In this lesson, you use Revit to change the carport so it can accommodate two cars instead of one. This gives us a chance to demonstrate the dynamic capability of the File Link Manager.
Use Revit to edit the carport:
- Open the Revit window once again.
- On the Project Browser panel at the left, double-click Floor Plans
 Carport.
Carport. 
Revit displays the carport floor plan.
-
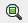 Zoom in to get a good view of the carport area.
Zoom in to get a good view of the carport area. 
- Click to select axis 1, the left side of the carport.

- Drag axis 1 to the left, to a point near the axis A and B markers.
Revit expands the size of the carport.
 Note: The upright posts are constrainted to the roof of the carport, so when you increase the size of the roof, the posts move along with it.
Note: The upright posts are constrainted to the roof of the carport, so when you increase the size of the roof, the posts move along with it. - In the Project Browser panel, double-click 3D Views
 Exterior.
Exterior. 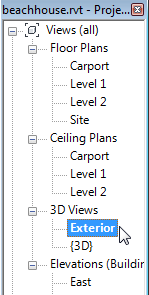
- If you adjust the 3D view, you can see that the carport is now big enough for two cars.
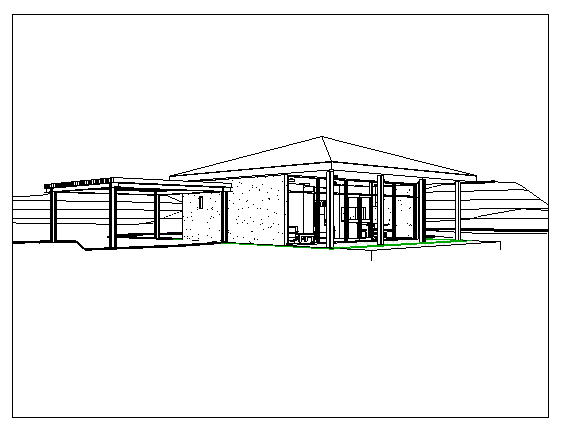
- Open the
 Application menu and choose Export
Application menu and choose Export  FBX. Note: At this point, Revit might prompt you to save the project. You don’t need to save the project to proceed with this tutorial.
FBX. Note: At this point, Revit might prompt you to save the project. You don’t need to save the project to proceed with this tutorial.Revit opens a file dialog.
- In the file dialog, choose the same
beachhouse.fbx
that you created earlier, then click Save.
Revit warns you that you are about to overwrite beachhouse.fbx .
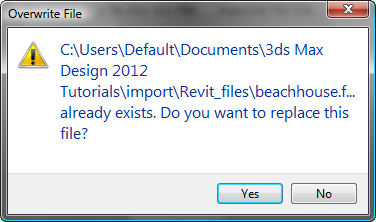
- Click Yes.
- Exit Revit.
You won’t be using Revit any further in this tutorial.
Note: You don’t need to save changes to beachhouse.rvt .
To complete this procedure, you must have Revit installed on your workstation. If you do not have Revit installed, proceed directly to the next procedure, "Reload the FBX file."
In 3ds Max, reload the FBX file:
- Open the 3ds Max window once again.
- If you skipped the Revit procedure, do the following:
- Use Windows Explorer to copy the beachhouse.fbx file from the \import\revit_files\updated_fbx subfolder to the main \import\Revit_files folder. This file has been set up for you. Overwrite the previous version of beachhouse.fbx.
- From the
 Application menu, choose References
Application menu, choose References  Manage Links.
Manage Links. 3ds Max opens the File Link Manager dialog.
- On the File Link Manager dialog, go to the Files panel.
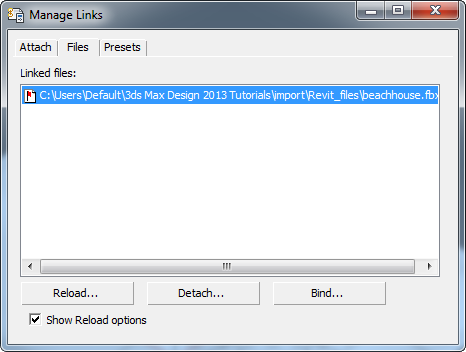
The entry for beachhouse.fbx now shows a red flag icon: This indicates that the FBX file has changed.
- Click Reload.
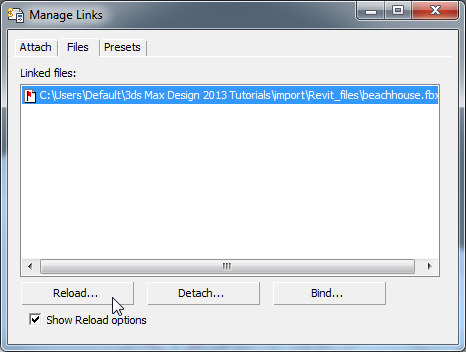
3ds Max opens a File Link Settings: Revit Files dialog.

- Accept the default options for reloading the FBX file, and click OK.
3ds Max displays a progress bar while it reloads the FBX file. Leave the File Link Manager dialog open for now.
-
 Select the SunAndSky-002 Daylight object, and go to the
Select the SunAndSky-002 Daylight object, and go to the  Motion panel.
Motion panel. - On the Motion panel, verify that the Daylight settings are as they were before:
- Hours=15
- Minutes=17
- Month=5
- Day=10
- Location = Boston, MA
Correct these values if you need to, then in the Location group, change the value of North Direction back to 300.0.
You need to reset the North Direction because Revit saved Daylight values to the FBX file.
- Activate the 3D View: Exterior viewport, and
 render the scene.
render the scene. 
Now the beach house has a double-wide carport in 3ds Max as well as in Revit.
Bind the FBX geometry to 3ds Max:
- On the File Link Manager dialog
 Files panel, click Bind.
Files panel, click Bind. 
3ds Max displays a warning that you are about to break the live link.
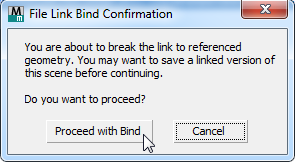
- Click Proceed With Bind.
3ds Max binds the geometry and converts it to Mesh objects.
-
 Close the File Link Manager dialog.
Close the File Link Manager dialog. From this point on in this tutorial, you will work exclusively with 3ds Max geometry and lighting.
In the next lesson, you use an “mr Sky Portal” object to take some of the daylight and channel it into the beach house, to give its interior more ambient illumination.
We don’t plan to revise the beach house model further in Revit, so at this point, you will bind the model to 3ds Max. This has the advantage of making the beach house geometry into full-fledged mesh objects that you can edit with the 3ds Max tools.