The Channel Info utility gives game artists and others direct access to objects' channel information that might not otherwise be easily available. All objects in 3ds Max have mapping channels, which hold information pertinent to texture mapping as well as vertex color, illumination, and alpha. Mesh objects also have geometry and vertex-selection channels. The Channel Info utility lets you view an object's channels, give them meaningful names, delete unused channels, and copy information between channels.
The utility's Map Channel Info dialog shows all the channel data for selected objects. It displays the number of channels, the number of vertices per channel, and how much memory the channel uses. It also lets you name channels, as well as clear (or delete), copy, and paste channels. Each of these actions except renaming puts a modifier on the stack to achieve the results.
Procedures
To use the Channel Info utility:
-
 Select an object or objects to use with the utility.
Select an object or objects to use with the utility. - Open the utility.
The Map Channel Info dialog opens.
- To create a map channel, click any channel and then click the Add button.
The new, empty channel appears at the end of the list.
- Most channels have three components. For example, a mesh or map channel has X, Y, and Z components, and an alpha channel has R, G, and B components. To expand all three-component channels, click the SubComp button. To collapse all expanded channels, click SubComp again.
- To copy one channel to another, click the source channel, click Copy, and then click the destination channel and click Paste.
In some cases, you might need to expand or collapse the component display (see previous step). For example, when copying a vertex selection (vsel) channel to a map channel, you must paste the vsel channel to a component channel.
- To minimize a channel's memory footprint, click the channel and then click the Clear button.
This removes most all or of the data from the channel, so first make sure the data is unnecessary or is available elsewhere. If the cleared channel is the last one in the list, it might be deleted from the list.
Interface
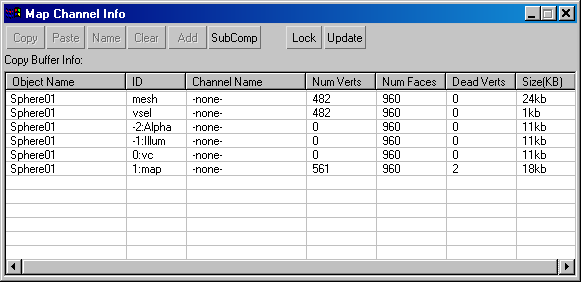
The primary user interface of the Channel Info utility is the Map Channel Info dialog, which you open by clicking the utility's Channel Info button on the command panel. This modeless dialog shows information about all map channels belonging to the current selection, at the object level. If you change the selection, the dialog automatically updates to reflect the selection.
The dialog consists of two parts: a button toolbar at the top, and a tabular display of map channels belonging to each object in the current selection.
Channel Info toolbar
- Copy
-
Copies the channel data from the highlighted channel to the copy buffer, where it becomes available for pasting. After you copy a channel, its name appears on the line below the button toolbar.
- Paste
-
Pastes the contents of the copy buffer to the highlighted channel.
You can copy and paste only between channels with the same topology, or you can copy from any channel to a channel with no vertices.
Source and destination channels need not be of the same type. For instance, you can copy from a mesh channel to a map channel, and vice-versa.
- Name
-
Lets you rename the highlighted channel. Click this button to open a small dialog that displays the current channel name and lets you edit this name or enter a new one from the keyboard.
- Clear
-
Use this function to remove channels or delete data from a map channel (including alpha, illumination, and vertex color channels). Clear has no effect on geometry or vertex selection channels.
The specific result depends on the type of object and which channel you clear. With respect to reducing the object's memory footprint, the utility is most effective with Editable Poly objects.
-
Geometric primitive or Editable/Edit Mesh object Deletes the highlighted texture map channel if it is the last map channel in the object, and it's not the default map channel (1:map). If the highlighted channel is not the last, Clear deletes all vertices in the channel. The faces remain, so the memory-footprint reduction is partial. Note: This also applies to objects that collapse to editable mesh, such as Loft objects.
- Editable Poly object Deletes the highlighted texture map channel if it is the last map channel in the object, and it's not the default map channel. If the highlighted channel is not the last, Clear deletes all vertices and faces in the channel.
- Patch object Deletes the highlighted texture map channel if it is the last map channel in the object, and it's not the default map channel. If the highlighted channel is not the last, Clear has no effect.
Note: When you use the Clear function, 3ds Max adds a UVW Mapping Clear modifier to the object's modifier stack. You can recover the deleted data by removing the modifier from the stack, or changing its Map Channel setting. -
Geometric primitive or Editable/Edit Mesh object Deletes the highlighted texture map channel if it is the last map channel in the object, and it's not the default map channel (1:map). If the highlighted channel is not the last, Clear deletes all vertices in the channel. The faces remain, so the memory-footprint reduction is partial.
- Add
-
Appends a new map channel to the object's channel list. If multiple objects are selected, Add becomes available only after you click a track, so 3ds Max knows which object to add the channel to.
Note: If you apply mapping with a channel number higher than any existing channels, 3ds Max automatically creates all intermediate channels. For example, if you apply a UVW Mapping modifier to a standard object and set Map Channel to 5 in the modifier, 3ds Max adds map channels 2, 3, 4, and 5. - SubComp
-
Toggles display of the channels' subcomponents. When displayed, you can rename, copy, and paste each subcomponent independently of its parent channel.
Each channel except vsel has three subcomponents. Mesh and map channels' subcomponents are labeled X, Y, and Z; those of alpha, illumination, and vertex color channels are R, G, and B (red, green, and blue).
- Lock
-
Retains the current mapping data information in the table even if you change the selection.
For example, if you want to see mapping data for a specific object or objects constantly, first select the objects and then click Lock. Thereafter, if you select different objects in the viewport, the table continues to display the data for the selection when you clicked Lock. If you turn off Lock, the table updates to show data only for the current selection.
If you click Update when Lock is on, 3ds Max will refresh the table contents to reflect the current selection, and then retain that data.
- Update
-
Refreshes the displayed data to reflect any changes in the objects or mapping, or, when Lock is on, the selection.
For example, if you apply mapping to an object, or change its mapping, click Update to display the changes in the Map Channel Info dialog.
Channel Info table
The table functions similarly to a spreadsheet. If not all rows or columns are visible, you can scroll the table using standard methods, including rolling the mouse wheel for vertical scrolling. To highlight a row, click anywhere in the row. You can highlight only one row at a time. To resize a column, drag the vertical divider at the right of the column heading. To automatically set a column's width to the size of the longest entry, double-click the vertical divider to the right of the column heading.
Following is a brief explanation of each of the columns in the table:
- Object Name
-
The name of the object. If you change the name in the Modify panel, click the dialog's Update button to display the new name in the dialog.
- ID
-
The type of channel. The available channel types are:
-
mesh/poly The object's mesh or poly data, depending on whether it's a mesh or poly object: vertices and faces. You can copy this channel and paste it to any other three-component channel.
This channel is not available for patch objects.
-
vsel The vertex selection. You can copy this channel and paste it to other channels' subcomponents.
This channel is not available for patch objects.
-
-2:Alpha The vertex alpha channel. You can transfer all vertex alpha values between objects with the same topology by copying and pasting this channel.
You can apply vertex alpha information to objects with the VertexPaint modifier, and to editable surfaces with the Vertex Properties settings (editable poly) and Surface Properties (editable mesh and editable patch).
-
-1:Illum The vertex illumination channel. You can transfer all vertex illumination values between objects with the same topology by copying and pasting this channel.
You can apply vertex illumination information to objects with the VertexPaint modifier, and to editable surfaces with the Vertex Properties settings (editable poly) and Surface Properties (editable mesh and editable patch).
-
0:vc The vertex color (vc) channel. You can transfer all vertex color values between objects with the same topology by copying and pasting this channel.
You can apply vertex color information to objects with the VertexPaint modifier, and to editable surfaces with the Vertex Properties settings (editable poly) and Surface Properties (editable mesh and editable patch).
-
1:map The default mapping channel. You can transfer all UVW mapping information between objects with the same topology by copying and pasting this channel.
You can create additional mapping channels by various means, including with the Channel Info utility.
-
mesh/poly The object's mesh or poly data, depending on whether it's a mesh or poly object: vertices and faces. You can copy this channel and paste it to any other three-component channel.
- Channel Name
-
The name of the channel. By default, a channel has no name, as indicated by the entry “-none-”. To name or rename the channel, click the channel to highlight it and then click the Name button at the top of the dialog, or right-click the channel and choose Name from the right-click menu.
Note: Most channels can be split into subcomponents. You can name the subcomponents separately from the channel itself. - Num Verts
-
The number of vertices in the channel. To paste one channel to another, they must have the same number of vertices.
Some channels have faces but no vertices. This is typically the case with Alpha, Illumination, and vertex color channels in newly created non-poly objects. In such cases, these channels function as placeholders for the corresponding data should you add it later. They do consume a small amount of memory, so if you have no intention of using a channel, you can save some memory by converting the object to Editable Poly.
- Num Faces
-
The number of faces in the channel.
If a channel has faces but not vertices, that means it's a placeholder. See Num Verts, preceding, for more information.
- Dead Verts
-
The number of unused map vertices in the channel. Such vertices can be left over from sub-object editing.
- Size(KB)
-
The approximate amount of memory consumed by the channel. Use this figure to check for unused channels that are using up memory.