Use Natural Neighbor Interpolation (NNI) to estimate the elevation (Z) of an arbitrary point (p) from a set of points with known elevations.
The NNI method uses information in the triangulation from the known points to compute a weighted average of the elevations of the natural neighbors of point p. The number of neighbors (the number of points whose Z-values are averaged to get the interpolated value) depends on the triangulation: it is the number of points to which a new point (p) would be connected if inserted into the surface:
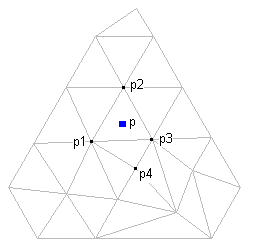
Using NNI, you select only the output locations of the interpolated points. The elevations of the interpolated points are always based on the weighted average of the elevations of the existing neighboring points. The outcome of the NNI method is more predictable than the Kriging method. NNI interpolates only within the surface, whereas Kriging can extrapolate beyond the surface border based on a selected polygon.