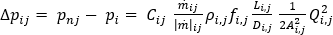The Darcy-Weisbach equation calculates the pressure drop due to friction in a straight length of pipe or duct.
The fundamentally most sound and versatile equation for frictional head loss in a pipe or duct is the Darcy-Weisbach equation.
The Darcy-Weisbach equation is given by:
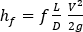
where
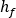 is the pressure loss in meters,
is the pressure loss in meters,
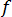 is the friction factor, V is the mean fluid velocity in the channel, D is the diameter of the channel, L is its length, and
is the friction factor, V is the mean fluid velocity in the channel, D is the diameter of the channel, L is its length, and
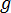 is gravitational acceleration.
is gravitational acceleration.
The functional behavior of the dimensionless friction factor,
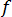 , is displayed fully in the
Moody diagram, which is valid for both compressible and incompressible fluids. To solve the friction factor numerically, the Moody diagram must be reduced to a form that can be programmed, using approximations such as the Swarmee-Jain approximation of the Colebrook-White equation.
, is displayed fully in the
Moody diagram, which is valid for both compressible and incompressible fluids. To solve the friction factor numerically, the Moody diagram must be reduced to a form that can be programmed, using approximations such as the Swarmee-Jain approximation of the Colebrook-White equation.
To correlate the Darcy-Weisbach equation to the work-energy principle equation, the Darcy-Weisbach equation must be rewritten in terms of the volumetric flow rate:
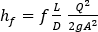
and then written in terms of pressure, rather than height:
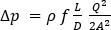
Referring back to the work-energy principle equation, for each element in the computational domain, and adding frictional head loss to the equation, then the discretized form of the Darcy-Weisbach equation can be written: