4. Start Working with Commands
Commands are key to using AutoCAD efficiently. You can access them by using your mouse, Command line, Dynamic Input, or a combination of all three.
The following video demonstrates some of the learning objectives covered in this topic:
Learning Objectives
Prerequisites
You should know how to do the following before continuing:
Prepare for the Exercises
To follow along with the exercises in this topic, download the ZIP file containing the sample drawings.
![]() Download: Sample drawing files used for the following exercises
Download: Sample drawing files used for the following exercises
The ZIP file contains all drawings used for the exercises and only needs to be downloaded once. Keep the ZIP file to restore the original state of the sample drawings.
Start a Command
You can start a command by using the ribbon, toolbars, and menus at the top of the application. But the most efficient way to start a command on AutoCAD is the Command window, which is what we'll cover here.

Notice that as you start to type a command, it completes automatically. When several possibilities are available such as in the example below, make your choice by clicking it or using the arrow keys and then pressing Enter or the spacebar.
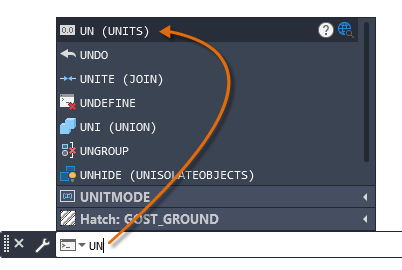
Some commands have abbreviated names or command aliases. For example, you can enter c as an alias for CIRCLE. After you type the command on the command line, press Enter or the spacebar to start the command. You can also repeat the previous command by pressing Enter or the spacebar.
Try It: Draw with Commands
In this exercise, draw a circle with a command or command alias.
Type in c or CIRCLE into the Command window, and press Enter. We'll pick this up in the next section.
Enter Values in Response to a Command Prompt
Often when you enter a command, the Command window will ask you to enter a value in response. This could be strings, coordinates, or numeric values.
Try It: Specify Values in Command Prompts
In this exercise, draw a circle of a specific size using the Command prompt.
From the previous exercise, you should be seeing this:

Pick a point on your drawing as the center point.
Then, the Command line will ask you for the radius of the circle.

Enter a value or pick a point on your drawing, and press Enter.
End the command by pressing Esc.
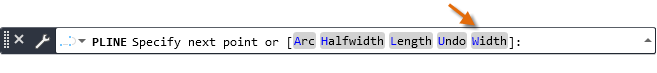
Use Command Options
When you start a command, you will often see a set of options on the Command line. These will appear in brackets, with blue letters signifying the alias you can type in to choose the option.
Try It: Draw a 2-Point Circle
In this exercise, use the command option 2P to draw a 2-point circle.
- Type in c or CIRCLE on the Command line.
- When the command options appear, type in or click 2P to draw a 2-point circle.
- Type in coordinates or click in the drawing to determine the first point of the circle.
- Then, type in absolute or relative coordinates or click in the drawing to determine the second point.
Try It: Draw a Line
In this exercise, use command options to create a line.
- Type in l or LINE on the Command line. Specify your first point by typing in the absolute coordinates or clicking.
- When the command options appear, type in the absolute or relative coordinates of the next point in the line. Or click or type U for Undo.
- Repeat this with the third point of the line.
- Then, for the fourth point in the line, you will have two command options: Close and Undo. Click or type in c or u for these options. Close will create a closed shape out of your four lines.
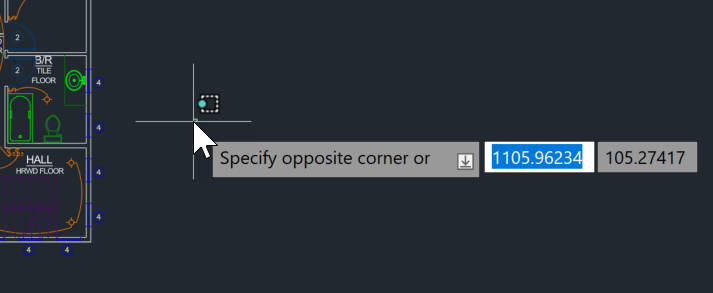
Use Dynamic Input
If your Dynamic Input is enabled, you will see a prompt at the cursor where you can enter commands and specify command options and values.
Try It: Draw a 2-Point Circle
In this exercise, use Dynamic Input to draw a 2-point circle.
- Type in c or CIRCLE on the Command line.
- When the command options appear, type in 2P to draw a 2-point circle.
- Type in coordinates to determine the first point of the circle.
- Type in absolute or relative coordinates to determine the second point.
Try It: Draw a Line
In this exercise, use Dynamic Input to draw a line.
- Type in l or LINE on the Command line.
- Where you see Specify first point:, type in the coordinates of the first point in the line.
- Where you see Specify next point:, type in the absolute or relative coordinates of the next point in the line. Or type u for Undo.
- Repeat this with the third point of the line.
- Then, for the fourth point in the line, you will have two command options: Close and Undo. Type c or u for these options. Close will create a closed shape out of your four lines.
Cancel and Undo Commands
Here's how to cancel or undo commands.
Cancel a Command
If you accidentally click in the screen, display a shortcut menu, or start a command, you can always escape by pressing the ESC key on your keyboard.
Cancel a Selection
When you click in the drawing area and move the mouse, you are in object selection mode. Press ESC to cancel.
Undo (or Redo) Commands
Occasionally you will need to undo some of your work. Two standard toolbar buttons reverse mistakes in your drawings.
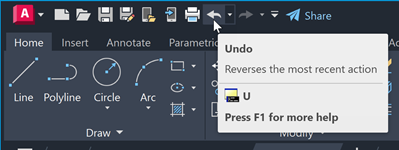
- Undo. You can backtrack previous actions. For example, click Undo to delete an object that you just created.
- Redo. You can reinstate the actions that you backtracked with Undo. For example, click Redo to restore the object you just deleted.
Summary
You've just learned how to work with commands: start them, enter values and options, use Dynamic Input, and cancel and undo commands.
Related Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| DSETTINGS | Sets grid and snap, polar and object snap tracking, object snap modes, Dynamic Input, and Quick Properties. |