Insert symbols and details into your drawings from commercial online sources or from your own designs.
Some Basic Definitions
In AutoCAD, a block is a collection of objects that are combined into a single named object. The following are some examples of a variety of blocks at different scales.
There are three elements involved for inserting blocks in a drawing.
- A block definition. This data is stored in a drawing file or drawing template file in a non-graphical format. Block definitions can easily be imported from any drawing file or existing blocks in any drawing file. You can also create block definitions from selected objects in the current drawing.
- A block reference. When you insert a block, the graphics are generated from the block definition.
- A block insertion tool. Use the Blocks palette to insert blocks.
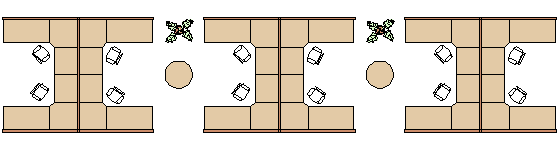
For example, the following drawing contains four block definitions: Cubicle, Chair, Table, and Plant. There are three block references to Cubicle, twelve block references to Chair, two block references to Table, and two block references to Plant.
Sources for Blocks
Typically, you insert a block into the current drawing from one of these sources:
- Any drawing file. For example, you might create a drawing of a standard detail view. You can then insert this drawing as a block into your current drawing.

- One or more block definitions contained within a drawing file. For example, you can create a drawing that only contains block definitions of trees. You can then insert any of these blocks from that drawing into your current drawing. A drawing file that contains a family of related blocks is commonly termed a
block library drawing.
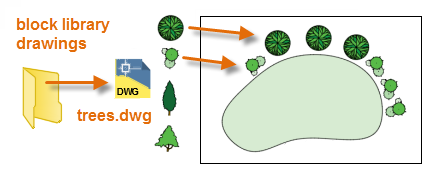
- One or more block definitions created in your
current drawing. For example, you might want to create a block from a set of objects that appear repeatedly in that drawing, such as a cubicle arrangement. All the blocks previously listed could be included together in a
single, three-cubicle block.

Once you insert a block, you can easily move, copy, rotate or scale it.
Insert a Block
The Blocks palette is used to insert blocks.
- Click
.

This opens the Blocks palette and makes it active. By default it is docked on the right-side of the application.

Display Options Toolbar
 Displays the blocks in the current drawing.
Displays the blocks in the current drawing.
 Displays recently inserted or created blocks. The recent list persists across drawings and sessions.
Displays recently inserted or created blocks. The recent list persists across drawings and sessions.
 Displays the blocks that you have selected as favorites from the Blocks list.
Displays the blocks that you have selected as favorites from the Blocks list.
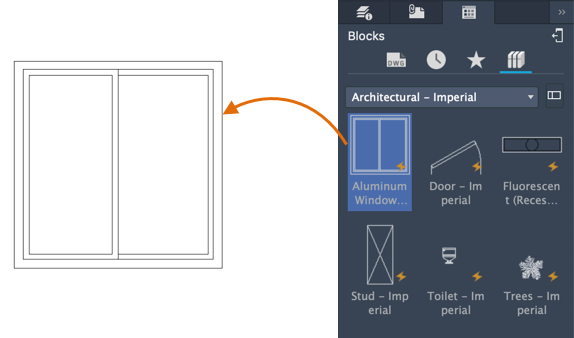
 Displays the blocks from a selected block library. Select the library from the drop-down.
Displays the blocks from a selected block library. Select the library from the drop-down.
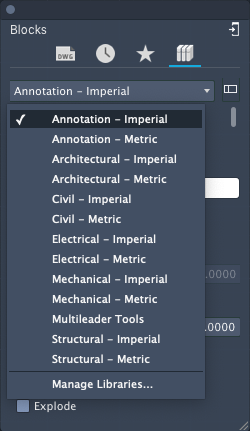
- Select the display option for block libraries.

Each of these block libraries contain a set of related block definitions.
- Select a block library that interests you.
- From the Blocks palette, double-click to place the block, or drag to place it. When you double-click to place the block you can use object snaps for more precision.
You can also browse to a drawing file and insert it as a block or display the blocks on the drawing in the Blocks palette.
- Select the display option to show the blocks from the current drawing.

- Click the plus sign icon.
- Browse to the drawing file you want to insert.
Create a Drawing for Use as a Block
Often, individual drawing files are created to be used as blocks and saved in a folder with similar drawing files. This method is an alternative to accessing the block definitions stored in a single drawing.
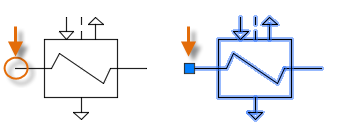
When you create a drawing file for use as a block, make sure that you locate an object at the origin point (0,0). This will serve as the default insertion point of the block. Later, when you insert the block, it is attached to your cursor at the insertion point. The insertion point is circled on the block below.
If you select a block that's already been inserted, it displays a grip at the insertion point. You can easily move and rotate this block using this grip.
In the following example, a drawing file is inserted into the current drawing to provide a standard detail view.
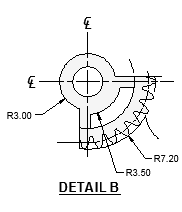
Custom title blocks and drawing borders are also created as drawing files that can be inserted later or included in drawing template files.
Inserting a drawing file as a block provides a static reference to the specified drawing. For a reference that automatically updates when it's changed, you would attach the drawing as an external reference instead. For more information, search the Help system for xrefs.
Manage Block Definitions and Data in a Drawing (Optional)
You can create, remove, and modify block definitions directly in the current drawing for special circumstances.
- Remove unused block definitions from a drawing with the PURGE command. Purging a drawing of unused block definitions can reduce the size of a drawing. You can purge only those block definitions that aren't used by any block references in the drawing.
- Create new block definitions directly in the current drawing with the BLOCK command. Creating block definitions is useful either if you need a block that's unique to that drawing or if you want to create a block library drawing that contains a family of related block definitions.
- Disassemble a block reference into its constituent objects with the EXPLODE command. Exploding block references provides an easy way to define new versions of a block definition with the BLOCK command or to save the resulting objects to a new drawing file with the WBLOCK command.
Suggestions and Recommendations
Several different methods are commonly used for saving and organizing block definitions.
- Create an individual drawing file for each block that you intend to use. You save these drawing files in folders that contain families of related drawing files.
- Create drawing files called block library drawings. Each one of these drawings contains a family of related block definitions. When you insert a block library drawing into your current drawing, all the blocks that are defined in that drawing become available to your current drawing.
- Include the block definitions for title blocks and commonly used symbols in your drawing template files to make them available immediately when starting a new drawing.