Heat Sinks
View more information about the heat sink material correlations and governing equations here.
Micro Channel
Total thermal resistance:
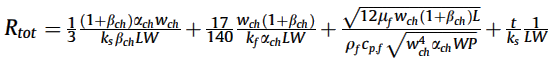
Pressure drop:
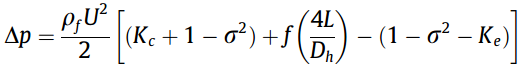
Contraction and expansion coefficients:
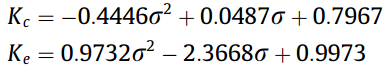
Nusselt number:
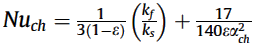
Friction factor correlation:
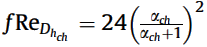
The correlations for micro channel configurations are subject to geometric and operating conditions:
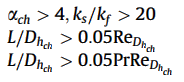
Pin-Fin
Total thermal resistance:
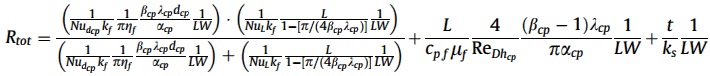
Pressure drop:
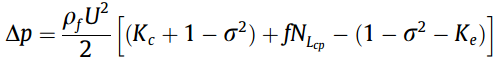
Contraction and expansion coefficients:
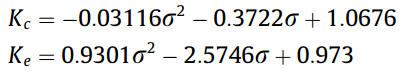
Nusselt number:
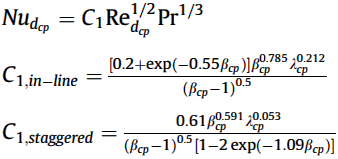
Friction factor correlation for inline:
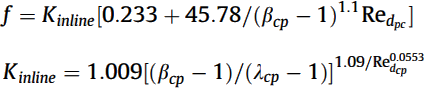
Friction factor correlation for staggered:

The correlations for the pin-fin configurations are subject to geometric and operating conditions:
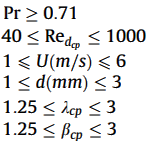
Offset Strip
Total thermal resistance:
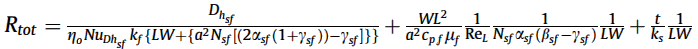
Pressure drop:
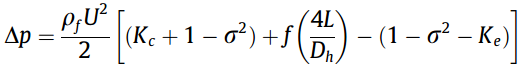
Contraction and expansion coefficients:
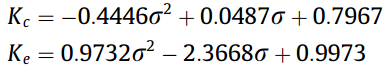
Nusselt number:
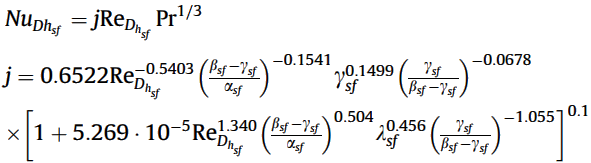
Friction factor correlation:
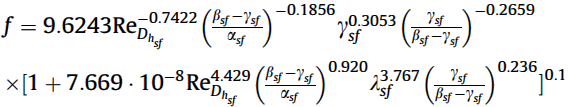
The correlations for the offset strip configurations apply to all gases and most liquids with moderate Pr.
Variables and nomenclature
The following common variables are used in the heat sink correlations:
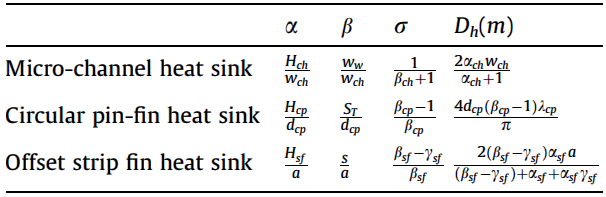
Nomenclature
a is the offset strip fin length (m)
b is the offset strip fin thickness (m)
cpf is the specific heat (J/kg K)
d is the diameter (m)
Dh is the hydraulic diameter (m)
f is the friction factor
H is the fin height (m)
k is the thermal conductivity (W/m K)
Kc is the coefficient of abrupt contraction
Ke is the coefficient of abrupt expansion
L is the length of heat sink in flow direction, length of heated area (m)
Lc is the characteristic length (m)
N is the number of fins
NT is the number of fins in lateral direction
NL is the number of fins in flow direction
Nuch is the Nusselt number based on channel width and height
Nud is the Nusselt number based on diameter d
NuDh is the Nusselt number based on hydraulic diameter Dh
NuL is the Nusselt number based on length L
P is the power (W)
Pr is the Prandtl number
R is the thermal resistance (K/W)
Red is the Reynolds number based on diameter d
ReDh is the Reynolds number based on hydraulic diameter Dh
ReL is the Reynolds number based on length L
ST is the circular pin fin lateral fin spacing (m)
SL is the circular pin fin streamwise fin spacing (m)
s is the offset strip fin lateral fin spacing (m)
t is the base thickness (m)
U is the velocity (m/s)
wch is the micro-channel width (m)
ww is the micro-channel fin thickness (m)
W is the width of heat sink (m)
Greek symbols
α is the fin height to fin characteristic length Lc ratio
β is the lateral fin spacing to fin characteristic length Lc ratio
Δp is the pressure drop (Pa)
ε is the porosity defined as wch/(wch + ww)
ν f is the fin efficiency
ν o is the overall heat sink efficiency
γ sf is the offset strip fin width to fin length ratio defined as b/a
λ cp is the streamwise pitch defined as SL/dcp
μ is the viscosity (kg/m s)
ρ is the density (kg/m3)
σ is the unit frontal-area ratio
Subscripts
ch denotes channel
cp denotes circular pin-fin
f denotes fluid
s denotes solid
sf denotes offset strip fin
tot denotes total
Reference
For further details, including optimization and comparative studies, reference the International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer. (20 May 2009). Multi-objective thermal design optimization and comparative analysis of electronics cooling technologies. (Publication 52 (2009) 4317-4326). Sidy Ndao, Yaov Peles, Michael K. Jensen.