
Super shapes are primitives based on cubes and spheres that are capable of creating complex organic shapes. However, due to the highly mathematical nature of these shapes, we recommend creating a base shape with the default values and then experimenting with the Random button in the associated superShape node to get a shape close to what you desire. You can then use the Attribute Editor to tweak that shape.
A polySuperShape node is created whenever a super shape primitive is created.
- Shape
- Determines the base shape. Options include Super Ellipse, Spherical Harmonics, and Ultra.
- Radius
- Determines the size of the primitive based on the distance from its center to its pole.
- Horizontal Divisions, Vertical Divisions
- The number horizontal and vertical subdivisions (per quadrant) on the base mesh.
- Create UVs
- Determines how default UVs are created for the primitive. Options include None, Pinched at Pole, and Sawtooth at Pole.
- Random
- Generates a primitive of the current Shape with random attributes. Useful for quickly creating interesting start points.
- Reset
- Sets all attributes back to their default values for the chosen Shape.
Helix
This section is common to all super shapes and allows you to form the geometry into a spiral shape before applying their respective super shape properties.
- Merge Vertices
- Merges the vertices on each end of the helix. If enabled, the rest of the Helix attributes won't have any effect.
- Horizontal Revolutions
- Determines the number of spirals.
- Vertical Revolutions
- Determines the fullness of the coil.
- Vertical Offset
- Determines the stretch of the coil.
- Internal Radius
- Determines the diameter of the inner coil.
- X Offset, Z Offset
- Offsets the coil's scale in the respective direction.
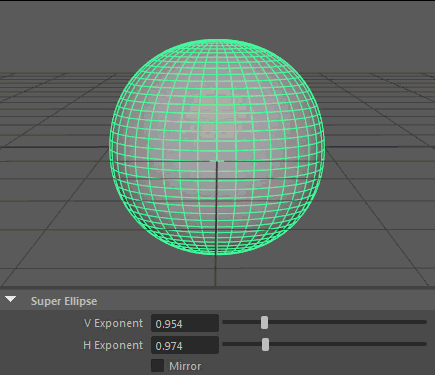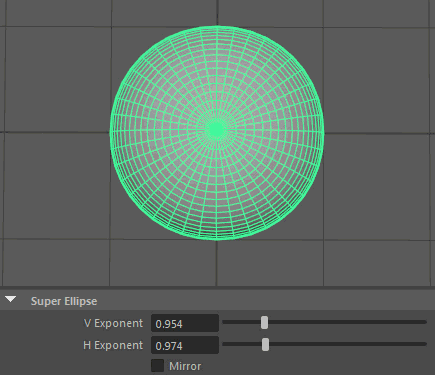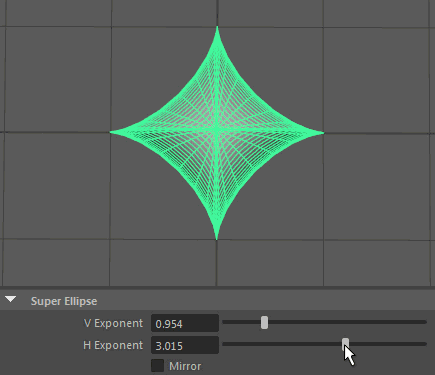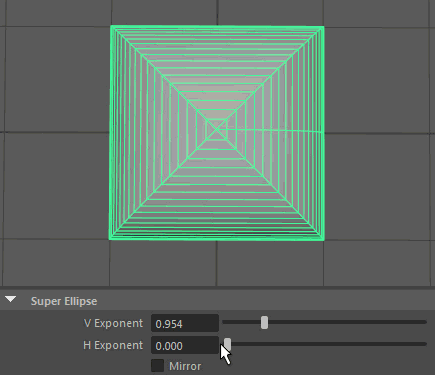
Super Ellipse
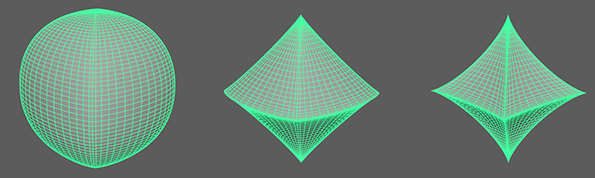
A Super Ellipse generates primitives using an exponential equation along x and y, resulting in arcs or inverse arcs along each axis.
This section contains attributes specific to the Super Ellipse Shape.
- V Exponent
-
Controls the exponent used to calculate the parabolic arc along the vertical.
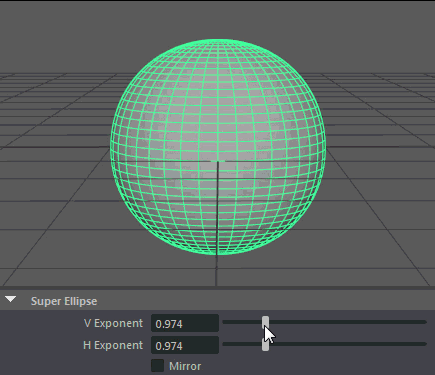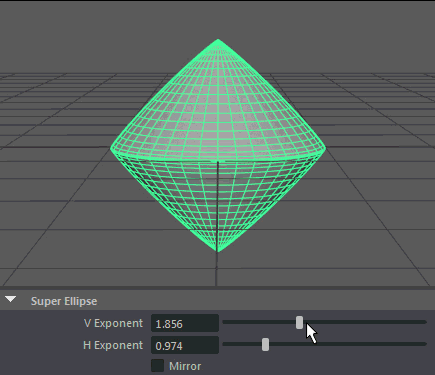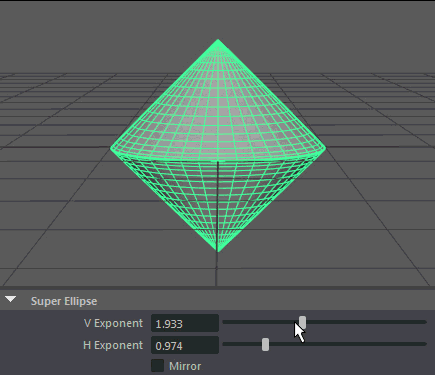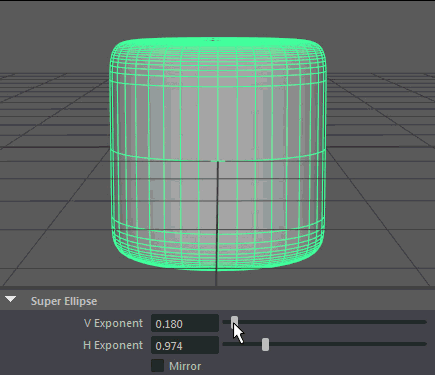
- H Exponent
-
Controls the exponent used to calculate the parabolic arc along the horizontal.
- Mirror
- Forces the H Exponent to match the V Exponent.
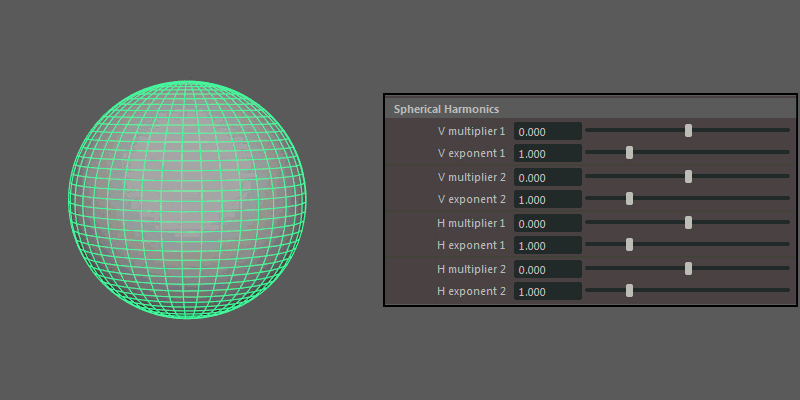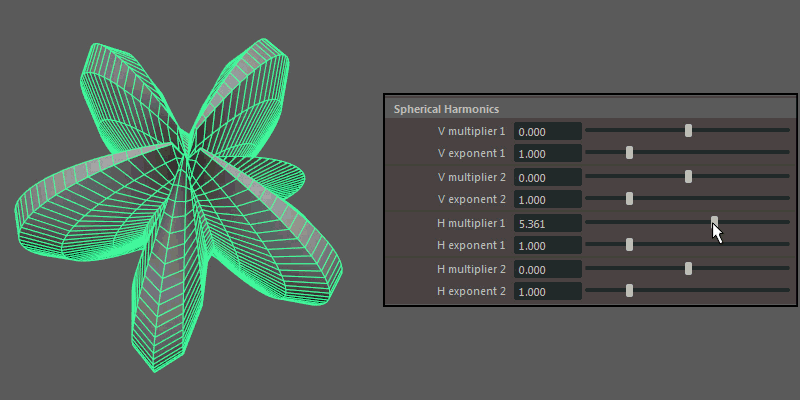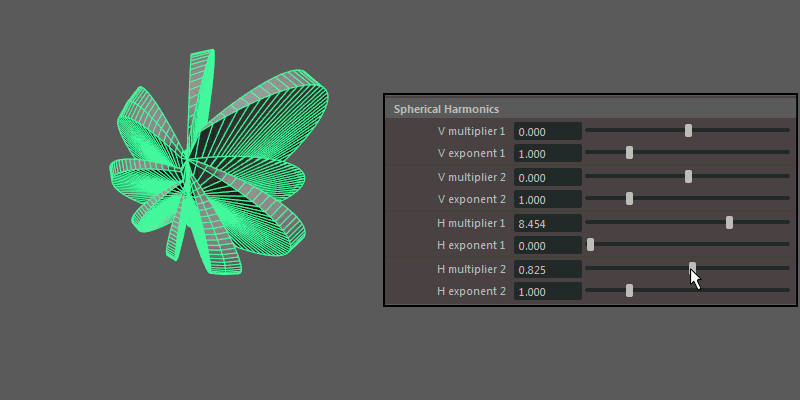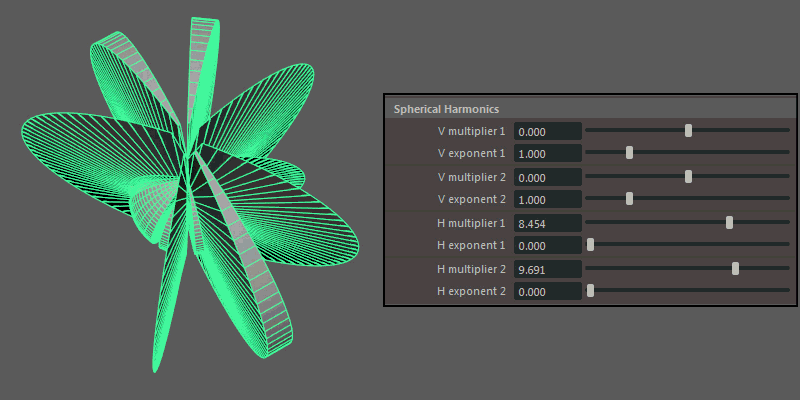
Spherical Harmonics

Spherical Harmonics apply a series of frequency equations to the surface of a sphere, resulting in pulsing topology.
This section contains attributes specific to the Spherical Harmonics Shape.
- V multiplier, V exponent
-
Controls the mathematical variables used to determine the shape along the vertical.
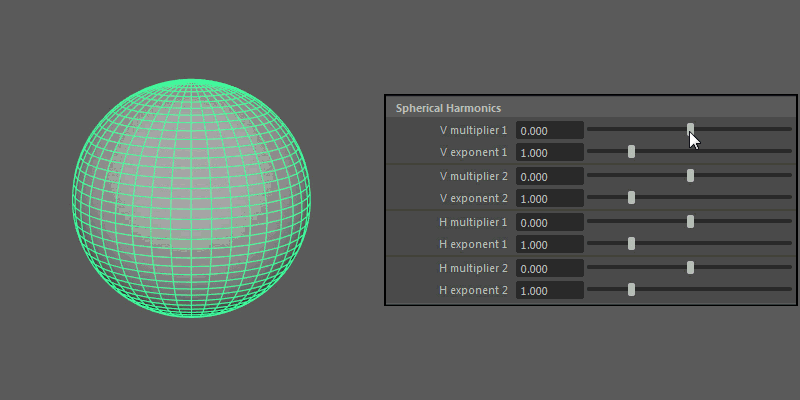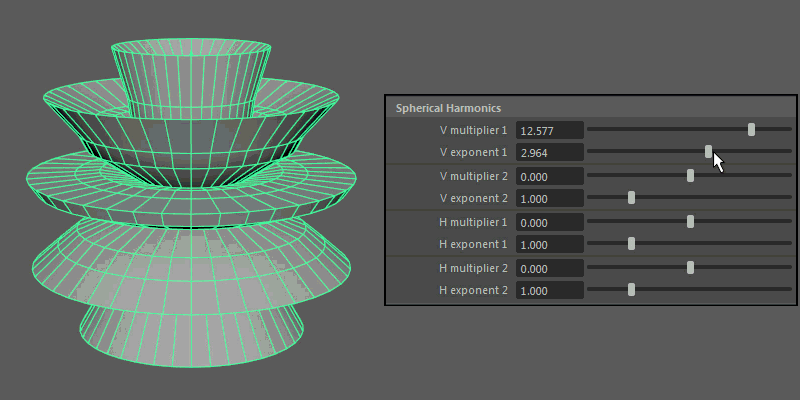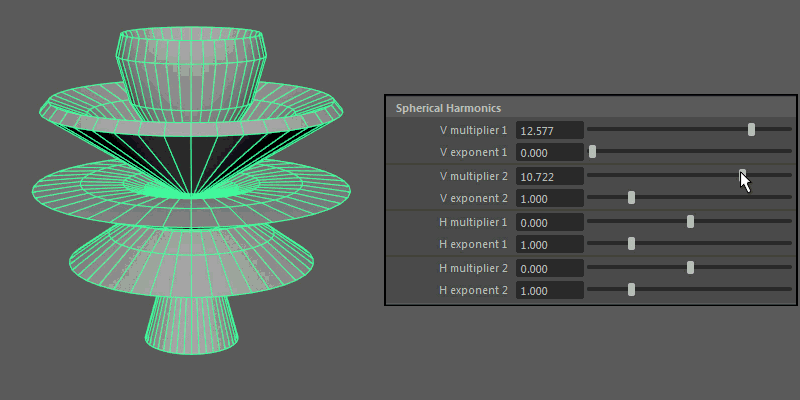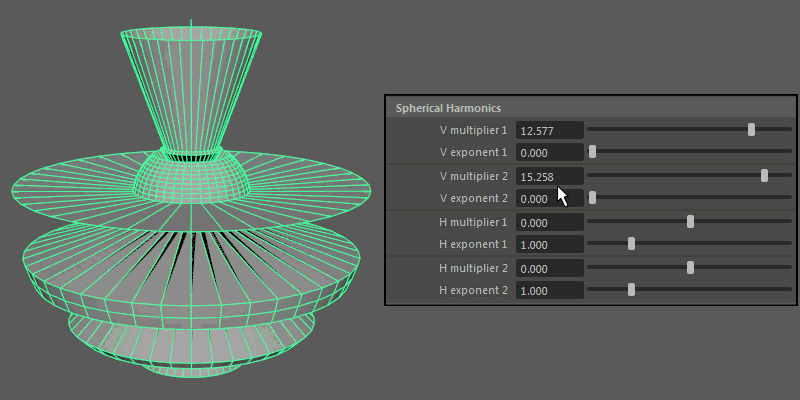
- H multiplier, H exponent
-
Controls the mathematical variables used to determine the shape along the horizontal.
Ultra
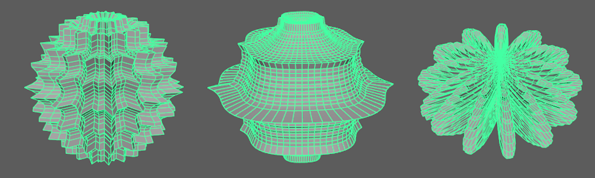
This section contains options specific to the Ultra Shape. Ultra shapes use an algorithm specifically designed to create organic-looking shapes.
Horizontal
Controls the pattern across the ultra shape's latitude.
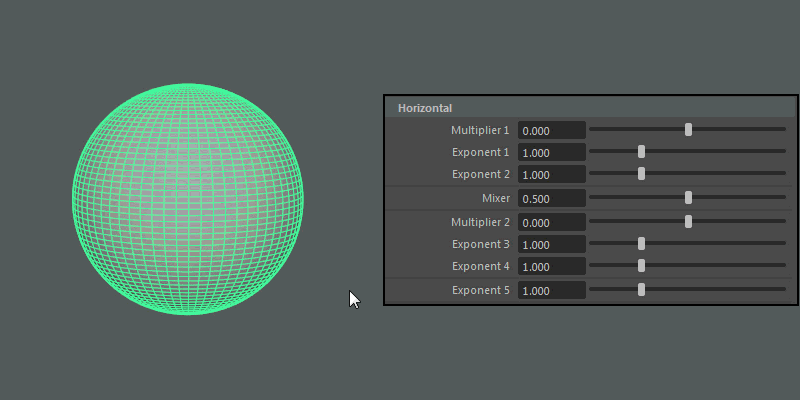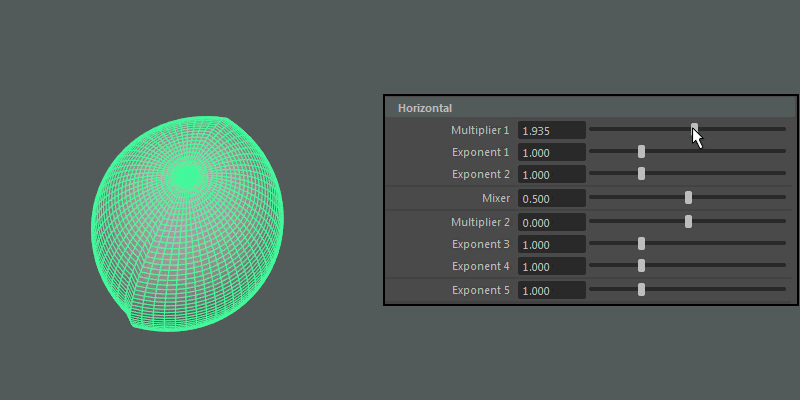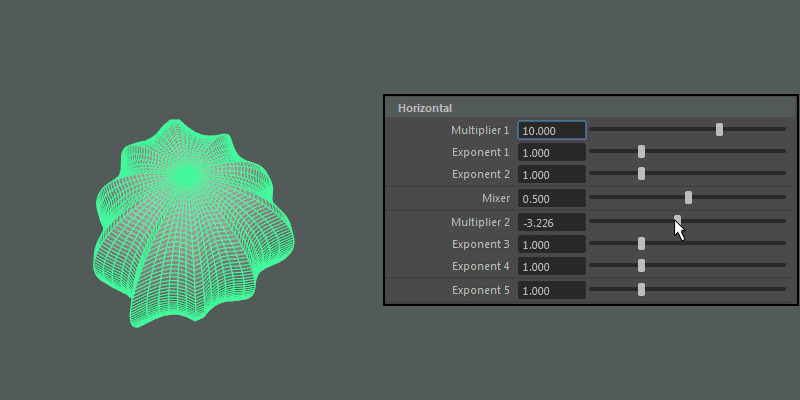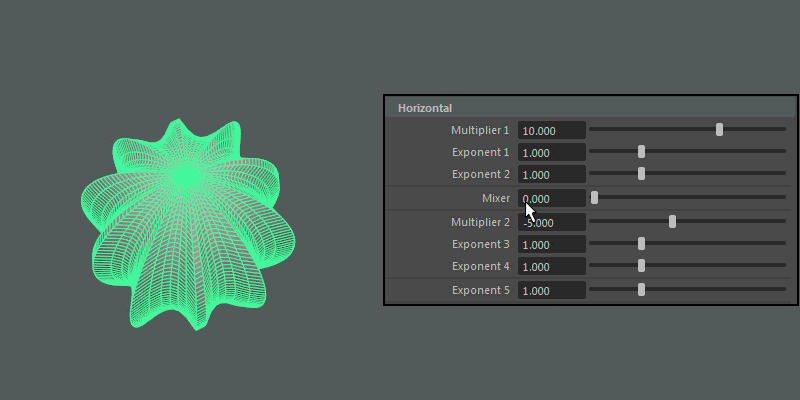
- Multiplier 1, Multiplier 2
-
Controls the main horizontal protrusions from the ultra shape. Both values can exist on the ultra shape at once, and you can blend between them using the Mixer attribute.
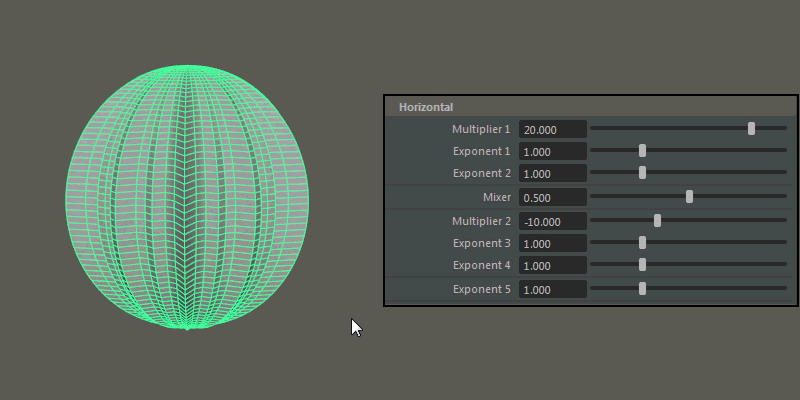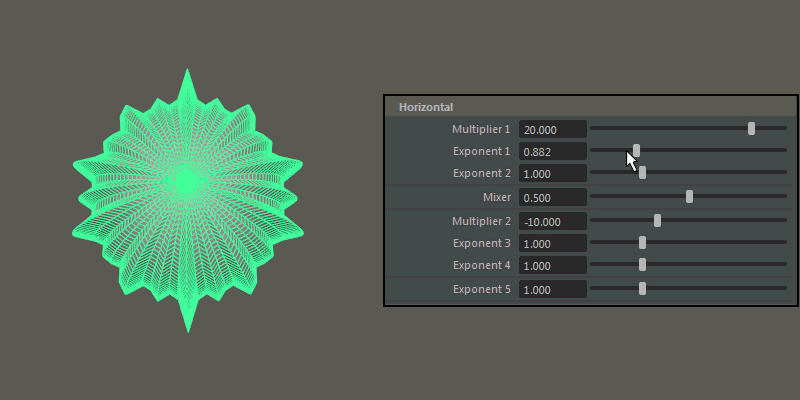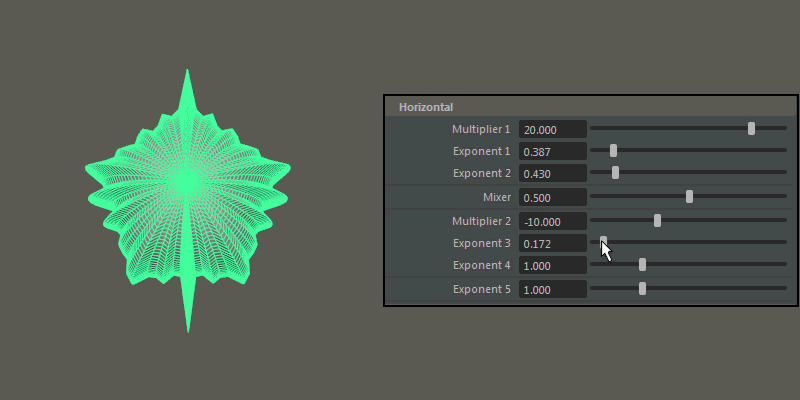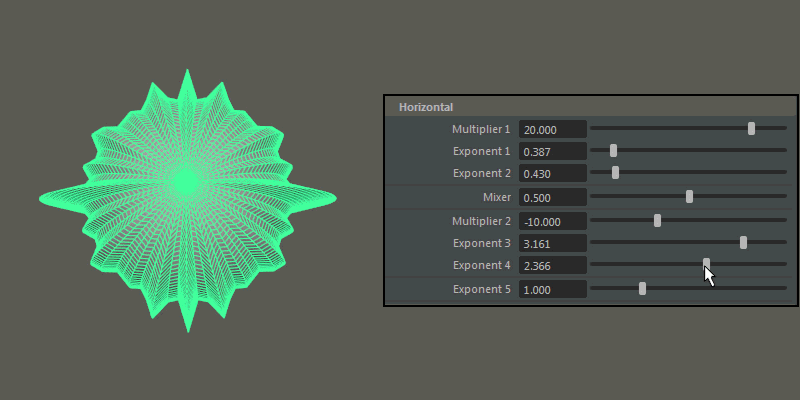
- Exponent 1, Exponent 2, Exponent 3, Exponent 4
-
Controls the extent of the horizontal extrusions for Multiplier 1 (Exponent 1 and 2) and Multiplier 2 (Exponent 3 and 4) respectively.
- Exponent 5
- Controls the overall extent of the horizontal protrusions resulting from the previous Multipliers and Exponents.
Vertical
Controls the pattern across the ultra shape's longitude.
- Multiplier 1, Multiplier 2
-
Controls the main vertical protrusions from the ultra shape. Both values can exist on the ultra shape at once, and you can blend between them using the Mixer attribute.
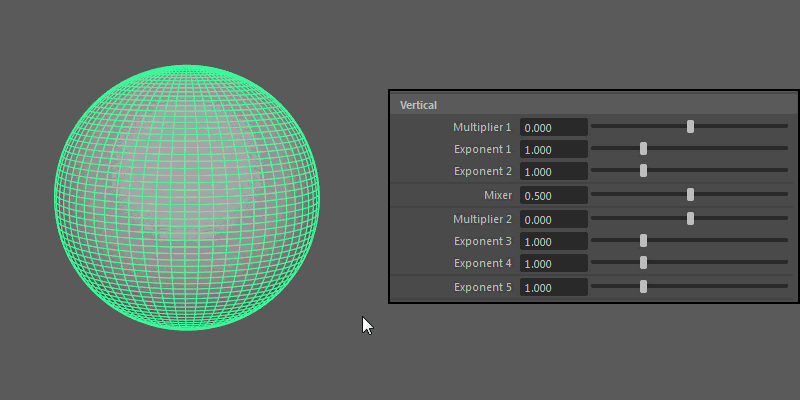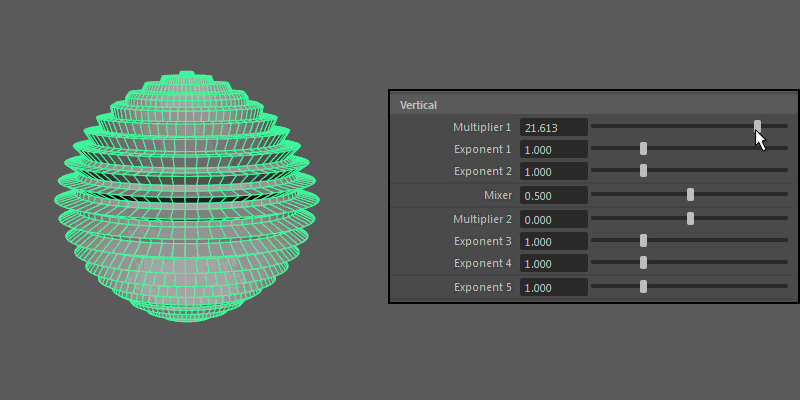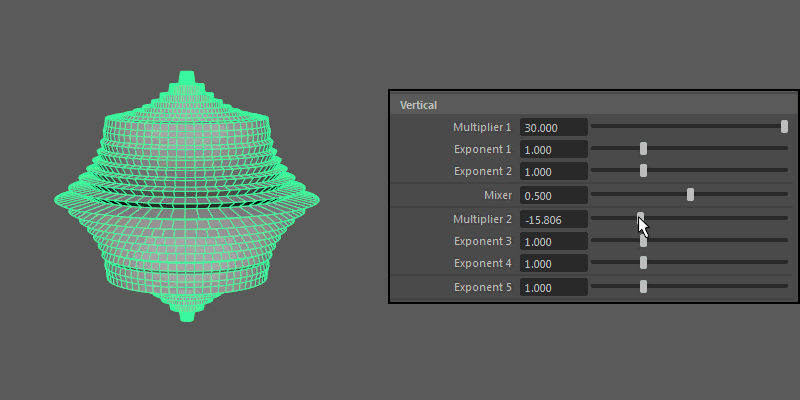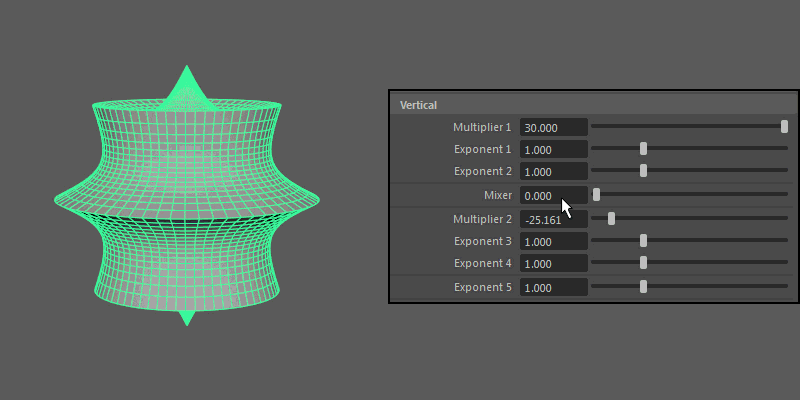
- Exponent 1, Exponent 2, Exponent 3, Exponent 4
-
Controls the extent of the vertical extrusions for Multiplier 1 (Exponent 1 and 2) and Multiplier 2 (Exponent 3 and 4) respectively.
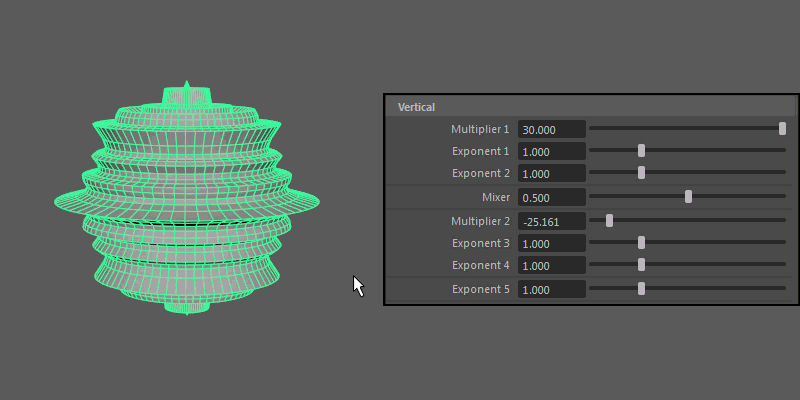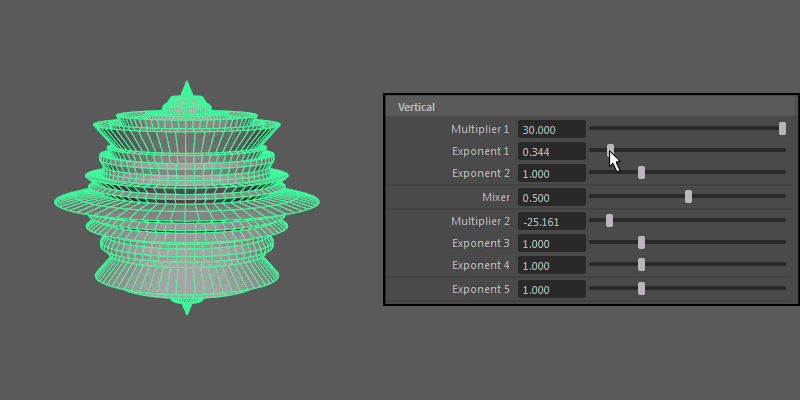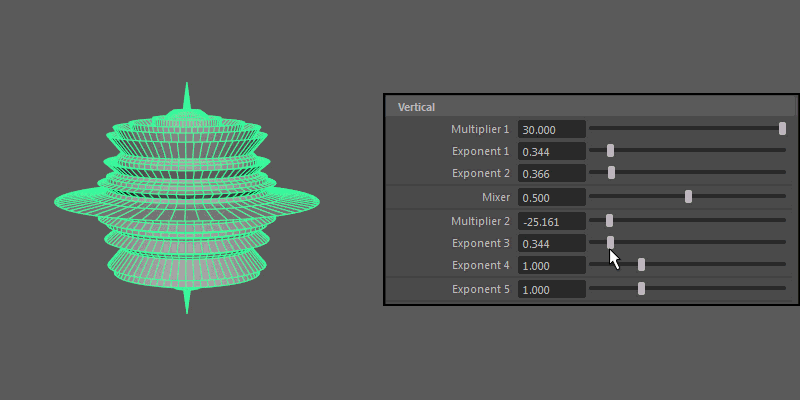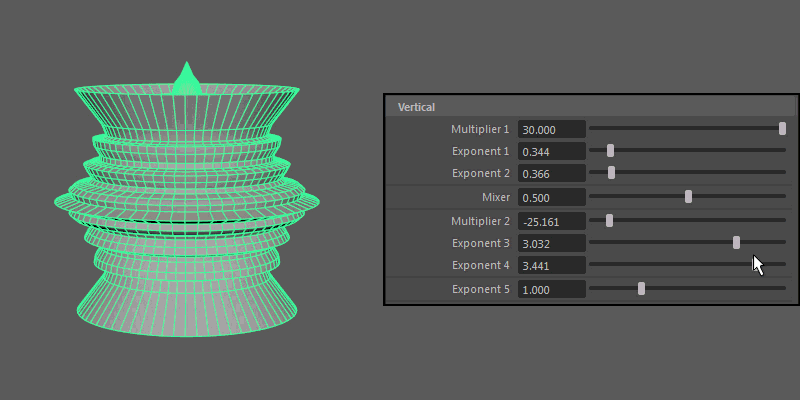
- Exponent 5
- Controls the overall extent of the vertical protrusions resulting from the previous Multipliers and Exponents.