Depending on the look you are trying to apply to an object or the scene, you can select from among different shader algorithms. The differences between the shader types are sometimes subtle, as they build upon the same algorithms, such as Fresnel or the Oren-Nayar diffuse model.
Some of the settings in the Shader menu change depending on the shader type chosen. See the following sections for the specific settings for each shader type.
- Shader Type box
- Select a shading algorithm, or turn shading off.
Physically Based Shader
Use the Physically Based shader (PBS) to accurately represent real-world materials. In a PBS workflow, some Physically Based shader settings override the Geom, Material, or Surface node settings. For example, specular and shine settings in the Material or Geom menu do not have any effect.
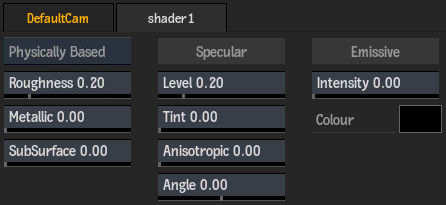
- Roughness field
- Displays how the light reflects from the surface, based on the roughness of the material. Use a lower value for pure specular, or a higher value for high dispersion. Editable.
- Metallic field
- Displays the relative weight between the dielectric and metallic BRDF model, where 0 is pure dielectric and 1 is metallic. Editable.
- SubSurface field
- Displays the diffuse part to approximate a subsurface scattering effect for the dielectric model (has no effect on the metallic model). Editable.
- Specular Level field
- Displays the Fresnel F0 specular reflectance at normal incidence for the dielectric model (for the metallic model the F0 follows the Base Color of the material). Editable.
- Specular Tint field
- Displays the contribution of the Base Color (Diffuse) to tint the specular for the dielectric model (has no effect on the metallic model). Editable.
- Anisotropic field
- Displays the distortion of the specular lobe, according to the tangent and bi-normal angles. Editable.
- Anisotropic Angle field
- Displays the rotation of the distortion of the anisotropic specular lobe. Editable.
- Emissive Intensity field
- Displays the intensity of the light emitted by the material. Editable.
- Intensity Colour pot
- Displays the colour of the emitted light by material. Click to change the colour.
Car Paint Shader
Use the Car Paint shader to blend between two colour tones, based on the viewing angle and the normal of the object. This shader includes Cook-Torrance shaders and Fresnel controls for the specularity.
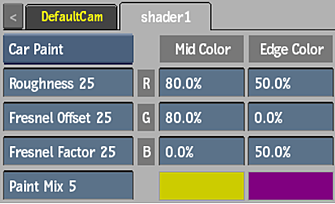
- Roughness field
- Displays the shape of specularity of the shader.
- Fresnel Offset field
- Displays the total amount of specular light.
- Fresnel Factor field
- Displays the amount of specular light at grazing angles.
- Paint Mix field
- Displays the viewing angle of the normal that occurs between parallel (mid colour) and perpendicular (edge colour). Editable.
- Red Mid Colour field
- Displays the red mid colour value. Editable.
- Green Mid Colour field
- Displays the green mid colour value. Editable.
- Blue Mid Colour field
- Displays the blue mid colour value. Editable.
- Mid colour pot
- Diplays the mid colour. Editable.
- Red Edge Colour field
- Displays the red edge colour value. Editable.
- Green Edge Colour field
- Displays the green edge colour value. Editable.
- Blue Edge Colour field
- Displays the blue edge colour value. Editable.
- Edge colour pot
- Displays the edge colour. Editable.
Fresnel Shader
The Fresnel shader contains only Fresnel controls for the specularity.
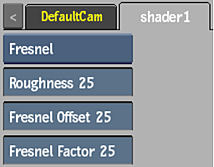
- Roughness field
- Displays the shape of specularity of the shader.
- Fresnel Offset field
- Displays the total amount of specular light.
- Fresnel Factor field
- Displays the amount of specular light at grazing angles.
Cook-Torrance Shader
Use the Cook-Torrance shader for high specularity materials, such as metals or shiny plastics. This shader includes Fresnel controls for specularity.
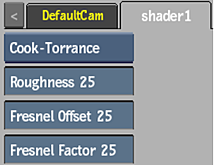
- Roughness field
- Displays the shape of specularity of the shader.
- Fresnel Offset field
- Displays the total amount of specular light.
- Fresnel Factor field
- Displays the amount of specular light at grazing angles.
Anisotropic Shader
Use the anisotropic shader to control the specular effect of the highlights.
- X Roughness field
- Displays the shape of specularity of the shader along the X axis. Editable.
- Y Roughness field
- Displays the shape of specularity of the shader along the Y axis. Editable.
- Fresnel Offset field
- Displays the total amount of specular light.
- Fresnel Factor field
- Displays the amount of specular light at grazing angles.