 Scale
Scale
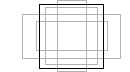
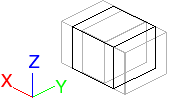
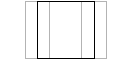
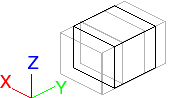
Scales the picked objects uniformly along all axes. Scaling changes the size of objects by changing their scale proportionally in all three dimensions.
You can also apply scaling to an image plane’s two dimensions. You can type a value that applies to all dimensions equally or use different mouse buttons to apply to different dimensions.
Access this tool from the Transform palette:
Scale objects proportionally
- Select the Scale tool
 .
. - Drag to scale the object uniformly along all axes, or type a scaling value.
How different mouse buttons work in the different windows
Notes and tips
To scale in different amounts for different dimensions, use non-proportional scaling by selecting Transform > Non-p Scale
 .
.You cannot scale curve-on-surface elements, as they are projections onto a surface.
The effect of a scale operation depends on the location of the scale pivot point of the object and the addressing mode, relative, or absolute. By default, all geometry has an initial scale factor of 1, meaning 100% of its size.
- Relative scaling is based on the current original size of the object. For example, if you scale to 1.5 and then scale again to 2.0, the object is now three times as big as when you started.
- Absolute scaling is based on the original size of the object. For example, if you scale to 1.5 and then scale again to 2.0, the object is now twice as big as when you started.