Result Quantities
The Result Quantities dialog lists the results quantities that are available for viewing after the analysis is completed.
The default quantities are the most widely used, but additional quantities are available if needed.
After running the analysis, to output additional quantities, select them from this list, set the number of iterations to 0, and click Solve. These additional quantities will be available for viewing on the Results task.
Example selecting optional output quantities
Options
By default, the film coefficient result quantity is calculated based on heat transfer results (thermal residual). However, sometimes it is advantageous to obtain film coefficient data based on the flow solution. This is accomplished by using an empirical correlation. The dialog is accessed by clicking the Options button on the Optional Post-Processor Output dialog. The dialog is shown:
This dialog allows the film coefficient to be calculated in two ways.
The first uses the energy equation solution in the fluid and calculates the residual heat going to the walls.
The second uses an empirical formulation of the form:
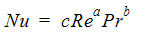
Nu is the Nusselt number, Re is the local Reynolds number, and Pr is the Prandtl number. The flow solution is used to calculate the Reynolds and Prandtl numbers. Use either the default values for a, b, and c, or select new values. Note that the definition of Reynolds number and Nusselt number requires a length constant. If you are unsure what to use for these length scales, use the default of 1.
Vorticity
Vorticity is the measure of the spin (angular speed) of a fluid particle. The mathematical definition of vorticity is the curl of the velocity vector. Another way to look at it is that vorticity is twice the angular rotation (omega). Since omega is a measure of the net angular rotation, vorticity is a measure of the local spin of the fluid particle. (If omega, the angular velocity, = 0, then the flow is irrotational and the vorticity is zero.)
Stream Function
The Stream Function output quantity is available for 2D simulations. It can be used to plot the trajectories of particles in a steady state, incompressible flow. The difference between the stream function values at any two points gives the volumetric flow through a line connecting the two points. Keep in mind that streamlines are tangent to the flow velocity vector of the flow, and the stream function is constant along a streamline.
Information partially sourced from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stream_function
Additional Output Quantities
To learn more about thermal comfort, click here.
To learn more about smoke visibility, click here.