The following types of spaces can be modeled in AutoCAD Architecture 2025 toolset:
Associative and Non-Associative Spaces
Associative spaces are generated from boundary objects. When the boundary objects change, the space updates accordingly.
In addition to associative spaces you can also create non-associative spaces with user-defined geometry. A non-associative space can stand alone in the drawing, but you can use it to generate calculations just like you would use an associative space.
Non-associative spaces can be connected to boundary objects after their creation; similarly, associative spaces can be disconnected from their boundary objects.
2D Spaces
2D spaces display spatial information in 2 plan dimensions.
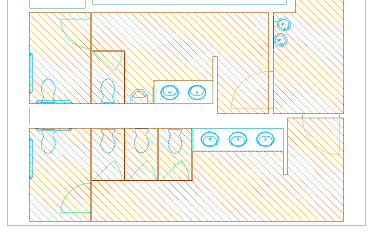
2D spaces in Plan view
The Z direction is by default set to 0 and ignored during creating, editing, and scheduling the space. 2D spaces can be rectangular or polygonal. 2D spaces can either be non-associative or associative. A 2D space can be bounded by 3D objects and linework. 2D spaces are typically used for Plan views, where 3D information is not needed.
Extruded 3D Spaces
An extruded 3D space is similar to a 2D space, but has a user-defined extrusion height. Extruded spaces are useful for regularly shaped 3D spaces like uniform-height rooms in a building. Extruded spaces can have floor and ceiling components and space above the ceiling and below the floor. The space above the ceiling is often used to place ductwork, cables and electrical installations in a room.
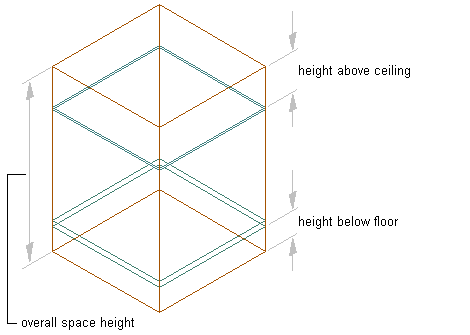
Space height components
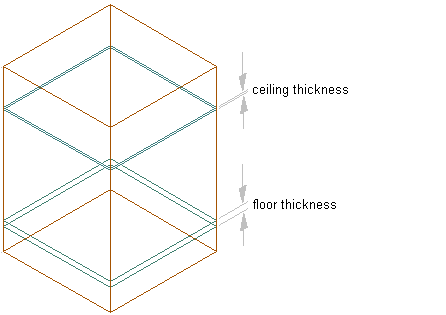
Space ceiling and floor components
Extruded 3D spaces can be associative to 3D objects and linework, but they are bounded only in the X and Y directions. The Z direction is defined by the extrusion height. If you need a space that is fully bounded by objects in all 3 spatial dimensions, you need to generate a 3D freeform space.

Additional space dimension components
3D Freeform Spaces
3D freeform spaces are generated from boundary objects, like walls and slabs, and are associative to them. Associative 3D freeform spaces must be bounded in all directions to form a valid boundary shape. A 3D freeform space is a complex 3D geometry with any number of surfaces needed to generate the space shape.
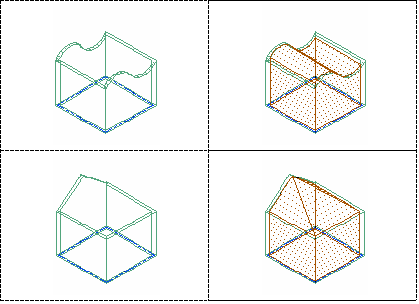
Some examples for 3D freeform spaces