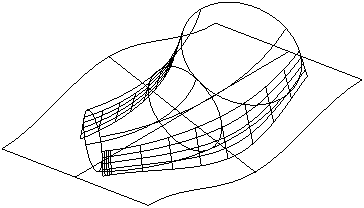
Split and draft surfaces play an important role in designing components and tooling for material-forming applications. In most mold or die applications it is vital to establish the natural split line, and to design a split surface for machining. In most cases, you must use a draft angle in the surface of a mold or die to enable the product to be withdrawn.
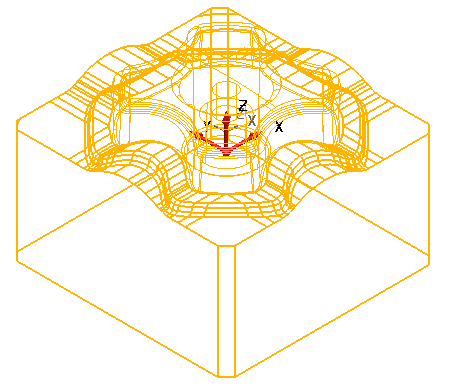
In PowerShape, you can create split and draft surfaces. There is also a wizard to help you create a mold for a single, connected solid.
Split line
A surface's natural split line or occluding boundary is the line around a surface where the surface, when looked at along the draw axis (that is, the direction in which the mold or die is to open), just dips out of sight
 .
.
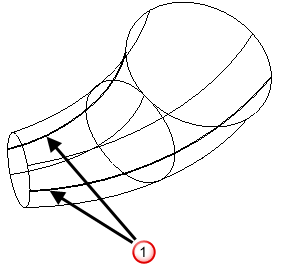
PowerShape can find the natural split line automatically and generate new curves to represent this line. For further details see Creating a draft curve. Alternatively, you can specify a curve by creating a composite curve from existing geometry, for example, edges of surfaces. For further details see Creating a composite curve by tracing.
Split surface
A split surface is a surface created from the split line and is also known as a 'run-off' surface.
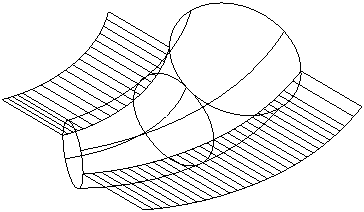
Draft surface
A draft surface is one which projects from a model onto a split surface at a small angle, as shown below. The draft angle ensures that the component separates from the mold cavity.