Viscoelastic Material Property Definition
Description: Specifies viscoelastic material properties for use in nonlinear analysis.
Format:
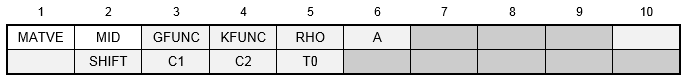
Example:

| Field | Definition | Type | Default | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MID | Unique material identification number or identification number of a MAT1 entry. | Integer > 0 | Required | ||
| GFUNC | Identification number of a TABVE entry. The TABVE table contains a series of shear modulii and decay coefficients to represent the shear modulus relaxation function of the material. | Integer > 0 or blank | |||
| KFUNC | Identification number of a TABVE entry. The TABVE table contains a series of bulk modulii and decay coefficients to represent the bulk modulus relaxation function of the material. | Integer > 0 or blank | |||
| RHO | Mass density. | Real or blank | 0.0 | ||
| A | Thermal expansion coefficient. | Real or blank | 0.0 | ||
| SHIFT | Time-temperature superposition shift law, selected by one of the following values:
|
Integer | WLF | ||
| C1, C2 | Material constants used by the WLF or Arrhenius shift function. | Real | 0.0 | ||
| T0 | Reference temperature used by the WLF or Arrhenius shift function. | Real ≠ 0.0 if SHIFT = 2 | Required if SHIFT = 2 |
Remarks:
- This entry is ignored unless the DT entry on NLPARM is not blank.
- If a MAT1 entry with the same MID is used, the E, G, and NU fields will be used to define defaults when GFUNC and/or KFUNC are blank.
- Viscoelasticity uses the Generalized Maxwell Model. The deviatoric stress is given by:
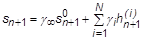
where the stress at each relaxation component is calculated by:
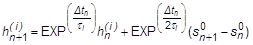
and
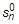 and
and
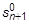 are deviatoric stresses without relaxation.
are deviatoric stresses without relaxation.
The viscoelastic relaxation occurs in the shear and/or bulk modulus. The modulus E in the following figure should be interpreted either shear modulus G or bulk modulus K.
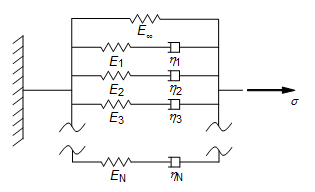
Figure 1. Viscoelastic Material Idealization
Where,
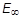 is stiffness at an infinite time
is stiffness at an infinite time
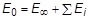 is stiffness at the initial time
is stiffness at the initial time
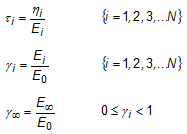
The
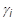 and
and
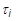 terms are defined using the
TABVE Bulk Data entry where 0 ≤ N ≤ 120.
terms are defined using the
TABVE Bulk Data entry where 0 ≤ N ≤ 120.
- Viscoelastic material properties strongly depend on temperature. Instead of estimating material properties at different temperatures, an assumption called thermorheological simplicity is used in which the relaxation curve at high temperature is identical to that at low temperature when the time is properly scaled. The relaxation times in the Prony series are scaled by the following equation:
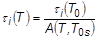
where two different scaling functions are supported.
- William-Landel-Ferry:
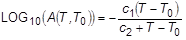
- Arrhenius:
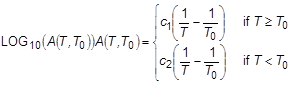
- William-Landel-Ferry: