It’s possible to move ArmControl so that the mechanical arm fully extends to a straight position or orients itself to other positions that you don’t necessarily want.
You can limit the range of motion of the arm to ensure that the IK system poses in a predictable manner. In the following section, you limit the motion for the IK system as follows:
- Lock the translation of the control object (ArmControl) so that it can only move in Y and Z. By locking the X channel so it cannot be selected or modified, the arm will not be able to move from side to side.
- Lock the rotations on the swiveling base for the arm so it only rotates about its Y axis, and not about its X or Z axes.
- Limit the translations for the Arm Control so the mechanical arm cannot fully extend to a straightened position.
To lock the Translate X channel for ArmControl
- In the Outliner, select the ArmControl node.
- Open the Channel Box to view the transform channels for ArmControl.
- Set all Translate or Rotate channels to 0, if they are not already.
- In the Channel Box, select the Translate X channel by clicking on its name.
- Right click on the word
Translate X.
A drop-down menu appears.
- From the drop-down menu, choose
Lock Selected.
The numerical field for Translate X is dimmed indicating that the channel is locked. If you try to move ArmControl in X, it will not be possible unless you unlock the Translate X channel.
To lock the Rotate X and Z channels for SwivelBase
- In the Outliner, select only the SwivelBase node.
- Open the Channel Box to view the rotation channels for SwivelBase.
- Set all Translate or Rotate channels to 0, if they are not already.
- In the Channel Box, select the Rotate X and Rotate Z channels by Ctrl-clicking on their names.
- Right-click on either of the selected names and select Lock Selected from the drop-down menu that appears.
To confirm that the Rotate X & Z channels are locked
- In the Outliner, ensure only the SwivelBase node is selected.
- From the side view's panel menu, select Panels > Orthographic > top.
- In the panel menu, select Shading > Smooth Shade All.
- Dolly the top view so you can fully view the mechanical arm as shown below.
- Using the
Channel Box, rotate SwivelBase by typing 45 in the
Rotate Y channel and pressing Enter.
SwivelBase rotates in the view but the mechanical arm does not rotate.
You first might think something is wrong because SwivelBase and all of the arm’s skeletons and surfaces are parented into the same hierarchy.
If you discover that something doesn’t work in the manner you originally anticipated when setting up an IK system, it’s useful to stop and diagnose why something is working the way it is (or not working the way it should). In that way you can retrace your actions to determine where the problem resides.
In this example, ArmControl and IK Handle are not parented into the SwivelBase hierarchy.
Because ArmControl and IK Handle control the movements of the mechanical arm, they must be parented into the SwivelBase hierarchy in order for the arm to rotate when SwivelBase is rotated.
To parent the IK Handle into the skeleton hierarchy
- In the Outliner, select the SwivelBase node.
- In the
Channel Box, reset the
Rotate Y channel for SwivelBase to 0.
Setting any previous transformations to zero is necessary before parenting the IK Handle beneath SwivelBase in the hierarchy.
- Unselect the SwivelBase node before performing the following steps.
- In the
Outliner, Control-select the nodes named ikHandle1, ArmControl, and SwivelBase.
The order of selection is important. You want to Shift-select the items that will be the child nodes first, and then Shift-select the item that will be the parent node last.
- In the main menu, select
Edit > Parent (Hotkey p).
In the Outliner, IKHandle and ArmControl are now child nodes for the SwivelBase node in the skeleton hierarchy.
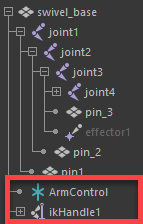
- In the Outliner, select only SwivelBase.
- Using the
Channel Box, set
Rotate Y for SwivelBase to 45.
When SwivelBase is rotated, the mechanical arm rotates because of its relationship within the hierarchy.
- Reset the Rotate Y value for SwivelBase back to 0.
Finally, you want to limit how far Arm Control can translate away from the base of the model so the arm does not extend to a fully straightened position.
To determine the settings for the translation limits you need to examine the position of the mechanical arm in various positions while simultaneously viewing the translation values in the Channel Box.
To determine translation limits for the Arm Control
- In the Outliner, select ArmControl.
- Ensure the Channel Box is open so you can view the translate channels for ArmControl.
- In the view, select Panels > Orthographic > side.
- Press 4 to return to wireframe mode.
- Dolly the side view so you can fully view the mechanical arm.
- Select the Move Tool.
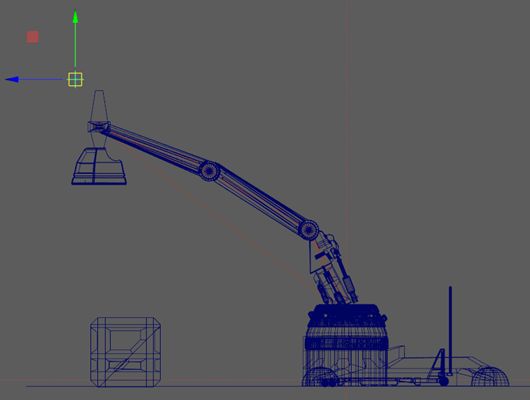
- In the side view, middle-click and drag the mouse diagonally until the mechanical arm is fully extended as shown below.
- In the
Channel Box, observe the number that displays in the
Translate Y and Z channels.
When the arm is diagonally articulated above the cargo box, it is almost fully extended when the translation values are roughly as follows:
- Translate Y: 6.5
- Translate Z: 3
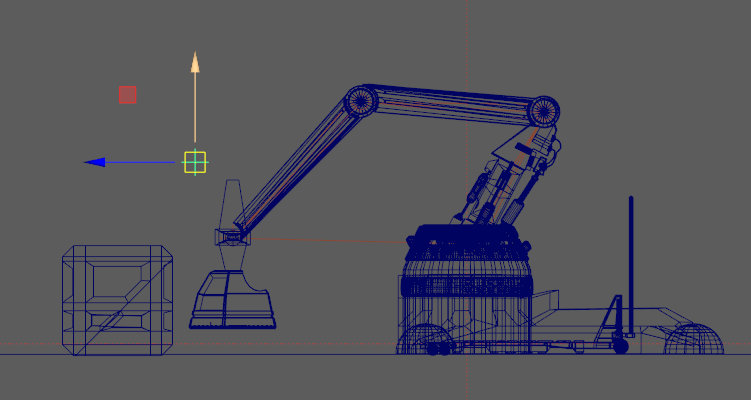
- In the side view, press the middle mouse button and drag the mouse diagonally until the mechanical arm is almost fully compressed as shown below.
- In the
Channel Box, observe the numbers that display in the
Translate Y and Z channels.
When the arm is articulated to a compressed pose, the translation values are roughly as follows:
- Translate Y: -15
- Translate Z: -8.5
These minimum and maximum values will be used in the steps that follow as the minimum and maximum translation limits for the ArmControl.
To set translation limits for the Arm Control
- In the Outliner, select the ArmControl node.
- Open the
Attribute Editor (Window > Attribute Editor or click on the
Show/Hide Attribute Editor icon on the
Status Line).
The Attribute Editor displays the nodes associated with Arm Control.
- In the
Attribute Editor, click the ArmControl tab.
If the ArmControl tab is not visible, use the left and right scrolls arrows to scroll the view sideways to view it.
- In the Attribute Editor, expand the Limit Information attributes, and then the Translate attributes.
-
In the
Translate attributes, click the
Trans Limit Y and
Trans Limit Z check boxes for both the
Min and
Max values, then set the following values:
- Trans Limit Y (Min): -15
- Trans Limit Y (Max): 6.5
- Trans Limit Z (Min): -8.5
- Trans Limit Z (Max): 3
- Hide the Attribute Editor.
- Select ArmControl.
- In the side view, move ArmControl to test the range of movement for the IK system.
The mechanical arm moves with a limited range of motion.