Modeling mesh objects differs from modeling 3D solids and surfaces in some important ways.
Mesh objects do not have the mass and volume properties of 3D solids. However, they do offer unique capabilities that enable you to design less angular, more rounded models. Mesh objects are easier to mold and reshape than their solid and surface counterparts.
The capabilities described in this section apply only to mesh objects created in AutoCAD-based products, release 2010 and later. They cannot be used with legacy polyface or polygon mesh.
About Mesh Faces
Mesh objects are composed of faces and facets.
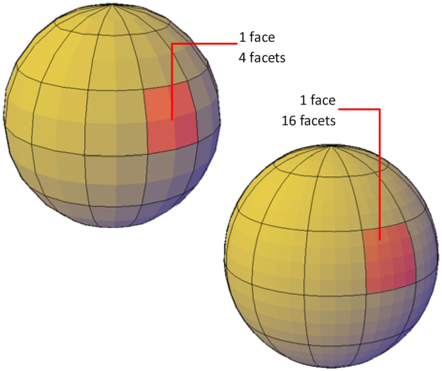
Faces are non-overlapping units that—along with their edges and vertices—form the basic editable units of a mesh object. When you move, rotate, and scale individual mesh faces, surrounding faces are stretched and deformed in order to avoid introducing gaps. When gaps occur, you can often close them by smoothing the object or refining individual faces.
About Mesh Facets
Mesh faces have underlying structures, known as facets. The density of the facet grid corresponds to the smoothness of the mesh. As the smoothness level is increased, the density of the underlying facet grid also increases. When you want to confine detailed mesh editing to a smaller area, you can convert facets to editable faces by using refinement.
Unlike faces, facets cannot be individually modified. However, you can make them more visible by modifying the VSLIGHTINGQUALITY system variable.
About Mesh Modeling
You can work with mesh objects in the following ways:
- Add smoothness. Increase or decrease smoothness levels to round the overall shape of the model. The underlying density of the mesh facet grid increases as the mesh object smoothness level increases (MESHSMOOTHMORE, MESHSMOOTHLESS).
- Refine the object to reset the baseline smoothness level. Refine a mesh object to convert the underlying facet grid to editable faces. Refinement also resets the lowest level of smoothness that can be applied to the object (MESHREFINE).
- Refine a face. Restrict the refinement to a specific mesh face. This method avoids resetting the smoothness baseline.
- Crease an edge. Remove the smoothness from specified edges. You can also remove an existing crease (MESHCREASE).
- Split or merge faces. Divide an existing face into separate components along a specified path. Merge two or more faces to create a single face (MESHSPLIT, MESHMERGE).
- Collapse vertices. Alter the mesh model by collapsing the vertices of adjacent faces to a single point (MESHCOLLAPSE).
- Spin edges. Spin the shared edge of adjacent triangular faces to alter the shapes and orientation of the faces (MESHSPIN).
- Extrude a face. Extend a specified face by extruding it into 3D space. Unlike 3D solid extrusion, a mesh extrusion does not create a separate object (MESHEXTRUDE).
- Repair holes. Close a gap between faces by selecting the surrounding edges. Holes in mesh objects can prevent you from converting a mesh object to a solid object (MESHCAP).
Use Grip Editing with Mesh
You can manipulate the entire mesh model or individual subobjects using the following methods:
- Subobject selection and editing. Select faces, edges, and vertices the same way you select 3D solid subobjects. Press and hold Ctrl while selecting a subobject. The subobject highlighting indicates what is selected. Press and hold Shift and click again to remove the selection from a subobject. By turning on the Subobject Selection Filter, you can restrict selection to a specific subobject, which you can select without pressing and holding Ctrl.
- Gizmo editing. When you select a mesh object or subobject, the 3D Move, Rotate, or Scale gizmo is displayed automatically. (You can set which gizmo is displayed by default.) Use these gizmos to modify the selection uniformly, or along a specified plane or axis.
Because dense meshes can be difficult to work with, you can change settings to improve the display and behavior of grips.
- Set the subobject selection filter: Set the DEFAULTGIZMO system variable or use the shortcut menu to select only faces, edges, or vertices.
- Set whether a grip is active immediately when you select the subobject: Set the GRIPSUBOBJMODE system variable.