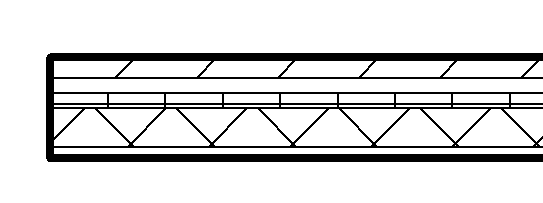
Walls, floors, ceilings, and roofs can be composed of parallel layers.
A compound element can consist of a single continuous layer of material (such as plywood) or multiple layers (such as gypsum board, studs, insulation, air spaces, bricks, and sheathing). In addition, each layer within the component serves a particular purpose. For example, some layers provide structural support, while others act as thermal barriers. Revit considers the function of each layer, and joins corresponding layers in adjacent compound structures by matching their functional priority.
You can represent each layer by setting the layer's material, thickness, and function. When a view's detail level is set to Medium or Fine, the layers of the compound element are represented. Lines between layers in a compound structure display using the Common Edges subcategory of the element. Override host layers for additional control over the layer display in compound structure. At Coarse detail level, only the boundaries of the compound element display. A coarse scale fill pattern and coarse scale fill color can be set in the type properties of the compound element.
You typically see compound geometry in floor plans, reflected ceiling plans, and sections. In the following example, a 7-layer wall is displayed in a plan view.