There are two ways to created revolved features: from a sketch profile or from a primitive.
The primitive shape creation commands create full revolutions only. They do not create surfaces or partial revolutions.
Create a Revolved Feature from a Profile
- In the browser, select an unconsumed 2D sketch that represents a profile or cross-section of the revolved feature or body you want to create.
- On the ribbon, click 3D Model tab
 Create panel
Create panel  Revolve
Revolve  .
. If there is only one profile in the sketch, it is selected automatically. Otherwise, select a sketch profile.
- In the Revolve dialog box, click Profile and then select the profile to revolve.
- Click Axis and then select an axis from the active sketch plane.
- If there are multiple bodies in the part file, click the Solids selector in the Shape tab of the Revolve dialog box to choose the participating body.
- If you select an open profile in a part file, specify whether you want to Match Shape and, if so, select the side to keep. Selecting Match Shape creates a flood-fill revolved feature. The open ends of the profile are extended to the axis of revolution (if possible), or to the bounding box of the body. The Match Shape revolution generates a stable and predictable body for topology changes on the defining faces.
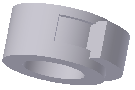 Clear the Match Shape option to close the open profile by extending the open ends to the part, and closing the gap between them. The revolution is created as if you specified the closed profile.
Clear the Match Shape option to close the open profile by extending the open ends to the part, and closing the gap between them. The revolution is created as if you specified the closed profile.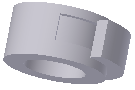
- Specify the Output type:
- Solid
 . Creates a solid feature from an open or closed profile. Open profile selection is not available for base features.
. Creates a solid feature from an open or closed profile. Open profile selection is not available for base features. - Surface
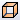 . Creates a surface feature from an open or closed profile. Functions as a construction surface on which to terminate other features, or a split tool to create a split part, or split a part into multiple bodies. Surface selection is not available for assembly extrusions or primitives.
. Creates a surface feature from an open or closed profile. Functions as a construction surface on which to terminate other features, or a split tool to create a split part, or split a part into multiple bodies. Surface selection is not available for assembly extrusions or primitives.
- Solid
- For non-base features, specify an Operation:
- Join
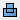 . Adds the volume created by the revolved feature to another feature or body. Not available in the assembly environment (not available in Inventor LT).
. Adds the volume created by the revolved feature to another feature or body. Not available in the assembly environment (not available in Inventor LT). - Cut
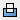 . Removes the volume created by the revolved feature from another feature or body.
. Removes the volume created by the revolved feature from another feature or body. - Intersect
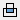 . Creates a feature from the shared volume of the revolved feature and another feature. Deletes material that is not included in the shared volume. Not available in the assembly environment (not available in Inventor LT).
. Creates a feature from the shared volume of the revolved feature and another feature. Deletes material that is not included in the shared volume. Not available in the assembly environment (not available in Inventor LT). - New Solid
 . Creates a solid body. Each solid body is an independent collection of features separate from other bodies. A body can share features with other bodies.
. Creates a solid body. Each solid body is an independent collection of features separate from other bodies. A body can share features with other bodies.
- Join
- Using the Extents list and related options, determine the method for the revolution and set its angular displacement around the centerline:
- Angle. Revolves the profile through the specified angle. Direction arrows specify direction of revolution. Click an arrow to indicate revolution direction or to divide the angle equally in both directions.
- Angle – Angle. Accepts two angular values to revolve the profile in two directions, one positive and one negative. To activate Angle-Angle, choose Extents > Angle and then click Asymmetric. Enter displacement values for each angle. Click Flip to reverse the two angular displacements so that the positive angle becomes negative and the negative angle becomes positive.
- To Next. (Not available for base features or assembly extrusions.) Selects the next possible face or plane on which to terminate the revolution in the specified direction. Dragging the profile flips the revolution to either side of the sketch plane. Click the body to end the feature creation.
- To. Terminates the revolved feature on the selected face or plane, or on a face that extends beyond the termination plane. Select a sketch point, work point, model vertex, or an end termination plane.
For assembly revolved features (not available in Inventor LT), faces and planes that reside on other components can be selected. The selected faces or planes must reside on the same assembly level as the assembly revolution being created.
- Between. Selects beginning and ending faces or planes on which to terminate the revolution.
For assembly revolved features (not available in Inventor LT), faces and planes that reside on other components can be selected. The selected faces or planes must reside on the same assembly level as the assembly revolution being created.
- Full. Revolves the profile 360 degrees. Click the direction of the revolution.
- Symmetric. Revolves in two directions with half the total value. Enter one angular value.
- Asymmetric. Revolves in two directions with different values. Enter a value for the positive angle and enter a second value for the negative angle.
- On the More tab of the Revolve dialog box, clarify To and Between extents by choosing a solution method:
- Alternate Solution. When a solution is ambiguous, specifies an alternate termination plane.
- Minimum Solution. When options for termination faces are ambiguous, specifies that the revolution terminates on the closest face. With Minimum Solution deselected, the revolution terminates on the farthest face.
- Infer iMate . (Optional) Places an iMate on a full circular edge. Autodesk Inventor attempts to place the iMate on the closed loop most likely to be useful. In most cases, place only one or two iMates per part.
- Click OK.
Create Revolved Feature from a Primitive
- Click 3D Model tab
 Primitives panel Sphere
Primitives panel Sphere  or 3D Model tab
or 3D Model tab  Primitives panel Torus
Primitives panel Torus  .
. - Select a sketch plane. The sketch plane can be an origin plane, a work plane, or a planar face.
- Define the shape by doing one of the following:
- For a sphere, click to define the center and then click to define the diameter.
- For a torus, click to define the center, click to define the center of the section, and then click to define the diameter of the section.
- If there are multiple bodies in the part file, click the Solids selector in the Shape tab of the Revolve dialog box to choose the participating body.
- Specify an Operation:
- Join
 . Adds the volume created by the revolved feature to another feature or body. Not available in the assembly environment (not available in Inventor LT).
. Adds the volume created by the revolved feature to another feature or body. Not available in the assembly environment (not available in Inventor LT). - Cut
 . Removes the volume created by the revolved feature from another feature or body.
. Removes the volume created by the revolved feature from another feature or body. - Intersect
 . Creates a feature from the shared volume of the revolved feature and another feature. Deletes material that is not included in the shared volume. Not available in the assembly environment (not available in Inventor LT).
. Creates a feature from the shared volume of the revolved feature and another feature. Deletes material that is not included in the shared volume. Not available in the assembly environment (not available in Inventor LT). - New Solid
 . Creates a solid body. Each solid body is an independent collection of features separate from other bodies. A body can share features with other bodies.
. Creates a solid body. Each solid body is an independent collection of features separate from other bodies. A body can share features with other bodies.
- Join
- (Optional) On the More tab of the Revolve dialog box, select Infer iMate to place an iMate on a closed loop.
- Click OK.