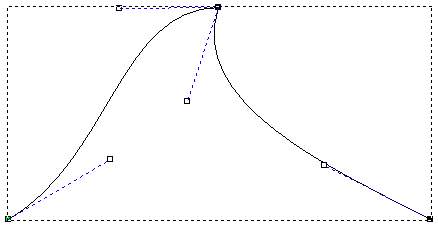
You can smooth any node in a vector other than the start node or the last node in an open, ungrouped vector.
When smoothing, the span on either side of a node is converted to a Bézier curve span. ArtCAM adds control points to the node, giving you control over the degree of curvature in the whole vector.
To smooth nodes:
- Select
Vector > Node Editing or click the
Node Editing
 button.
button.
- Select the vector containing the point you want to smooth. The selected vector is surrounded by a bounding box, within which you can see the spans, nodes and control points that make up the selected vector. All unsmoothed nodes are black.
- Position the cursor over the node you want to smooth. When the cursor changes from
 to
to
 , right-click to display its context menu.
, right-click to display its context menu.
- From the context menu, select
Smooth Node to convert the spans on either side of the node to Bézier curves. The node turns blue.
For example, the node in the middle of the vector shown below has been smoothed:
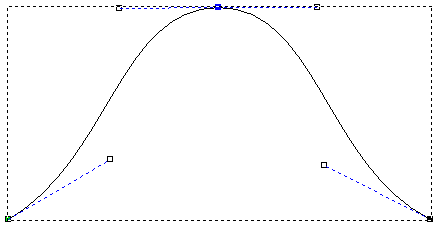
If you move one of the control points next to the smoothed node, the other one moves too. This simultaneous movement preserves the tangency between the two Bézier curve spans.
To smooth a group of nodes:
- Select
Vector > Node Editing or click the
Node Editing
 button.
button.
- Select the vector containing the nodes that you want to smooth. The selected vector is surrounded by a bounding box, within which you can see the spans, nodes and control points that make up the selected vector.
- Select the nodes you want to smooth.
- Right-click any of the selected nodes to display their context menu.
- Select Smooth Node to convert the spans on either side of the selected nodes to Bézier curves.
To remove the smoothing option from a smoothed node:
- Select
Vector > Node Editing or click the
Node Editing
 button.
button.
- Select the vector containing the smoothed nodes from which you want to remove smoothing. The selected vector is surrounded by a bounding box, within which you can see the spans, nodes and control points that make up the selected vector.
- Position the cursor over a smoothed node. When the cursor changes from
 to
to
 , right-click to display its context menu.
, right-click to display its context menu.
- Deselect
Smooth Node. The node turns black.
Although the span on either side of the node remains as a Bézier curve span, deselecting the Smooth Node option causes the control point on either side of the node to affect its adjoining Bézier curve span only, rather than the whole vector.
In this example, you can see that moving one control point no longer moves the other: