You can use callbacks to link an attribute to a complex script that performs any number of functions. For example, callback scripts can be used to adjust the Attribute Editor controls in a way that affects your scene.
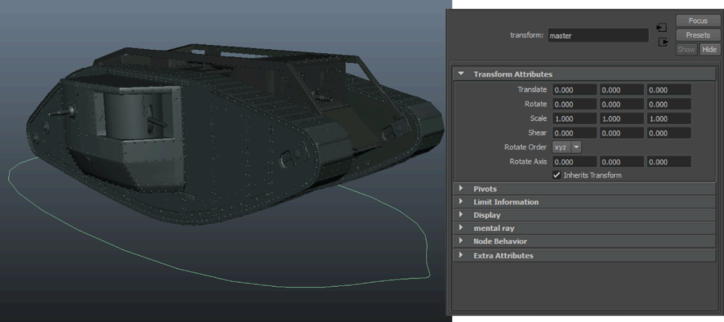
The following image shows a tank created in Maya. Its master node is selected and it appears in the Attribute Editor with the default view selected.
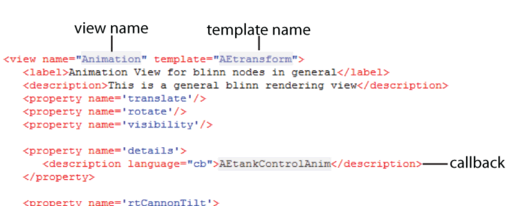
In the following image, a view called
Animation has been selected. This view has been customized to meet the needs of an Animator. For example, the
Details attribute is turned off. As a result, the tank's details are hidden in the scene.


This view has been created in a custom template named
AETransformTemplate.xml, which calls a procedure named
AEtankControlAnim:

AEtankControlAnim can be created in MEL or Python (see Create custom attribute controls) and contains the callback script.
The callback script completes two tasks:
- It creates the control based on the attribute type.
For example, the Details attribute includes the following line of code in its attribute declaration:
<attribute name='details' type='maya.bool'>
Since the type is maya.bool, the Attribute Editor creates a checkbox. For a list of types see Attribute types. - It runs a second script, a change command, when the value of a control is changed. This keeps the Attribute Editor and the attribute in sync.
To make changes to the
Details attribute, several extra lines of code are added to the
AEtankControlAnim procedure.


The change command named
tankControlAnimCB launches the second script, which makes sure the
Details checkbox is turned off in the
Attribute Editor layout.
Tip: See
Avoid unneccessarily dirtying your scene when using callbacks to clear your scene's dirty state with a command flag.