Bitmap Values
Value> Bitmap Value
The Bitmap class provides storage of 3ds Max bitmaps and low-level access to them.
Bitmaps can be temporary objects that are resident only in memory, or they can be associated with a file on the disk.
Those bitmaps associated with files have a non-null .fileName property and are either load-only or save-only, but not both (this is with respect to file I/O; all bitmaps in memory can have their pixels modified by the setPixel() functions).
You can make load-only bitmaps with the openBitmap() and selectBitmap() functions.
You can make temporary or save-only bitmaps with the bitmap() constructor, or with the render() , copy() , or getChannelAsMask() functions. To make them savable, they must have a valid file name, supplied either on the constructor with a fileName: parameter or by setting the .fileName property.
Some properties for saving bitmaps in different formats are exposed in the various BMPIO classes, such as BMP, JPEG, and TIF. These settings must be set before the filename property on the bitmap image.
For example, to save two versions of the same jpeg image, but with different quality settings:
dib = gw.getViewportDib()
jpeg.setQuality 20
dib.filename= @"C:\temp\myjpeg20.jpg"
save dib
jpeg.setQuality 90
dib.filename= @"C:\temp\myjpeg90.jpg"
save dibConstructors
bitmap <width <height> [filename:<filename_string>] \
[numframes:<integer>] \
[color:<color>] \
[gamma:<float>] \
[pixelAspect:<float>] \
[channels:<channel_name array>]\
[hdr:<boolean>] \
[iconName:<filename>]\
[iconSize:<point2>]\
[colorSpace:<string>]
Creates an empty bitmap. The bitmap value returned is a savable bitmap.
The filename: parameter allows you to set the name of the file in which the bitmap will be saved using the save method. Specifying an existing bitmap file name does not load the contents of the bitmap file into the bitmap value.
The numframes: parameter allows you to create a multi-frame bitmap.
The color: parameter allows you to set the initial color of all pixels in the bitmap.
EXAMPLES
b = bitmap 320 240 color:white
The gamma: parameter allows you to set the gamma for the newly created bitmap.
EXAMPLES
b = bitmap 320 240 gamma:1.9
render camera:c to:b
The pixelAspect: parameter allows you to set the pixel aspect for the newly created bitmap.
Once created, it is not possible to change the gamma or pixel aspect of a bitmap, though you can copy one bitmap into a newly created one that has a different gamma or pixel aspect to achieve this effect.
The channels: parameter lets you specify the channels to be created. It is also available as a property. For a list of valid names, see the getChannel method documentation.
When the optional hdr: parameter introduced in 3ds Max 8 is set to true, the constructor creates a 32 bit per channel bitmap value instead of an 8 bit per channel bitmap value.
The iconName: parameter allows you to specify an icon file to load. The iconSize: parameter specifies the icon's size at 100% DPI scaling.
openBitMap <filename_string> [colorSpace:<string>] [gamma:<float>]Returns a bitmap value containing the contents of the specified bitmap file. The bitmap value returned is a load-only bitmap.
If the specified bitmap file does not exist, a runtime error is generated in 3ds Max 9 and earlier.
If the specified bitmap does not exist, a value of undefined is returned in 3ds Max 2008 and higher.
 NEW in 3ds Max 2024:
If the optional
NEW in 3ds Max 2024:
If the optional colorSpace keyword parameter is specified, it is the requested color space name. Note that this may not be the actual color space applied to the bitmap if the requested one is unavailable. This keyword parameter is only effective if an OCIO-based color management mode is active.
If the optional gamma keyword parameter is specified, it is the gamma value. Noet that this parameter is only effective if the gamma-based color management mode is active.
selectBitMap [caption:<open_dialog_title_string>]This method displays an Image Input selection browser for the user to select a bitmap file. Returns a bitmap value containing the contents of the selected bitmap file, or the value undefined if the user presses Cancel in the browser. The bitmap value returned is a load-only bitmap.
<bitmap>copy <bitmap>Copies an existing bitmap, creating an unique instance of the bitmap.
If the source bitmap is load-only, the bitmap value returned is a temporary bitmap value with a null filename and just one frame.
If the source is a multi-frame file, it snaps the current frame into the new copy, which becomes frame 0.
Properties
<bitmap>.filename : StringLets you get or set the file name associated with the bitmap.
<bitmap>.palette : ArrayYields an array of 256 colors (a bug in the current 3ds Max SDK prevents working with paletted files of other than 256 entries). Take care accessing this array with color indexes retrieved by the getIndexedPixels() function described below because these indexes are 0-based and MAXScript array indexes are 1-based. Yields undefined if the bitmap is not paletted. Currently, you cannot create a paletted bitmap in MAXScript. However, you can read and write to a pre-existing paletted bitmap.
<bitmap>.frame : IntegerGet and set the current frame number in a multi-frame file. Setting this property is permitted only on load-only bitmaps. The frame number is 0-based for inherently multi-frame files such as, .avi and .mov.
<bitmap>.numframes : IntegerThe number of frames in a multi-frame file, yields 1 for a single image file.
<bitmap>.height : Integer, read-onlyReturns bitmap's height in pixels.
<bitmap>.width : Integer, read-onlyReturns bitmap's width in pixels.
<bitmap>.gamma : FloatGet and set the gamma value of the bitmap.
<bitmap>.inputGamma : {#auto | #default | Float}Returns the input gamma mode of the bitmap.
This value reflects the Gamma mode that was set when a bitmap value was loaded from an image file.
See Bitmap Gamma and MAXScript for details.
Available in 3ds Max 2014 and higher.
<bitmap>.inputGammaValue : FloatReturns the actual input gamma value of the bitmap.
See Bitmap Gamma and MAXScript for details.
Available in 3ds Max 2014 and higher.
<bitmap>.aspect : Float, read-onlyReturns the bitmap's pixel aspect. Note that this is the aspect of the pixel, not the aspect of the bitmap image.
<bitmap>.channels : ArrayThis property lets you get and set the bitmap channels available in the bitmap. For a list of valid names, see the getChannel method documentation.
EXAMPLES
b = bitmap 100 100 channels:#(#weight)
--> BitMap:
b.channels
--> #(#weight)
b.channels = #(#zDepth)
--> #(#zDepth)
<bitmap>.hasAlpha : Boolean, read-onlyThis property contains true if the bitmap has an alpha channel and false if it does not.
Color Management Properties
 NEW in 3ds Max 2024:
These properties are part of the OCIO color management workflow.
NEW in 3ds Max 2024:
These properties are part of the OCIO color management workflow.
.colorSpaceThe color space name that is assigned to the bitmap.
.colorSpaceSourceThe source of the assigned color space. Can be:
#notSet- no color space is set#inputRules- color space set by input rules#userDefined- color space set by user#heuristics- color space set by heuristics other than the input rules
.colorSpaceReqThe name of the requested color space.
.colorSpaceReqSourceThe source of the requested color space. Can be one of:
#notSet- no color space is requested#inputRules- color space requested by input rules#userDefined- color space requested by user#heuristics- color space requested by heuristics other than the input rules
.colorSpaceStatusThe current status of the color space assignment. Can be one of:
#notSet- color space is not set#normal- color space is assigned and working normally#forcedDefault- color space assignment failed, default fallback applied#invalid- color space assignment failed, no fallback available
.colorSpaceRuleIf the color space was assigned by input rules (ie, .colorSpaceSource is #inputRules), this property holds the name of the input rule that assigned the color space.
Methods
display <bitmap> caption:<string>Opens a virtual frame buffer (VFB) displaying the image.
Changes to the bitmap are not automatically displayed to the VFB.
To update the VFB, you need to call this function again.
Setting the frame property of the bitmap value updates the VFB.
Each bitmap has its own VFB (if you display two different bitmaps, two VFBs will be displayed).
Since 3ds Max 2015, if the optional keyword argument caption: is specified as string, it will be displayed as the caption in the title bar of the VFB.
unDisplay <bitmap>Close the VFB associated with the bitmap if open.
<boolean>save <bitmap> [frame:<integer>] [gamma:{#auto|#default|<float>}] [quiet:<boolean>]Saves the current state of the bitmap. Make sure that the file name is set first.
When saving multi-frame image files, the effect of the frame: keyword parameter is different depending on the type of output file.
Inherently multi-frame files such as, .avi and .mov ignore the frame: parameter and always write to the next output file frame in sequence on each save() . You cannot randomly write frames or rewrite frames that are already saved.
Saving image sequences (such as, .bmp, .jpg, and .tga) requires supplying the frame: parameter and causes the frame number to be appended to the output file name for each frame saved. This effectively generates a sequence of image files suitable for building an IFL.
The output file remains open until you call close on the bitmap.
The save() function can only be called on a savable bitmap. You will get a runtime error if you attempt to save a bitmap opened with openBitmap() or selectBitmap() .
The gamma: keyword parameter can be used in 3ds Max 2014 and higher to set the Gamma mode or Gamma Override value:
#autois the new, intelligent mode. It uses the file information when present, or intelligently chooses gamma based on whether the file is Floating point or not. This is the default behavior.#defaultis actually the old legacy mode which only exists for backwards compatibility.- If set to a floating point value, the Gamma will be overridden by that value.
For details on the quiet: option that was added to this method in 3ds Max 8, please see Quiet Mode
The method will return True on success or False if the saving failed (for example, if attempting to overwrite an existing read-only file) in 3ds Max 8 and higher.
close <bitmap>Closes the bitmap file associated with the bitmap if it is open for output. A bitmap file is opened for output when you call save on the bitmap value the first time. If a Virtual Frame Buffer (Rendered Frame Window) associated with the bitmap is open, it will be closed. This function also frees all memory allocated by the bitmap, including the internal pixel frame buffer. If you are generating many bitmaps, say in a rendering loop, you can use the close() function to free these large amounts of memory, which is otherwise not released until the next garbage collection.
free <bitmap>Frees the memory used by the bitmap value without waiting for garbage collection.
Available in 3ds Max 9 and higher.
copy <source_bitmap> <dest_bitmap>Copies the source bitmap to the destination bitmap. If the size of the two bitmaps is different, the image will be scaled to fit the destination bitmap.
gotoFrame <bitmap> <frame>Position multi-frame file (avi, flc, and so on) to frame frame . This method is permitted only on load-only bitmaps. The frame number is 0-based for inherently multi-frame files such as, .avi and .mov. Updates VFB if open.
getPixels <bitmap> <coord_point2> <num_pixels> linear:<boolean>Retrieve a sequence of pixels from a row in the bitmap as an array of color values.
The coord_point2 argument specifies the starting pixel coordinate with [0,0] at the top-left-hand pixel.
The .x component of the Point2 coordinate is the column, and the .y component is the row.
The sequence must come from one row only. You cannot retrieve a sequence of pixels that spans multiple rows.
Using any out of-bounds coordinates or retrieving over row boundaries will fail and yield an empty array.
The optional linear: keyword parameter introduced in 3ds Max 2014 can be set to True to access linear values with Gamma of 1.0, or False to access raw data (default, old behavior prior to 3ds Max 2014).
setPixels <bitmap> <coord_point2> <color_value_array>Sets the sequence of pixels in a row in the bitmap starting at the Point2 coordinate to the values in the given array. The .x component of the Point2 coordinate is the column and the .y component is the row. The number of pixels to set is taken from the size of the array. As with getPixels() , you cannot set pixel sequences across a row boundary.
getIndexedPixels <bitmap> <coord_point2> <num_pixels>Retrieve a row of pixels as an array of palette index numbers. The coord_point2 argument specifies the starting pixel coordinate with 0,0 at the top-left-hand pixel. The index numbers are origin 0.
This is in keeping with indexed color conventions, but not MAXScript's. Take care accessing any retrieved palette array using these numbers because the retrieved palette is returned as a MAXScript array and these arrays use 1-based indexes. You cannot get pixels sequences that cross row boundaries.
setIndexedPixels <bitmap> <coord_point2> <number_array>Sets the row of pixels starting at the Point2 coordinate to the color indexes in the given array. The number of pixels to set is taken from the size of the array. The color indexes are zero-based. You cannot set pixels sequences that cross row boundaries.
getChannel <bitmap> <coord_point2> <chan_name>Retrieves the g-buffer channel data for the named channel for the pixel specified by 2D coordinate. The chan_name argument specifies the channel identifier, chosen from the following:
#zDepth
#matID
#objectID
#UVCoords
#normal
#unClamped
#coverage
#node
#mask
#shaderColor
#shaderTransparency
#velocity
#weightIf the bitmap contains the requested channel, the returned value is always an array of values, one for each layer present in the channel at that pixel, ordered from front to back. If the bitmap does not contain the requested channel, the function returns the value undefined . Typically, you get bitmaps containing channels by opening .rla files or using the MAXScript render() function with the channels: parameter supplied. You will get multiple values in the array if the front objects have any transparency.
FOR EXAMPLE
getChannel bm [x,y] #zDepth
might return:
#(-354.413, -354.467, -355.271, -1e+030)
indicating there is a front surface with non-zero transparency at depth -354.413, another at -354.467, and a final one at -355.271. The -1e+30 value represents the background image plane.
You can retrieve the #node channel (if it was generated) to get the actual scene objects at those depths,
getChannel bm [x,y] #node
might return:
#($Sphere:Sphere02 @ [-4.7,24.3,0.0], $Sphere:Sphere02 @ [-4.7,24.3,0.0],$Sphere:Sphere01 @ [-8.3,56.2,5.7])
The type of values returned in the array depend on the channel, as follows:
#zDepth: <float>
#matID: <integer>
#objectID: <integer>
#UVCoords: <point2>
#normal: <point3>
#unClamped: <color>
#coverage: <float>
#node: <node>
#shaderColor: <color>
#shaderTransparency: <color>
#velocity: <point2>
#weight: <color>See the 3ds Max Software Development Kit Help file for information on the data stored in the g-buffer channels.
getChannelAsMask<bitmap> <chan_name> [to:<bitmap>] \
[fileName:"filename_string"] [pixelAspect:<float>] \
[gamma:<float>] [layer:<integer>] [invert:<boolean>] \
[node:<node> |objectID:<integer> |matID:<integer>] \
[velocity:#angle | #magnitude] | [angle:<float>]Builds and returns a separate 8-bit gray-level bitmap suitable for use as a mask in materials, maps, effects, and so on. This bitmap corresponds roughly to the display you see in the visual frame buffer if you select a g-buffer channel to view. In addition, you can cause this mask to be masked itself to a selected node, object ID, or material ID. The parameters are as follows:
<bitmap>The source bitmap containing the source g-buffer channel data.
<chan_name>The channel from which to generate a mask. The chan_name values are as described for the getChannel() method.
The mask is a single 8 bit value while the channel might be a complex value of some kind. In each case, a mapping to 8 bits is performed.
Unless noted differently below, this mapping is the same mapping used by 3ds Max to generate monochrome images in the Virtual Frame Buffer.
to:<bitmap>Specifies an existing bitmap to write the mask into. Its width and height must match the source bitmap.
fileName:"filename_string"Specifies the file name associated with the generated bitmap.
gamma:<float>Specifies the generated bitmap's gamma value.
pixelAspect:<float>Specifies the generated bitmap's pixel aspect. Note that this is the aspect of the pixel, not the aspect of the bitmap image.
layer: <integer>Specifies the channel layer of the source bitmap to extract data from. Defaults to 1.
invert:<boolean>If true , inverts the generated bitmap. Defaults to . false .
node:<node> objectID:<integer> matID:<integer>Specifies a sub-mask. If one of these parameters is supplied, the generated mask is clipped to contain data only in pixels where the given node, objectID, or materialID is visible. To use this sub-masking, you must ensure the #node , #objectID , or #matID channel is present in the source bitmap. Further, if the #coverage channel is present in the source bitmap, the sub-mask is anti-aliased by the coverage data.
velocity:#angle | #magnitude angle:<float>These parameters can only be specified if the selected channel is #velocity . The default velocity parameter value is #magnitude . These parameters control the generated bitmap as follows:
velocity:#angleGenerated bitmap pixel values are proportional to angle of pixel movement direction with an angle of direction of 0 degrees (horizontal to the right) mapping to a luminance value of 0, 180 degrees mapping to a luminance value of 127, and 360 degrees mapping to a luminance value of 255.
velocity:#magnitudeGenerated bitmap pixel values are proportional to velocity magnitude. High velocities are darker than low velocities.
angle:<float>Generated bitmap pixel values are proportional to movement direction deviation from the given angle with a luminance value of 255 at the exact angle and falling off to a luminance value of 0 at 10 degrees from the specified angle. The specified angle is relative to 0 being horizontal to the right.
CompareBitmaps {<filename>File1 | <bitmap>bitmap1} {<filename>File2 | <bitmap>bitmap2}\
<int>tolerance(# different pixels) <int>variation(0-255)\
useAlpha:<boolean>errorMsg:<&string>In 3ds Max 9 and higher, returns true if the bitmaps compare as the same, false if not.
More than'tolerance' number of pixels must be different before the comparison fails.
Two pixels are considered the same if the difference in each component value is less than or equal to 'variation'.
If useAlpha is true, the alpha component value is also tested. If false (the default), the alpha component is not tested.
If specified, the errorMsg keyword variable (passed by reference) will contain an error message.
The potential messages are:
"Passed."
"Different Pixels: #" (where # is the number of pixels that are different)
"One or both Bitmaps not found"
"Bitmaps have different sizes"
pasteBitmap <src_bitmap> <dest_bitmap> (<src_box2> | <src_point2>) <dest_point2> \
[maskColor:<color>type:{#paste|#composite|#blend|#function}] \
[function:<composite_fn>] [alphaMultiplier:<float>]Copies a block of pixels from the source bitmap to the destination bitmap.
Available in 3ds Max 2008 and higher. Previously, available in the Avguard Extensions.
The position of the source block is specified by src_box2 or src_point2, and the destination by dest_point2.
The width and height of the block is specifed by src_box2 or, if src_point2 is specified, by the remaining size of the source bitmap.
The width and height will be clamped to prevent either source or target overruns.
If
maskColor:is supplied, pixels with this color in src_bitmap are not copied to dest_bitmap.If
type:is#paste(the default), the source is pasted on the destination ignoring all alpha.If
type:is#composite, the source alpha of the source is used:clamp (R = S + D * (1-S.alpha)).If
type:is#blend, the source alpha of the source is used:R = S * S.alpha + D * (1-S.alpha).For both
type:#compositeandtype:#blend,R.alpha = S.alpha + D.alpha * (1-S.alpha).The
type:#compositeis typically used for pre-multiplied alpha images.If
type:is#compositeor#blend, the source alpha is multiplied by thealphaMultiplier:value, which defaults to a value of 1.0 if not supplied.If
type:is#function, an optionalfunction:parameter can specify a user-defined function taking 4 arguments - the source pixel color, the source pixel location, the second source pixel color, and second source pixel location. The second source is the destination bitmap. The return result of the function is stored in the destination bitmap's pixel.Only RGBA information is copied - no channel data is copied.
EXAMPLE
bm1=bitmap 100 100 color:red
bm2=bitmap 100 100 color:green
bm3=bitmap 100 100 color:blue
pasteBitmap bm2 bm1 (box2 0 0 25 50) [50,50]
display bm1
pasteBitmap bm1 bm3 [25,25] [25,50] maskColor:green
display bm3
RESULTS:
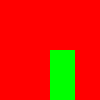
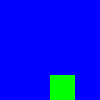
CUSTOM COMPOSITING EXAMPLE
resetMaxFile #noPrompt--start a new scene
--Create a teapot and two slightly offset target cameras
theTeapot = teapot wirecolor:white segs:10
theTarget1 = targetObject pos:[-1,0,10]
theCamera1 = TargetCamera pos:[-10,-130,30] target:theTarget1
theTarget2 = targetObject pos:[1,0,10]
theCamera2 = TargetCamera pos:[10,-130,30] target:theTarget2
--Create two bitmaps to render and process
b1 = bitmap 320 240
b2 = bitmap 320 240
--Render the two cameras into the two bitmaps
render camera:theCamera1 to:b1 vfb:off
render camera:theCamera2 to:b2 vfb:off
--This is the custom compositing function:
fn compfn c1 p1 c2 p2 =
(
res = c2--the result will contain the G and B of b2
res.r = c1.r--but the R from b1
res--then we return the resulting color value
)
--Perform the compositing using the above function:
pastebitmap b1 b2 [0,0] [0,0] type:#function function:compfn
display b2

This method is typically 3 to 5 times faster than using getPixels/SetPixels in a MAXScript loop depending on the complexity of the custom function.
For an example of modifying a single bitmap using this method, see the third example in the Never get a single pixel when you can get a whole line topic of the MAXScript Frequently Asked Questions.
getBitmapInfo {<filename> | <bitmap>}Returns information on the specified bitmap file as a 13 element array. Available in 3ds Max 2008 and higher. Previously, available in the Avguard Extensions.
Array elements are:
Expanded bitmap file name as String
Device name as String
Bitmap width as Integer
Bitmap height as Integer
Number of bits for each RGB component value as Integer
Number of bits for alpha component as Integer.
The aspect ratio of the bitmap as Float
The gamma of the bitmap as Float
Whether the bitmap has alpha as a Boolean
First frame as Integer
Last frame as Integer
The bitmap type (from BitmapInfo::Type()) as Integer. See topic "Bitmap Types" in the SDK help file for more info on the bitmap types.
The bitmap flags (from BitmapInfo::Flags()) as Integer. See topic "Bitmap Flags" in the SDK help file for more info on the meaning of each bit.
EXAMPLE:
print (getBitmapInfo (getDir #maxroot +"\\maps\\OAKLEAF.TGA"))
RESULT:
"C:\Program Files\Autodesk\3ds Max 2015\maps\OAKLEAF.TGA"
"Targa Image File"
152
256
8
8
1.0
2.2
false
0
0
3
0
OK
forceReloadBitmapFile <bitmap>Forces the reloading of the Bitmap File associated with the specified bitmap.
Available in 3ds Max 2015 and higher.
<boolean>registerFileChangedFunction <bitmap> <callback_functions>Registers a File Change Callback Function for the bitmap specified by the first argument.
The second argument must be a MAXScript function expecting one argument.
Returns True on success, False on failure.
Available in 3ds Max 2015 and higher.
FOR EXAMPLE:
b = bitmap 100 100 --Create a new bitmap value
b.filename = @"c:\temp\testme.bmp" --Give it a file name
save b --Save it to file
--Now open the file for reading
b1 = openbitmap @"c:\temp\testme.bmp"
--Define and register a callback function to monitor bitmap file changes
fn onFileChanged arg = format "Bitmap Value File Modified: %\n" arg
registerFileChangedFunction b1 onFileChanged
setPixels b [50,50] #(red) --Write a pixel into the original bitmap value...
save b --...and save it to disk
--The change to the file on disk will trigger the callback function!
--> Bitmap Value File Modified: BitMap:c:\temp\testme.bmp
<enum>validateColorSpace <bitmap> NEW in 3ds Max 2024:
Checks and validates the assigned color space against the currently available color spaces. If the assigned color space is missing or not available in the current setup, then it assigns a valid color space based on the requested color space, file input rules and other settings and/or heuristics.
NEW in 3ds Max 2024:
Checks and validates the assigned color space against the currently available color spaces. If the assigned color space is missing or not available in the current setup, then it assigns a valid color space based on the requested color space, file input rules and other settings and/or heuristics.
Returns the status of the assigned color space after validation and possible assignment, one of:
#notSet- color space is not set#normal- color space is assigned and working normally#forcedDefault- color space assignment failed, default fallback applied#invalid- color space assignment failed, no fallback available
<enum>SetOutputColorConversion <bitmap> <enum outputConversion> [outputColorSpace:<string>] [outputDisplay:<string>] [outputViewTransform:<string>] NEW in 3ds Max 2024:
Sets the color space output conversion settings for the bitmap. The
NEW in 3ds Max 2024:
Sets the color space output conversion settings for the bitmap. The outputConversion can be one of:
#automatic#noConversion#colorSpaceConversion#displayViewTransform
If the outputConversion is set to #automatic or #noConversion, no other parameter needs to be specified. If outputConversion is #colorSpaceConversion, outputColorSpace needs to be specified
If outputConversion is #displayViewTransform, outputDisplay and outputViewTransform arguments need to be specified
The outputColorSpace keyword argument specifies the output color space to request.
The outputDisplay keyword argument specifies the output display to request.
The outputViewTransform keyword argument specifies the display/view transform to request.
<bitmap> colorConvert <bitmap> <colorspace_string>
<bitmap> colorConvert <bitmap> <displayname_string> <viewtransform_string> NEW in 3ds Max 2024:
Converts a source bitmap and returns it. There are two versions of this method. The first takes the name of a color space to convert the bitmap to. The other takes a display/view transform pair. This method throws a MAXScript runtime error if there is an issue with any of the passed parameters, for example if the bitmap is invalid, the specified color space / display / view transform does not exist in the current OCIO color management configuration, or if the view transform is not available for the specified display.
NEW in 3ds Max 2024:
Converts a source bitmap and returns it. There are two versions of this method. The first takes the name of a color space to convert the bitmap to. The other takes a display/view transform pair. This method throws a MAXScript runtime error if there is an issue with any of the passed parameters, for example if the bitmap is invalid, the specified color space / display / view transform does not exist in the current OCIO color management configuration, or if the view transform is not available for the specified display.
For example:
-- get color spaces
colorspaces = ColorPipelineMgr.GetFileIOColorSpaceList()
displays = ColorPipelineMgr.GetDisplayList()
-- get views for the first display
views = colorPipelineMgr.GetViewList displays[1]
dib = gw.getViewportDib()
-- first version: convert to a specified colorspace
dib2 = colorConvert dib colorspaces[1]
-- second version: convert to a specified display/view pair
dib3 = colorConvert dib displays[1] views[1]
format "dib colorspace: %" dib.colorspace
format "dib2 colorspace: %" dib2.colorspace
format "dib3 colorspace: %" dib3.colorspaceRelated Methods
<boolean>setSilentMode <boolean>Sets Silent mode on or off. If Silent mode is off, any errors occurring during bitmap input or output will result in an error message dialog being displayed by the 3ds Max bitmap I/O routines. If Silent mode is on, error message dialogs are not displayed. Returns a boolean signifying the prior Silent mode state.
The Silent mode state is an internal 3ds Max state, and other 3ds Max plug-ins can turn this state on or off. If you use this method, it is recommended that you turn the state on or off saving the return value, perform the bitmap input or output, and then restore the state to its original value.
silentMode()Returns a boolean signifying the Silent mode state.
selectSaveBitMap [caption:<open_dialog_title_string> ] [gamma:&gama_value] [metadata:&dataArray]Displays a 3ds Max bitmap save dialog and returns the fully-specified file path name as a string.
Returns undefined if the user cancels out of the bitmap save dialog.
If the optional gamma: keyword is provided in 3ds Max 2014 and higher, the by-reference variable passed as parameter will be set to the gamma mode value: #auto , #default , or a Float gamma override value.
If the optional metadata: keyword is provided in 3ds Max 2014 and higher, the by-reference variable passed as parameter will be set to the BitmapInfo expressed as an array of values that can be passed to the save() function's metadata: optional keyword. See Bitmap Gamma and MAXScript for details.
FOR EXAMPLE:
bitmap.filename = SelectSaveBitmap caption:"Select a file" gamma:&gma metadata:&data
if (bitmap.filename) do save bitmap gamma:gma metadata:datafreeSceneBitmaps()Frees up all the memory used by the image file bitmap caches. This is useful if memory is fragmented with a lot of different bitmaps and you want to have just the ones currently active reloaded.
getBitmapOpenFileName [caption:<title>] [filename:<seed_filename_string>] [metadata:&dataArray]
getBitmapSaveFileName [caption:<title>] [filename:<seed_filename_string>] [metadata:&dataArray]Displays the bitmap file selection dialog.
Both functions return a fully-specified file path name or undefined if the user cancels out.
If an existing file name is selected using the getBitmapSaveFileName() function, a File Exists/Confirm Overwrite dialog will be displayed.
If the optional metadata: keyword is provided in 3ds Max 2014 and higher, the by-reference variable passed as parameter will be set to the BitmapInfo expressed as an array of values that can be passed to the save() function's metadata: optional keyword. See Bitmap Gamma and MAXScript for details.
The getBitmapOpenFileName() function does not require that an existing file name be selected. A file name is returned if the user types a file name that does not exist. If necessary, you should check the file name that is returned to ensure the file exists.
When you open a bitmap file, an entire frame is loaded into memory. When you are finished processing a bitmap, it is a good idea to either call close() on the bitmap or assign the value undefined to the variable storing the bitmap value, and then manually run garbage collection ( gc light:true ) so that memory can be released. Another technique for conserving memory when using the render() or getChannelAsMask() functions repeatedly is to use the to:<bitmap> keyword argument which allows those functions to overwrite an existing bitmap’s pixel image with the new rendering or mask.
There is currently no access to the properties associated with some of the bitmap output plug-ins. This means that you cannot set the codec used for .avi files. The properties used are the properties that were last used when saving that file type in 3ds Max.
The following script shows how to properly create and save a multi-frame image file in AVI format.
SCRIPT
theTeapot=teapot()--something to render
animate on at time 10 \--set animate and time context
rotate theTeapot 180 z_axis--rotate the teapot
cam=targetcamera pos:[200,0,100] \--camera pointed at teapot
target:theTeapot
renderFrames=#{1,3,5..12}-- specify frames to render
b=bitmap 160 120 filename:@"c:\temp\testme.bmp"--create a new bitmap
for i= 1 to renderFrames.count do--loop though renderFrames
(
if renderFrames[i] then--if supposed to render frame...
(
at time i--set time context
render 160 120 camera:cam to:b-- render to bitmap frame
save b frame:i-- save each frame as you advance
)-- if you save AFTER the loop,
-- just the last frame is saved.
)
close b-- close the output file - this will also get rid of
--the reference to the bitmap value and free its memory.
OUTPUT:
$Teapot:Teapot004 @ [0.000000,0.000000,0.000000]-- result of line 1
OK-- result of lines 2 and 3
$Target_Camera:Camera005 @ [200.000000,0.000000,100.000000]-- result of lines 4 and 5
#{1, 3, 5..12}-- result of line 6
BitMap:c:\temp\testme.bmp-- result of line 7
OK-- result of for loop, lines 8 to 15
OK-- result of line 16
While the frame:i keyword argument to the save() method is optional for AVI files (they would advance automatically after each frame), Quicktime MOV files require it to save correctly. Otherwise, each rendered frame will overwrite the first frame in the file and the MOV would end up only one frame long.
The following script reads a bitmap file and outputs a script to Listener that implements a function to recreate the same bitmap. This function can then be copied into your script. This is useful for building button images in MAXScript so that you do not need to distribute bitmap files along with your script.
SCRIPT
(
b=selectbitmap()-- open image file browser
bname="bitmap_"+(getfilenamefile b.filename)-- build name from filename
w=b.width-- get properties of bitmap
h=b.height
format "----------\nfn load_% = (\n" bname -- start defining function
format "local %=bitmap % %\n" bname w h -- create bitmap in function
-- write out a function that unpacks an integer into a pixel color
format "fn unpack val = for p in val collect (r=p/256^2; g=p/256-r*256; b=mod p 256; color r g b)\n"
for r = 0 to h-1 do-- for each row in the bitmap
-- have function write the column of pixels to the bitmap
( format "setpixels % [0,%] (unpack #("bname r
pixels=getpixels b [0,r] w-- read in the column of pixels
for c = 1 to w do-- loop through each pixel
( p = pixels[c]-- get the pixel
-- pack the pixel into an integer and write it out
format "%" (((p.r as integer)*256+(p.g as integer))*256+(p.b as integer))
if c != w then-- if not at end of data
format ", "-- write a comma
else
format "))\n"-- else close out the line
)
)
format "return %\n" bname-- function returns the bitmap
format ")\n----------\n"-- finish off function definition
)
OUTPUT:
----------
fn load_bitmap_convert = (
local bitmap_convert=bitmap 4 4
fn unpack val = for p in val collect (r=p/256^2; g=p/256-r*256; b=mod p 256; color r g b)
setpixels bitmap_convert [0,0] (unpack #(12632256, 12632256, 12632256, 12632256))
setpixels bitmap_convert [0,1] (unpack #(255, 255, 255, 255))
setpixels bitmap_convert [0,2] (unpack #(255, 255, 255, 255))
setpixels bitmap_convert [0,3] (unpack #(255, 12632256, 12632256, 12632256))
return bitmap_convert
)
----------
Also see the example inPoint3 Values for another usage of class Bitmap.