Jump to:
- Context view tabs
- Status
- Actions
- Repair Scripts
- Shells
- View
- Repair module zoom commands
- Repair module selection info
Context view tabs
When you enter repair, the context view displays five tabs:
- Status
- Actions
- Repair Scripts
- Shells
- View
Status
The Status tab displays a number of properties about the part.
- Status: Indicates whether the mesh is closed and oriented.
- Statistics: Lists details about the number of edges, border edges, triangles, inverted orientation, shells, and holes on the part.
-
Highlighting: The highlighting section contains controls for making certain features of the part stand out more. Available features to highlight are holes, triangles, edges under a threshold angle, degenerate faces, and errors in general.
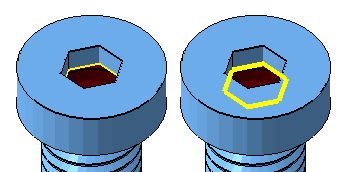
Highlighting errors in general draws a thicker line, and also draws it always on top.
Actions
The Actions tab offers a few details about the part features and also presents several commands to help repair your part.
- Close Holes: Reports the number of border edges and holes in the part. Provides functionality to quickly stitch triangles or remove trivial or all holes.
- Flipped Triangles: Reports the number of triangles with an inverted orientation and provides functionality to quickly fix any flipped triangles.
- Self-Intersections: Provides functionality to detect, split-off, or remove self-intersecting triangles.
Additional repair commands on the Actions tab include Remove Double Triangles, Remove Degenerate Faces, and Wrap Part Surface.
TopRepair Scripts
The Repair Scripts tab allows you to run, edit, create, and save repair scripts to quickly perform a series of repair operations to your part.
Repair actions available for use in repair scripts
- Stitch triangles – Merges open triangle edges that are very close and mostly parallel into one common edge
- Close all holes – Generate triangles along open triangle edges until a mesh becomes watertight
- Close trivial holes – Trivial holes are holes enclosed by exactly three triangles
- Remove double triangles – Remove triangles that got imported twice, typically from CAD imports
- Remove tiny shells – Shells with a volume below a threshold are removed
- Remove degenerated faces – Triangles with a side shorter than a threshold are collapsed into a single edge
- Invert Negative Shells – Flips all of a shell's triangles if the shell is considered inside-out
- Remove Self-Intersections – Triangles cutting through each other are split along the cuts, the created off-cuts are removed, and the created open triangle edges are stitched
- Split-off Self-Intersections – Ditto, but off-cuts are not deleted
- Fix Flipped Triangles – Attempts to orient all triangles into a common direction, outwards or inwards.
- Scale – Changes the size of a mesh proportionally
- Refine Triangles – Subdivides triangles
- Reduce Triangles – Decreases triangle count by merging triangles at the cost of the original shape
- Prefix-Suffix – Adds text before and/or after the part's original name
- Wrap Part Surface – Reduces a mesh to a surface formed by only its outermost shells and discards any internal structures
- Smooth Triangles – Averages sharp edges and blunts them with smoother transitions
- Z-Compensation – Compensates for energy penetration effects typically encountered with beam-type powder conversion processes
- Sanitize Duplicate Nodes – Fully separates shells that currently share nodes, but no volume, with each other
- Remove Problem Areas – Removes large collections of triangles that intersect in very little space
-
 Split non-manifold edges – Resolve the ambiguity in more than two triangles sharing a common edge
Split non-manifold edges – Resolve the ambiguity in more than two triangles sharing a common edge
Shells
The Shells tab displays a number of properties about the shells that make up the part. Properties include:
- Triangles
- Area
- Outbox Volume
- Part Volume
- Watertight
- Oriented
- Outbox
View
The View tab provides a number of options to control the visualization of the part features and the selection of surfaces.
- Part: Switches for showing textures (unavailable if the part has no texture) and for viewing the part transparently are located here.
-
Show Slim Faces: Provides functionality to color or highlight edges of triangles that are particularly narrow. The slider is used to define the maximum value for the smallest of the inner angles a triangle may have to be considered slim and therefore highlighted. If there are any such triangles present, and in case they do not immediately stand out,
Netfabb also displays this with
Status for Optimization Utility and an icon,
 or
or
 . Triangles too narrow can cause
Optimization Utility, which operates on a tetrahedral volume mesh to lattice or to lightweight parts, to retriangulate the input surface as this could otherwise produce less reliable results. You cannot control this remeshing in any way except choosing not to, so it can be beneficial to test for this during repair and possibly remesh the part before sending it over.
. Triangles too narrow can cause
Optimization Utility, which operates on a tetrahedral volume mesh to lattice or to lightweight parts, to retriangulate the input surface as this could otherwise produce less reliable results. You cannot control this remeshing in any way except choosing not to, so it can be beneficial to test for this during repair and possibly remesh the part before sending it over.
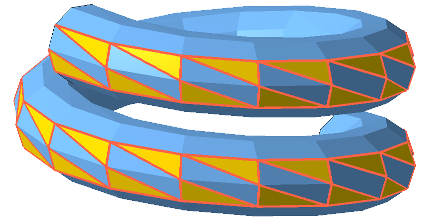
Triangles with their smallest inner angle being smaller than a threshold are highlighted.
-
Surface Selection: When you use the
 Surfaces mode from the menu, and you click a particular triangle, any adjacent triangle that is angled away from the previous one up to this angle becomes selected as well. This is useful for selecting surfaces up to a hard edge, for example, where you would not want a surface selection to bleed into areas you do not want to select.
Surfaces mode from the menu, and you click a particular triangle, any adjacent triangle that is angled away from the previous one up to this angle becomes selected as well. This is useful for selecting surfaces up to a hard edge, for example, where you would not want a surface selection to bleed into areas you do not want to select.
Zoom commands
Repair has zoom commands that are different from the standard ones as there is now only one part, and you gain access to the individual triangles of a mesh.
-
 Zoom to Part: The part is centered in the display and the zoom is such that the part fills the screen.
Zoom to Part: The part is centered in the display and the zoom is such that the part fills the screen.
-
 Zoom to Selected Triangles: The selection is centered in the display and the zoom is such that the selection fills the screen.
Zoom to Selected Triangles: The selection is centered in the display and the zoom is such that the selection fills the screen.
-
 Zoom to Selected Area: Allows you to click and drag a window to define the area to zoom into.
Zoom to Selected Area: Allows you to click and drag a window to define the area to zoom into.
Selection info
In the repair module, a new selection command is presented on the toolbar.
-
 Show selection info: Shows details about the selection including the number of triangles selected, the total surface area of the selection, the surface area for the last triangle selected, and the border length for the last triangle or patch of triangles selected.
Show selection info: Shows details about the selection including the number of triangles selected, the total surface area of the selection, the surface area for the last triangle selected, and the border length for the last triangle or patch of triangles selected.
 Toggle Selection
Toggle Selection