Parameters for Arc-Length Methods in Nonlinear Static Analysis
Description: Defines a set of parameters for the arc-length incremental solution strategies in nonlinear static analysis.
Format:
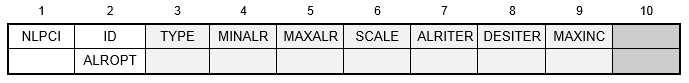
Example:

| Field | Definition | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Identification number that matches an associated NLPARM entry. | Integer > 0 | |
| TYPE | Constraint type. One of the following characters variables: CRIS, RIKS, or MRIKS. See Remark 2. | Character | CRIS |
| MINALR | Minimum allowable arc-length adjustment ratio between increments for the adaptive arc-length method. See Remarks 3 and 4. | 0.0 < Real ≤ 1.0 | 0.25 |
| MAXALR | Maximum allowable arc-length adjustment ratio between increments for the adaptive arc-length method. See Remarks 3 and 4. | Real ≥ 1.0 | 4.0 |
| SCALE | Scale factor (w) for controlling the loading contribution in the arc-length constraint. | Real ≥ 0.0 | 0.0 |
| ALRITER | Allowable arc-length adjustment ratio between iterations. See Remark 5. | Real ≥ 0 | 0.0 |
| DESITER | Desired number of iterations for convergence to be used for the adaptive arc-length adjustment. See Remarks 3 and 4. | Integer > 0 | 12 |
| MAXINC | Maximum number of controlled increment steps allowed within a subcase. See Remark 6. | Integer > 0 | 40 |
| ALROPT | Arc-length adjustment ratio method. One of the following characters variables: KRATIO, ITER, or BOTH. See Remark 7. | Character | BOTH |
Remarks:
- The NLPCI entry is selected by the Case Control command NLPARM = ID. There must also be an NLPARM entry with the same ID. The NLPCI entry is not supported in creep analysis or heat transfer solutions.
- The available constraint types are as follows:
- TYPE = CRIS:
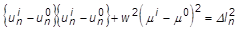
- TYPE = RIKS:
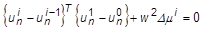
- TYPE = MRIKS:
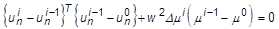
where,
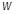 = the user-specified scaling factor (SCALE)
= the user-specified scaling factor (SCALE)
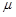 = the load factor
= the load factor
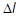 = the arc-length
= the arc-length
The constraint equation has a disparity in the dimension by mixing the displacements with the load factor. The scaling factor (
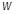 ) is introduced as user input so that the user can make constraint equation unit-dependent by a proper scaling of the load factor
) is introduced as user input so that the user can make constraint equation unit-dependent by a proper scaling of the load factor
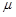 . As the value of
. As the value of
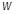 is increased, the constraint equation is gradually dominated by the load term. In the limiting case of infinite
is increased, the constraint equation is gradually dominated by the load term. In the limiting case of infinite
 , the arc-length method is degenerated to the conventional Newton's method.
, the arc-length method is degenerated to the conventional Newton's method.
- TYPE = CRIS:
- The MINALR and MAXALR fields are used to limit the adjustment of the arc-length from one load increment to the next by:
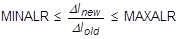
The arc-length adjustment is based on the convergence rate (i.e., number of iterations required for convergence) and/or the change in stiffness. For constant arc-length during analysis, use MINALR = MAXALR = 1.
- The arc-length
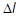 for the variable arc-length strategy is adjusted based on the number of iterations that were required for convergence in the previous load increment
for the variable arc-length strategy is adjusted based on the number of iterations that were required for convergence in the previous load increment
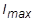 and the number of iterations desired for convergence in the current load increment (DESITER) as follows:
and the number of iterations desired for convergence in the current load increment (DESITER) as follows:

- The ALRITER field is used to limit the adjustment of the arc-length from one iteration to the next using:
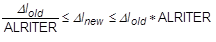
The default ALRITER value of zero disables limiting the arc-length adjustment during iterations.
- The MAXINC field is used to limit the number of controlled increment steps in case the solution never reaches the specified load. The default is the number of increments, NINC, specified on the corresponding NLPARM entry or 40 which ever is greater. This field is useful in limiting the number of increments computed for a collapse analysis.
- When ALROPT is set to ITER, arc-length adjustment is based on the convergence rate (i.e., number of iterations required for convergence). When ALROPT is set to KRATIO, adjustment is based on the change in stiffness. The default BOTH setting will consider both parameters.