You can select and modify edges on a 3D solid or surface.
Move, Rotate, and Scale Edges
Move, rotate, and scale the edges on 3D solids and surfaces using grips, gizmos, and commands.
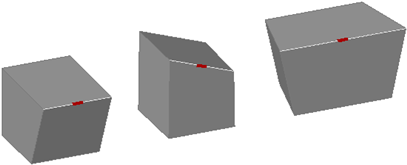
cubes with edges moved, rotated, and scaled
You can use MOVE, ROTATE, and SCALE to modify edges on 3D solids and surfaces just as you can for any other object. Press and hold Ctrl to select the edge.
If you move, rotate, or scale an edge on a 3D solid primitive, the history of the solid primitive is removed. The solid is no longer a true primitive and cannot be manipulated using grips and the Properties Inspector.
Edges on regions can be selected, but do not display grips. These edges can also be moved, rotated, and scaled.
Edge Modification Options
As you drag an edge, press Ctrl to cycle through modification options.
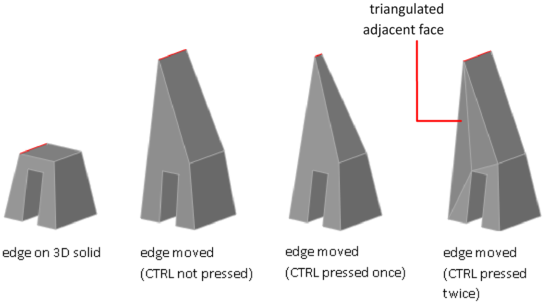
- Extend Adjacent Faces. When you move, rotate, or scale an edge without pressing Ctrl, the shared length of the edge and its vertices is maintained. However, the planes of the adjacent faces adjacent might be changed.
- Move Edge. When you move, rotate, or scale an edge and press and release Ctrl once while dragging, the edge is modified without its vertices. The surfaces of the adjacent faces are maintained, but the length of the modified edge might change.
- Allow Triangulation. When you move, rotate, or scale an edge and press and release Ctrl twice while dragging, the edge and its vertices are modified. (This behavior is the same as if you had not pressed Ctrl). However, if the adjacent faces are no longer planar, they are triangulated (divided into two or more planar triangular faces).
If you press and release Ctrl a third time, the modification returns to the first option, as if you had not pressed Ctrl.
Delete Edges
You can also delete edges that completely divide two coplanar faces using one of the following methods:
- Select the edge and press Delete.
- Select the edge and enter the ERASE command.
Fillet and Chamfer 3D Solids
Round, fillet, or bevel the edges of 3D solids using FILLETEDGE and CHAMFEREDGE.
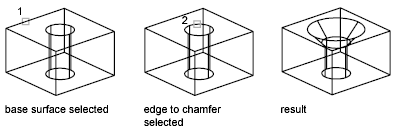
Use the fillet and chamfer grips to modify the fillet radius or the chamfer distance. The default fillet radius is set by the FILLETRAD3D system variable.
Color Edges
You can modify the color of an edge on a 3D object by selecting the edge and changing the Color property in the Properties Inspector.
Copy Edges
You can copy individual edges on a 3D solid object. Edges are copied as lines, arcs, circles, ellipses, or splines.
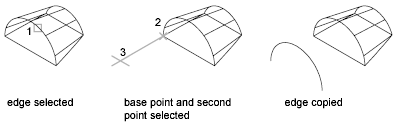
If you specify two points, the first point is used as a base point and a single copy is placed relative to the base point. If you specify a single point, and then press Enter, the original selection point is used as a base point. The next point is used as a point of displacement.