In this task, you will interpret four different circuit results.
-
Select Circuit coolant temperature result in the study tasks list.
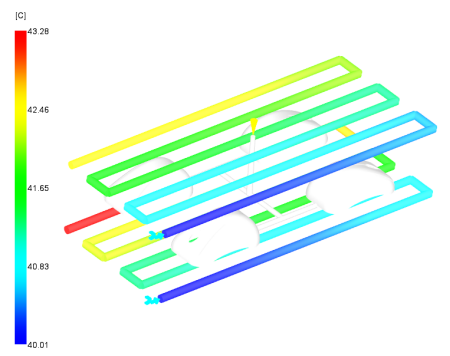
Figure 1: Circuit coolant temperature result
An increase in temperature more than 2-3C is a problem. The core side is slightly more than the guideline.
-
Select the Circuit Reynolds Number result.
The results are exactly 10,000 Reynolds number because this value was used as input for calculating flow rate. A Reynolds Number of 10,000 or more indicates turbulent flow, the most efficient form of flow for heat extraction.
-
Select the Circuit flow rate result.
The flow rate required to achieve 10,000 Reynolds number is just over 3.5 l/min. This flow rate is not high, so the mold is probably not be flow rate limited.
-
Click the Temperature, mold result.
This result represents the cycle averaged mold temperature at the mold surface or plastic/metal interface. The variation in temperature for an amorphous material like the ABS used here, is best when within +/- 10C from the target temperature. In this case, the target temperature is 60C. The range for this part is outside this range. Most of the part is too cool, in particular the cavity side. Also the core side is much hotter than the cavity side. This temperature distribution can contribute to the part warping.
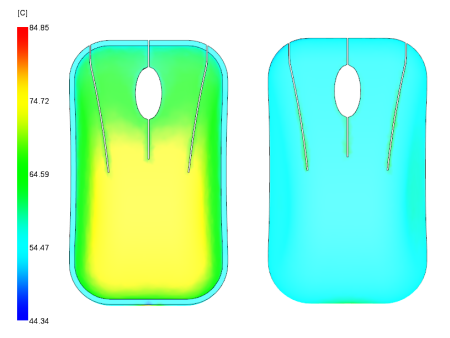
Figure 2: Temperature, mold result
Both the circuit coolant temperature and the circuit metal temperature indicate a problem.
These results are improved by:
- A higher coolant flow rate.
- More cooling channels/ circuits. Uneven cooling across the mold could result in different part quality depending on the cavity being reviewed.
- A longer cycle time.