The first time that you create a new Description, Maya creates an xgen folder in the set Maya project directory. By default, all XGen-related files, including Description XDSC files, point XUV files as well as Ptex files used for attribute maps, groomable splines, region maps, and masks, are stored in sub-folders within the project's xgen folder.
A ${DESC} variable specifies the main data path to the current Description. By default, this data path is set to the xgen folder for the Collection containing the Description. XGen uses this data path to access all the files and maps when the Description is previewed or rendered.
For example, after you set your Maya project and created the following:
- A Description named GrassDescription and a Collection named LandscapeCollection.
- On a polygon mesh named landScapeplane.
- Using guides to place the primitives.
Maya generates the following default data structure for XGen.
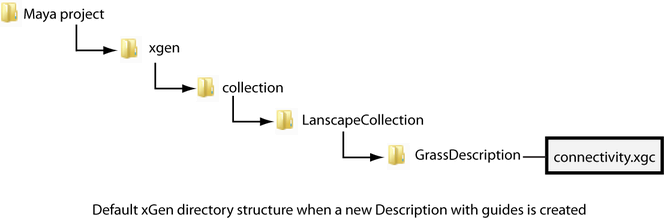
See Map file locations for information about locations of Ptex and Point maps.
User, Local, and Global file locations
You can specify user, local, and global locations for file repositories, expression libraries, and archive files. Use the following environmental variables to specify these locations:
- User: ${HOME}/xgen
- Local: ${XGEN_ROOT}
- Global: ${XGEN_LOCATION}
See Specify locations for user, local, and global file repositories.
XGen file types
- Collection (.xgen)
- Collection (XGEN) files store information about all associated Descriptions, which can include XGen modifiers, patch bindings, and guide attributes. These files are created when you create a Description or Collection. See XGen Collections.
- Description (.xdsc)
- Description XDSC files store information about a single XGen Description, including primitive attribute values, preview and render settings. These files are created when you export a Description. See XGen Descriptions and Save and load XGen files.
- Delta (.xgd)
- Stores information about changes made a Description Collection. Use this file to make edits to a Description while preserving its original state. See Save groom edits to delta files.
- Modifier (.xgfx)
- These files contain the attribute values an for instance of an XGen modifier. Use this file to transfer or reuse a modifier within the same Description or other Descriptions. Modifier files only contain information about the modifier attributes. They do not save information that the modifier uses as a reference. For example, the points and maps of a
Clumping modifier are not saved in the modifier file. You must copy this information.
See XGen Modifiers and Use Python commands to export and import XGen files.
- Archive (.xarc)
- References files associated with archived geometry including textures, Alembic, and render proxy files. See What are custom Archive primitives.
- Ptex (.ptex)
- Use Ptex files for region maps and masks. Create Ptex files in Maya using the Paint Tool or use a Ptex file created in Autodesk Mudbox 2012 (or later). Groomable spline attributes are also saved as Ptex files. See Ptex map file locations.
- XPD cache (.xpd)
- Contains information about the geometry, location, and attribute values of each primitive in the Description on a per-patch basis. See Groom Bake Modifier and Output Settings.
- Points (.xuv)
-
Saves generated primitive locations as points. See Use point maps and Generate Maps window.
- Particle database (.pda, .pdb)
- Saves generated primitives as particles. See Output Settings and Particle.
- Guide connectivity (.xgc)
- Stores information about how XGen interpolates the guides on the mesh surface. See Interpolation.