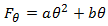Erosion
Autodesk® CFD uses the Edwards/Tulsa model to calculate the solid material erosion rate due to solid particles in a moving fluid. An example is sand particles immersed in flowing oil. The following equation describes the erosion empirical model:
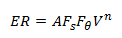
Where:
ER = Normalized Erosion Rate = mass of material lost to erosion/ mass of colliding particles
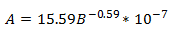
(B = Brinell harndess = 120 for Carbon Steel)
Fs = 1.0 | for sharp (angular) sand particles |
Fs = 0.53 | for semi-rounded sand particles |
Fs = 0.2 | for fully rounded sand particles |
|
| 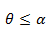 |
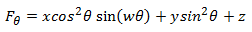 | 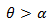 |
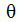 = particle impingement angle
= particle impingement angle
V = particle velocity
Erosion Model Constants for Carbon Steel
Constant | Value |
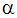 |  |
a | -33.4 |
b | 17.9 |
w | 1.0 |
x | 1.239 |
y | -0.1192 |
z | 2.167 |
n | 1.73 |
The erosion rate is calculated for a group of particles hitting a solid surface. The rate is accumulated and averaged over the entire surface. The value is then displayed as a scalar result quantity.
Reference
Edwards, Jermy K., McLaury Brenton S., Shirazi Siamack A. 2000. Evaluation of Alternative Pipe Bend Fittings in Erosive Service. Proceedings of FEDSM 2000. ASME Fluid Engineering Division Summer Meeting: 959-966
For more about using Erosion...