Texture-based Lightmaps
VRED 2022 introduced texture-based lightmaps for ambient occlusion, shadows, and light & shadows, including direct and indirect light, as well as IES and ray light profiles. Improvements to the Bake Light and Shadows module include CPU and GPU raytracing support, cluster support, the possibility to bake Ray files and caustics, uniform and cosine weighting for ambient occlusion, and new presets. We added photon tracing for computing lighting effects for lightmaps to Render Settings.

Texture Baking
It is now possible to bake high-quality results on low polygon objects without subdividing meshes. Use the Bake Type option to switch between vertex and texture bake lightmap generation.
It is important to know that the data baked into a lightmap cannot change at runtime. Realtime lights can be overlaid and used atop lightmapped scenes, but cannot interactively change the lightmap themselves.
Lightmap and Material UV Sets
With VRED 2022, every mesh got a second lightmap UV channel that can have an independent UV layout, compared to the material UV. Geometry exchanged via FBX with other tools keep the second lightmap UV channel for import and export. UVs can be easily transferred from one channel to another (see UV Sets > Copy to Lightmap UV Set/Copy to Material UV Set) in the UV Editor. Compared to the vertex-based approach, texture-based lightmaps require more video memory and, therefore, you need a good balance between texture size and quality. The Bake Light and Shadows module provides the possibility to autogenerate lightmap UVs based on a triplanar mapping or using the UV Editor unfold settings during the calculation. Depending on your scene data, certain objects might require manual reworking in the UV Editor for optimum results.
Lightmap Edge Dilation
Meshes must have proper UVs for calculating lightmaps. Ideally, lightmap UVs use the maximum available UV space, have little distortion and disconnected UV islands, with enough space in between for an edge dilation necessary for lightmap textures.
Lightmap Preview
Only available for nodes with the Texture Bake Type where bake calculations were preformed.
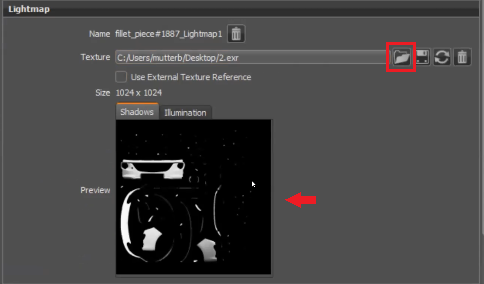
See a preview of the shadow and illumination maps of the lightmap for the geometry selected in the viewport. Load, save, reload, or delete a texture image, as well as set whether or not to use an external texture reference. See the Lightmap section for more information.
To better judge the baked result in the scene, toggle between the different Visualization modes in the Visualization menu or double-check the lightmap texture directly in the UV Editor.
Clustering for Texture-based Lightmaps
We added support for GPU and CPU clustering for texture-based lightmaps.
Keep the following in mind:
- The cluster must be started before users can distribute the calculation of lightmaps on a cluster.
- When calculating lightmaps with the GPU and the
localhostis part of the cluster setup, ensure the graphic card on thelocalhostmaster has enough memory, as the master has to hold the scene twice. - When calculating lightmaps with the CPU and the
localhostis part of the cluster setup, ensure you have enough RAM.
Use the VRED Cluster to distribute the calculation of lightmaps and lightmap UV generation on multiple machines.
It is not possible to use GPU Raytracing or VRED Cluster to calculate vertex-based shadows.
Weighting for Ambient Occlusion
Weighting is only available with Ambient Occlusion selected. It sets the weighting applied to ambient occlusion for both vertex and texture baking.
Uniform
This is the original setting for calculating weighting in VRED 2021.3 and earlier. Shadows are more uniform, but don't have as much variation and depth as with the Cosine setting.
Cosine
Provides a more realistic real-life result than uniform weighting. Shadows have more depth and are not as uniform.
Share Lightmaps for Clones
Share lightmaps for clones in a scene, when enabled. Disable to calculate different lightmaps for clones of the same geometry in the scene, before calculating the lightmap.
Find the Share Lightmaps for Clones option in the Bake Light and Shadows module > Lightmap section.
This is the expected behavior for clones with smart references:
Nodes in different file references cannot be clones - A node in file reference
a.vpbcannot be a clone of a node in referenceb.vpb. Since each file is stored separately, each belongs to the file-respective reference. A node within a file reference can also not be a clone of a node in the regular scene. In these cases, a copy of the node is required. Within the same file references, there are no limitations for clones.All "instances" of a file reference need to be clones - When reference
a.vpbis used multiple times, alla.vpbare clones. This also means all children of eacha.vpbinstance are clones of all othera.vpbchildren.Lighmaps can be different on clones - When having two clones of a box in the scene, you can calculate different lightmaps for these clones. Just uncheck Share lightmaps for clones, before calculating the lightmap.
The same clone in a file reference cannot have different lightmaps - A box is used in
a.vpbfile reference and the file reference is used twice in the scene. You cannot calculate different lightmaps for the box, since the file only exists once and is only written once. Therefore, the box is only stored once.You want different lightmaps on the same clone of a file reference - Manually change the scene to do this. In most cases, this would mean removing the file references and replacing them with normal group nodes.
Python for Lightmaps
We added the following Python commands for lightmaps to the Python documentation. Click the links below for information on that command.
- vrBakeService
- vrdVertexBake
- vrdVertexBakeSettings
- vrdTextureBake
- vrdTextureBakeSettings
- vrdIlluminationBakeSettings
- vrdLightmap
- vrBakeTypes.
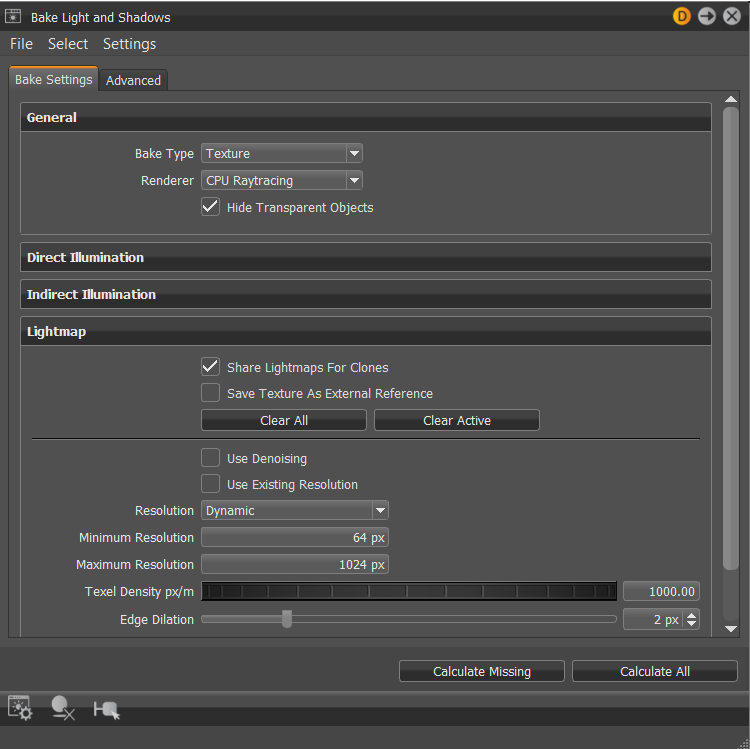
Bake Light and Shadow Module Improvements
Numerous improvements were made to the Bake Light and Shadows module. Added File and Select menus, more Settings options, Bake Settings and Advanced tabs with new sections and options, most of which relate to the new Texture bake type.
We added Python commands for lightmaps to the Python documentation. Check out Python for Lightmaps for a list of these new commands.
File Menu
We've added options for loading, saving, and updating paths locations for lightmaps. See the Bake light and Shadows File Menu section for information on each option.
Select Menu
We've added selection options to help identify nodes that have been baked or unbaked, have an active or non-active bake type.
Settings Menu Additions
We've added options for loading and saving lightmaps, as well as saving, editing, accessing bake presets.
Bake Settings Tab
The Bake Settings tab contains parameters for configuring direct and indirect illumination, subdivisions, lightmap behavior, lightmap UV generation, as well as setting the bake type and finally calculating the bake. Here are some of the highlights:
- For baking textures, start with Bake Type
- For setting the raytracing used, see Renderer
- For hiding glass and transparent objects, use Hide Transparent Objects
- If working with ambient occlusion, see Weighting
- For sharing lightmaps for clones in a scene, try Share Lightmaps for Clones
Advanced Tab
The Advanced tab contains parameters for seeing settings used to bake the selected object in the scene in the viewport. See the bake settings applied, as well as a preview of the shadow and illumination maps. Save the texture as an .exr file and use the Active Bake option to turn off baking or switch between texture and vertex.