
Common Material Attribute
The particle cloud shader is a volume material that you can assign to particles with a Cloud render type to achieve effects such as gas or clouds.
For information on creating and assigning materials, see Apply color and shading to an object.
You can set these attributes to a fixed value, or texture map them over the particles’ lifetime. If mapped, the V values of the map are mapped onto the particles’ lifetime. You can also control them with per-particle attributes using the Particle Sampler Info node.
- Color
-
The basic color of the particle cloud. The default color is a green-blue.
- Transparency
-
Controls how much you can see through the particle cloud. It is a color, so that you can control the transparency of the red, green, and blue channels separately. To make the cloud more opaque, set transparency to be darker. To make the cloud more transparent, set transparency to be brighter (transparency = 1-opacity).
- Incandescence
-
Use Incandescence to make the particle cloud brighter, as though it were a light source. By default, Incandescence is black, meaning no glow will be added.
Note:When Incandescence is turned on, although the particle cloud will glow, it will not cast light on other objects in the scene.
- Life Color
-
Determines the color at a particular time in the life of the particle. You can use the Particle Sampler Info node to animate this parameter over a particle’s lifetime (see Particle Sampler Info node).
- Life Transparency
-
Determines the transparency at a particular time in the life of the particle. You can use the Particle Sampler Info node to animate this parameter over a particle’s lifetime (see Particle Sampler Info node).
- Life Incandescence
-
Determines the incandescence at a particular time in the life of the particle. You can use the Particle Sampler Info node to animate this parameter over a particle’s lifetime (see Particle Sampler Info node).
- Glow Intensity
-
Controls how much of a halo-like glow effect will be added to the particle cloud. This glow effect is added as a post-process, after the rendering is completed. Glow Intensity is zero by default, meaning that no glow is added.
Transparency
- Density
-
Similar to transparency; it controls how dense the cloud of particles appears to be, and therefore how much of the background can be seen through it. Increase this value to make the cloud more dense.
- Blob Map
-
Specifies a scaling factor applied to the transparency of the particle cloud. You can connect a 3d texture to it in order to give some internal texture or shape to the cloud beyond what it gets from the particles.
- Roundness
-
Controls the noise’s irregularity. The smaller the value, the less rounded the shape.
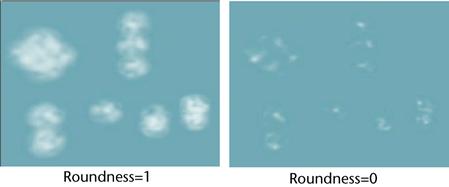
The following animation shows the Roundness attribute changing from 1 to 0.

- Translucence
-
Specifies a scaling factor for density that is used to compute shadows only. The larger the translucence value, the more light penetrates. The formula is:
density * (1 - translucence)
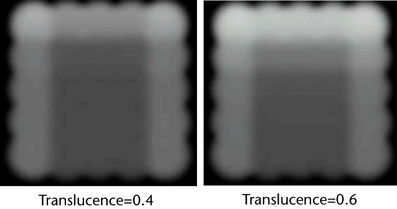
The following animation shows the Translucence attribute changing from 0.4 to 0.6:.

Built-in Noise
- Noise
-
Controls the jitteriness within the particle cloud. If it is set to zero, the cloud will look very smooth and uniform throughout. As the amount of noise increases, the cloud will appear noisier, like static on a television screen. Noise is set to 0.75, by default.
- Noise Freq
-
Determines the size of the noise artifacts when Noise is turned on. Higher values of Noise Frequency produce smaller, finer artifacts, and lower values produce larger, coarser artifacts. If Noise Frequency is set to zero, that is the same as turning Noise off.
- Noise Aspect
-
Controls the distribution of the noise (when Noise is turned on). It is zero by default, meaning that the noise is equally distributed in X and Y. Positive values make the noise run perpendicular to the particle’s path. Negative values make the noise run more parallel to the path.
- Noise Anim Rate
-
Specifies a scaling factor that controls the rate of built-in noise changes during an animation.
- Solid Core Size
-
Determines the size of the core, which is the area where the particle is opaque.
Surface Shading Properties
- Diffuse Coeff
-
Controls how much of the light in the scene is reflected from the particles. Most materials absorb some of the light falling on them, and scatter the rest.
The default value is 0.0. If you set this to 1.0, all the light falling on the material is reflected. Use a high value when you are creating dense clouds. If you set this to 0.0 (the minimum), no light is reflected and no surface shading occurs.
The surface color is modulated by the transparency. This value can be greater than 1.0, so the surface property can still appear even when the material is transparent.
- Surface Color
-
Specifies the basic color of the particle cloud surface (as opposed to the inside of the cloud). Diffuse Coeff must be set to a value greater than 0 to enable this option.
- Bump Mapping
-
Makes the surface appear rough or bumpy by altering surface normals (during rendering) according to the intensity of the pixels in the bump map texture. Diffuse Coeff must be set to a value greater than 0 to enable this option.
A bump map does not actually alter the surface. A silhouette of the surface will appear smooth.
- Translucence Coeff
-
Simulates the way light diffusely penetrates through translucent objects. This means that when light shines on one side of the object, the other side is partially illuminated. You can use this to create effects such as clouds, fur, hair, marble, jade, wax, paper, leaves, etc. If you set Translucence Coeff to 0 (the default), no light shows through the object. If you set Translucence Coeff to 1, all the light shows through. Diffuse Coeff must be set to a value greater than 0 to enable this option.
- Surface Shading Shadow
-
Determines if the surface shading is combined with the pre-illumination, which contains shadows, if enabled (see the Filter Radius attribute). Diffuse Coeff must be set to a value greater than 0 to enable this option.

This cloud shader uses Surface color and Surface Shading Shadow to create an explosion.
Pre-illumination Controls
- Filter Radius
-
Volumetric particles use pre-illumination, which evaluates the lighting at each particle’s center by default. This can sometimes cause popping if the illumination changes too fast in an animation, and is especially noticeable if Surface Shading Shadow is on.
Filter radius lets you filter the pre-illumination results so the value at each particle’s center will be the average of all the pre-illumination results within the filter radius. Higher values increase render time but produce smoother images.