard predators will pursue prey.
- Predator Search Distance
- The radius surrounding each predator that prey can be seen.
- Prey Strength
- A multiplier for the predator vector, which determines how hard prey will avoid predators.
- Prey Search Distance
- The radius surrounding each prey that predators can be seen.
Mesh Following
This allows you to constrain the points to a mesh, ensuring they stay on its surface.
- Input Mesh
- Displays the current input mesh that points will be constrained to.
- Connect Mesh
- Sets the currently selected mesh as the Input Mesh.
- targetPP
- A connection you can make in the node editor to make a PP array (such as one created by a Distribute node or SOuP scatter node) an attractor point.