You can use a bitmap file or a procedural map such as Reflect/Refract to control an object’s refraction.
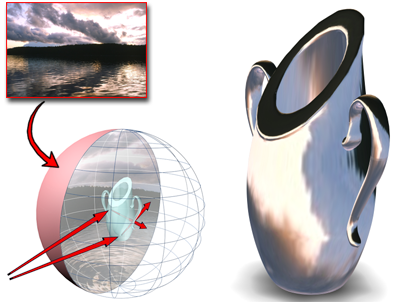
Refractions show the scene or background through a refractive object.
Usage of Refraction maps is similar to that of Reflection maps. Refraction maps the view onto the surface in such a way that the image looks like you're seeing it through the surface, rather than being reflected off it.
Like a Reflection map, a Refraction map does not require mapping coordinates because its orientation is locked to the world coordinate system rather than to the object. That is, as you move or rotate the object, the position of the refracted image remains fixed.
Setting the Index of Refraction
The physical properties of refractive objects often distort the image. This parameter is controlled by the parent material.
- Index of Refraction
-
The index of refraction (IOR) controls the amount by which the material refracts transmitted light. The IOR of air, 1.0, causes no distortion of objects behind the transparent object. At 1.5 the object behind distorts greatly (like a glass marble). At an IOR slightly less than 1.0, the object reflects along its edges, like a bubble seen from under water. Default=1.5 (the IOR of typical glass).
Common IOR values (assuming the camera is in air or a vacuum) are:
Material IOR Value Vacuum 1.0 (exactly) Air 1.0003 Water 1.333 Glass 1.5 to 1.7 Diamond 2.418 In the physical world, the IOR results from the relative speeds of light through the transparent material and the medium the eye or the camera is in. Typically this is related to the object's density. The higher the IOR, the denser the object.
You can also use a map to control the index of refraction. IOR maps always interpolate between 1.0 (the IOR of air) and the setting in the IOR parameter. For example, if you set the IOR to 3.55 and use a black-and-white Noise map to control IOR, the IORs rendered on the object will be set to values between 1.0 and 3.55; the object will appear denser than air. If, on the other hand, you set the IOR to 0.5, then the same map values will render between 0.5 and 1.0: As if the camera is under water and the object is less dense than the water.
Here are some more IOR values for various materials:
Material IOR Value Carbon Dioxide, Liquid 1.200 Ice 1.309 Acetone 1.360 Ethyl Alcohol 1.360 Sugar Solution 30% 1.380 Alcohol 1.329 Flourite 1.434 Quartz, Fused 1.460 Calspar2 1.486 Sugar Solution 80% 1.490 Glass 1.500 Glass, Zinc Crown 1.517 Glass, Crown 1.520 Sodium Chloride 1.530 Sodium Chloride (Salt) 1 1.544 Polystyrene 1.550 Quartz 2 1.553 Emerald 1.570 Glass, Light Flint 1.575 Lapis Lazuli 1.610 Topaz 1.610 Carbon Bisulfide 1.630 Quartz 1 1.644 Sodium Chloride (Salt) 2 1.644 Glass, Heavy Flint 1.650 Methylene Iodide 1.740 Ruby 1.770 Sapphire 1.770 Glass, Heaviest Flint 1.890 Crystal 2.000 Diamond 2.418 Chromium Oxide 2.705 Copper Oxide 2.705 Amorphous Selenium 2.920 Iodine Crystal 3.340 Tip: The Reflect/Refract map type used as a Refraction map doesn't effectively model a material surrounding an object, such as a pencil in a glass of water. For this effect, use either the Thin Wall Refraction or the Raytrace map type.
Procedures
To create an automatic refraction:
- Click the map button labeled Refraction.
3ds Max opens the Material/Map Browser.
- Choose Maps
 Standard
Standard  Reflect/Refract, and then click OK.
Reflect/Refract, and then click OK. Alternatively, you can use the
 Slate Material Editor to wire a Reflect/Refract map node to the Refraction component.
Slate Material Editor to wire a Reflect/Refract map node to the Refraction component. - On the parent materials’ Maps rollout, adjust the Amount to control how refractive the material is.
At a Refraction Amount of 100 percent, the material is extremely refractive, regardless of the material's Opacity setting. At a Refraction Amount of 0 percent, the map is turned off. When the Amount is less than 100 percent, both the Reflect/Refract map and the Opacity setting control transparency.
To assign a bitmap as a refraction map:
- In the Maps rollout, click the Refraction map button.
3ds Max opens the Material/Map Browser.
- Choose Maps
 Standard
Standard  Bitmap, and then click OK.
Bitmap, and then click OK. Alternatively, you can use the
 Slate Material Editor to wire a Bitmap node to the Refraction component.
Slate Material Editor to wire a Bitmap node to the Refraction component. 3ds Max opens a file dialog.
- Use the file dialog to choose the bitmap file.
- On the parent materials’ Maps rollout, adjust the Amount to control how refractive the material is.
For bitmapped refractions, you don't necessarily want to reduce the map Amount.