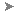Use this page of the Overlay Analysis dialog box to specify the Source and Overlay features, as well as the type of overlay analysis to perform. Overlay results use the split rules set in the Split and Merge Rules dialog box.

|
|
|
|
|
The Source and Overlay Type page of the Overlay Analysis dialog box includes the following options:
- Source
-
Specify the feature layer or feature class to use as the source.
- Overlay
-
Specify the feature layer or feature class to use as the overlay.
To use a feature layer, you must add it to your map. To use a feature class, you must connect to its data store, but you need not add it to the map.
The geometry in the feature classes or layers you select determines the other choices in the dialog box. You can combine only certain types of geometries. For example, Union, Paste, and Symmetric Difference support polygon/polygon comparisons only. Also, you cannot choose point geometries for both Source and Overlay. If you select point geometry for Source, you can select only polygon geometry for Overlay.
The available choices for Type depend on the geometry in the Source and Overlay.
If either the Source or the Overlay contains multiple geometries, you can select any feature class or layer in Overlay and any overlay operation in Type. However, the output may be empty if there are no valid geometry combinations.
- Type
-
Select the type of overlay comparison to perform. For more information on the available types, see About Overlays.
- Intersect: Determines the geometry that overlaps in the Source and Overlay features. Anything that does not overlap is discarded from the output.
- Union: Determines the geometry that exists in either the Source or Overlay geometry. Where the geometry intersects, additional features are created. The resulting layer is the sum of the two comparison layers.
- Erase: Determines the geometry from the Source that does not intersect with the Overlay. The intersecting pieces are discarded.
- Identity: Creates new features where the Source and Overlay features intersect.
- Clip: Like Intersect, Clip creates features from the areas of the Source that overlap with the Overlay. However, with Clip, only feature attributes from the Source are included in the resulting layer.
- Paste: Creates new features by pasting the Overlay features onto the Source features. All Overlay features become new features in the resulting layer. In addition, areas of the Source that do not fall within the geometry of the Overlay become features in the resulting layer.
- Symmetric Difference: Determines geometry of the Source and Overlay that do not overlap. Overlapping areas of the features are discarded in the output, so the resulting layer represents the areas that are mutually exclusive.