The door models provided let you control details of a door's appearance. You can also set the door to be open, partially open, or closed, and you can animate the opening.

Different door types in a model of a house
- The Pivot door is the familiar door that is hinged on one side only.
- The Bifold door is hinged in the middle as well as the side, like many closet doors. You can also make this type of door a set of double doors.
- The Sliding door has a fixed half and a sliding half.
The topic for each kind of door describes its unique controls and behavior. Most door parameters are common to all kinds of doors, and are described here.
- To pan the viewport, scroll the mouse wheel or drag with the middle mouse button.
- To orbit the viewport, press and hold Alt while scrolling the mouse wheel or dragging with the middle mouse button.
- To zoom the viewport, scroll the mouse wheel or hold down Alt+Ctrl and drag forward and back with the middle mouse button.
Doors and Materials
By default, 3ds Max assigns five different material IDs to doors. The aectemplates.mat material library includes Door-Template, a Multi/Sub-Object material designed to be used with doors. Each component of the door/material is listed below along with its corresponding Material ID.
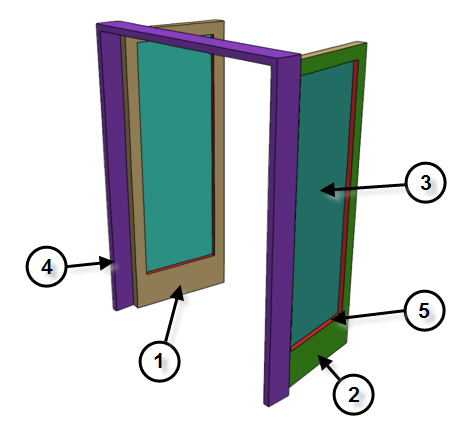
Material IDs for a door or window
| Material ID | Door/Material Component |
|---|---|
| 1 | Front |
| 2 | Back |
| 3 | Inner Bevel (used for glazing when Panels set to Glass or Beveled). |
| 4 | Frame |
| 5 | Inner Door |
Making an Opening for a Door
To make an opening in a wall, you can perform a Boolean operation with the wall as Operand A, and another object, such as a box, as Operand B. Then, you can create and add a door in the opening, and link it, if you choose, as a child of the wall.
Procedures
To create a door:
- On the Object Type rollout, click the button for the type of door you want to create.
- Choose options as needed, such as changing the default creation method. Turn off Create Frame to eliminate the door frame. Turn on Allow Non-vertical Jambs if you want an inclined door.
- Drag the mouse in the viewport to create the first two points, defining the width and angle of the base of the door.
- Release the mouse and move to adjust the depth of the door (default creation method), and then click to set.
By default, the depth is perpendicular to the line between the first two points and parallel to the active grid.
- Move the mouse to adjust the height, and then click to finish.
The height is perpendicular to the plane defined by the first three points and perpendicular to the active grid.
You can adjust the Height, Width, and Depth values on the Parameters rollout.
On the Creation Method rollout, you can change the creation order to width-height-depth instead of width-depth-height.
To create a door material:
- Create a door or select an existing door.
- Open the Material Editor, and select a slot for the material.
- Click the Type button below the Material Editor toolbar.
The Material/Map Browser dialog opens.
- In the Material list, double-click the Multi/Sub-Object item, and then on the Replace Material dialog that appears, choose either option and click OK.
- On the Multi/Sub-Object Basic Parameters rollout, click Set Number and change Number Of Materials to 5. Click OK.
- Optionally, change the sub-material names to those specified in the above table.
- Edit the material as you would any Multi/Sub-Object material.
To animate a door:
- Create a door or select an existing door.
If using an existing door, also access the Modify panel.
- Set the Parameters rollout
 Open parameter to the amount you want the door to be open at the start of the animation. If you want it to be closed, set it to 0.
Open parameter to the amount you want the door to be open at the start of the animation. If you want it to be closed, set it to 0. - Click the Auto Key button and advance to the first keyframe.
- Change the Open setting.
- Continue moving to any additional keyframes and changing the Open setting as necessary.
- Play the animation.
You can animate a door opening and closing by keyframing the Open setting.
Interface
The topic for each kind of door describes its unique controls and behavior. Most door parameters are common to all kinds of doors, and are described here.
Object Type rollout

There are three kinds of doors in 3ds Max:
- Pivot
-
The familiar door type that is hinged on one side only. See Pivot Door.
- Sliding
-
Has a fixed half and a sliding half. See Sliding Door.
- BiFold
-
Hinged in the middle as well as the side, like many closet doors. You can also use this type of door to make a set of double doors. See BiFold Door.
Name and Color rollout
Creation Method rollout
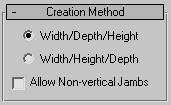
You define each type of door with four points: Drag the first two, followed by two move-click sequences. The Creation Method setting determines the order in which these actions define the door's dimensions.
- Width/Depth/Height (The default.) The first two points define the width and angle of the base of the door. You set these points by dragging in a viewport, as the first step in creating a door. The first point, where you click and hold before dragging, defines a point on the jamb at the hinge for single-pivot and bifold doors (both jambs have hinges on double doors, and sliding doors have no hinge). The second point, where you release the button after dragging, specifies the width of the door, as well as the direction from one jamb to the other. This lets you align the door with a wall or opening when you place it. The third point, where you click after moving the mouse, specifies the depth of the door, and the fourth click, where you click after moving the mouse again, specifies the height.
-
Width/Height/Depth Works like the Width/Depth/Height option, except that the last two points create first the height and then the depth. Note: With this method, the depth is perpendicular to the plane set by the first three points. Thus, if you draw the door in the Top or Perspective viewport, the door lies flat on the active grid.
- Allow Non-vertical Jambs
-
Lets you create tilted doors. Set snaps to define points off the construction plane. Default=off.
Parameters rollout
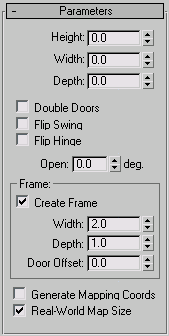
- Height
-
Sets the overall height of the door unit.
- Width
-
Sets the overall width of the door unit.
- Depth
-
Sets the depth of the door unit.
- Open
-
With Pivot doors, specifies in degrees the extent to which the door is open. With Sliding and BiFold doors, Open specifies the percent that the door is open.
Frame group
This group has controls for the door-jamb frame. Though part of the door object, the frame behaves as if it were part of the wall. It doesn't move when you open or close the door.
- Create Frame
-
This is turned on as a default to display the frame. Turn this off to disable display of the frame.
- Width
-
Sets the width of the frame parallel to the wall. Available only when Create Frame is on.
- Depth
-
Sets the depth of the frame as it projects from the wall. Available only when Create Frame is on.
- Door Offset
-
Sets the location of the door relative to the frame. At 0.0, the door is flush with one edge of the trim. Note that this can be a positive or negative value. Available only when Create Frame is on.
- Generate Mapping Coords
-
Assigns mapping coordinates to the door.
- Real-World Map Size
-
Controls the scaling method used for texture mapped materials that are applied to the object. The scaling values are controlled by the Use Real-World Scale settings found in the applied material's Coordinates rollout. Default=off.
Leaf Parameters rollout

Provides controls that affect the door itself (as opposed to the door unit, which includes the frame). You can adjust the dimensions of the door, add panels, and adjust the dimensions and placement of those panels. The total number of panels for each door element is the number of horizontal divisions times the number of vertical divisions. Pivot doors have a single door element unless they are double doors. BiFold doors have two door elements, or four if they are double doors. Sliding doors have two door elements.
- Thickness
-
Sets the thickness of the door.
- Stiles/Top Rail
-
Sets the width of the panel framing on the top and sides. This setting is apparent only if the door is paneled.
- Bottom Rail
-
Sets the width of the panel framing at the base of the door. This setting is apparent only if the door is paneled.
- # Panels Horiz.
-
Sets the number of panel divisions along the horizontal axis.
- # Panels Vert.
-
Sets the number of panel divisions along the vertical axis.
- Muntin
-
Sets the width of the separations between the panels.
Panels group
Determines how panels are created in the door.
- None
-
The door has no paneling.
- Glass
-
Creates glass panels with no beveling.
- Thickness
-
Sets the thickness of the glass panels.
- Beveled
-
Choose this to have beveled panels.
The remaining spinners affect the beveling of the panels.
- Bevel Angle
-
Specifies the angle of the bevel between the outer surface of the door and the surface of the panel.
- Thickness 1
-
Sets the outer thickness of the panel.
- Thickness 2
-
Sets the thickness where the bevel begins.
- Middle Thick.
-
Sets the thickness of the inner part of the panel.
- Width 1
-
Sets the width where the bevel begins.
- Width 2
-
Sets the width of the inner part of the panel.