Five-Sided Solid Element Connection
Description: Defines the connections of a five-sided isoparametric solid element with five to thirteen grid points.
Format:
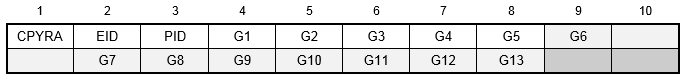
Example:

| Field | Definition | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| EID | Element identification number. | Integer > 0 | Required |
| PID | Property identification number of a PSOLID entry. | Integer > 0 | Required |
| Gi | Grid point identification numbers of connection points. | Integer ≥ 0 or blank, all unique | Required |
Remarks:
- Element identification numbers must be unique with respect to all other element identification numbers.
- The topology of the diagram must be preserved; i.e., G1, G2, G3, G4 define a quadrilateral face G1, G10, and G5 are on the same edge, etc.
- Any or all of the edge points, G6 through G13, may be deleted. If the ID of any edge connection points is left blank or set to zero (as for G6 and G13 in the example), the element equations are modified to give the correct results for the reduced number of connections. Corner grid points cannot be deleted.
- Components of stress are output in the volume coordinate system. (See the VOLUME command in Section 3, Case Control.)
- It is recommended that the edge grid points be located within the middle third of the edge.
- The element coordinate system is defined as follows:
The origin is located at the midpoint of a straight line joining points G1-G4. The x-axis passes through the midpoint of a straight line joining G2-G5. The z-axis is normal to a plane passing through the midpoints of straight lines joining G1-G4, G2-G5, and G3-G6.

Figure 1. CPYRA Element Connection
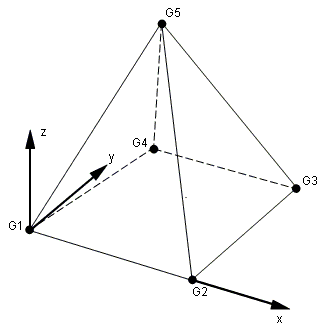
Figure 2. CPYRA Element Coordinate System