Calculate the cross-sectional area, yield, denier, lineal density, Tex, and deciTex for a roving process.
Navigate to to view the dialog window shown below.
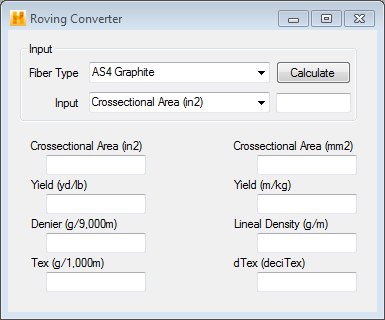
As shown above, three input fields are used for the roving conversion process. The converter will then calculate the results and populate the remaining fields. This is done in three steps as follows:
- Fiber Type - The fiber type is selected from a drop-down menu. The fibers listed in this drop-down box are the same fibers located in the data file tree within the fibers branch. The associated fiber density is used in the converter depending on what fiber is chosen.
- Input - There are eight options to choose from in the Input drop-down box.
- Cross Sectional Area (in2)
- Cross Sectional Area (mm2)
- Yield (yd/lb)
- Yield (m/kg)
- Denier (g/9000m)
- Lineal Density (g/m)
- Tex (g/1000m)
- dTex (deciTex)
Once an input option is selected, you must define the appropriate numerical input in the field to the right.
- Calculate - Once the input fields have been completed, click Calculate to determine the results. The remaining fields will be populated as follows:
- Cross Sectional Area - (units: in2, mm2) Defines the cross sectional area of a narrow bundle of fibers.
- Yield - (units: yd/lb, m/kg) Describes the length a bundle of fibers will reach per unit mass of the material.
- Denier - (units: g/9000m) Unit of measure for the linear mass density of fibers.
- Lineal Density - (units: g/m) Measure of mass per unit length for fibers.
- Tex - (g/1000m) Unit of measure for the linear mass density of fibers.
- deciTex - Unit of linear density equal to 1/10th of a Tex or 9/10ths of a denier.