Solid Element Anisotropic Material Property Definition
Description: Defines the material properties for linear temperature-independent, anisotropic materials for solid isoparametric elements.
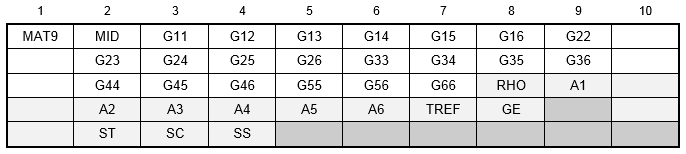
Format:
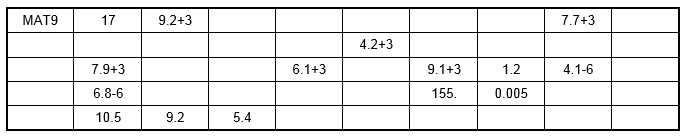
Example:
| Field | Definition | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| MID | Material identification number. | Integer > 0 | Required |
| Gij | Elements of the 6 x 6 symmetric material property matrix in the material coordinate system. | Real | Required |
| RHO | Mass density. | Real or blank | 0.0 |
| Ai | Thermal expansion coefficient vector. | Real or blank | 0.0 |
| TREF | Reference temperature for the calculation of thermal loads. | Real or blank | 0.0 |
| GE | Structural element damping coefficient. See Remarks 7 and 9. | Real or blank | 0.0 |
| ST, SC, SS | Allowable stresses in tension, compression, and shear, respectively. Required if composite element failure index is desired. | Real ≥ 0.0 or blank | 0.0 |
Remarks:
- The material identification number must be unique for all MATi entries.
- The third continuation entry is optional.
- The subscripts 1 through 6 refer to x, y, z xy, yz, zx of the material coordinate system (see the MCID field on the
PSOLID entry description). The stress-strain relationship is:

- MAT9 materials may be made temperature-dependent by use of the MATT9 entry. In STATIC solutions, linear elastic material properties will be updated as prescribed under the TEMPERATURE Case Control command.
- The mass density, RHO, will be used to automatically compute mass for all structural elements.
- Weight density may be used in field 8 if the value 1/g is entered on the PARAM, WTMASS entry, where g is the acceleration of gravity.
- To obtain the damping coefficient GE, multiply the critical damping ratio C/C0, by 2.0.
- TREF is used only as the reference temperature for the calculation of thermal loads in linear solutions. If TEMPERATURE(INITIAL) is specified, TREF will be ignored.
- If PARAM, W4 is not specified, GE is ignored in transient response analysis. (See Section 5, Parameters, for more information on W4.)