General Improvements
Find denoiser changes and options for setting the texture coordinate system used for texture projections. Check out the Streaming App, clamping, Scenegraph tree, Culled Backface, and raytracing statistics improvements. For OpenXR, we added passthrough support. Finally, for Python, you can now get profile information and trigger XR actions.
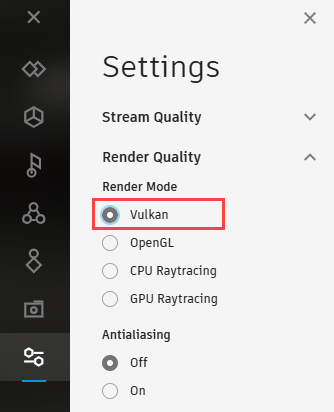
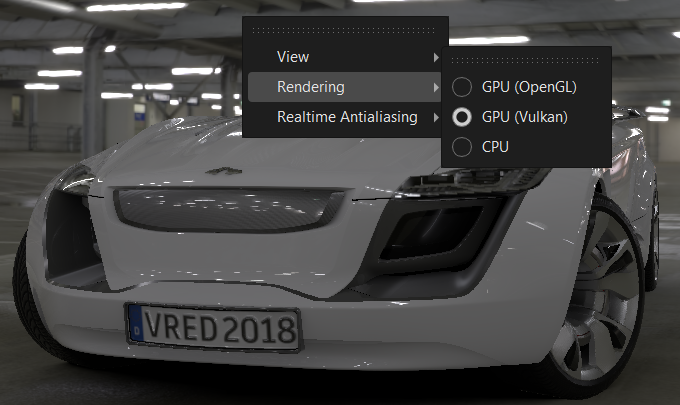
Vulkan in Streaming App and VRED Go
We added the Vulkan renderer to the Settings > Render Quality of the Streaming App and to the Rendering context menu of VRED Go.
| Streaming App | VRED Go |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Custom URL Routing
We've added support for custom URL routing in Streaming App to identify the VRED instance for a certain user. The app can now connect the stream to the root path after a custom URL path is used.
Use the following two new VRED Streaming App search parameters:
host- This sets the VRED host to connect to, which allows the user to serve the VRED Streaming App from any web server and define the VRED host via this parameter. This is an example value:127.0.0.1:8888.basePath- This sets the base path used for all connections to the VRED host. The additional path allows users to add router or load balancer information. This is an example value:my-instance.
Here is an example VRED Stream App URL with host and basePath parameters set:
https://localhost:8888/apps/VREDStreamApp?host=10.180.92.44:8888&basePath=vred-instance
It lets the Streaming App connect to the stream URL,wss://10.180.92.44:8888/vred-instance/socketStream, instead of the default behavior, wss://localhost:8888/socketstream.
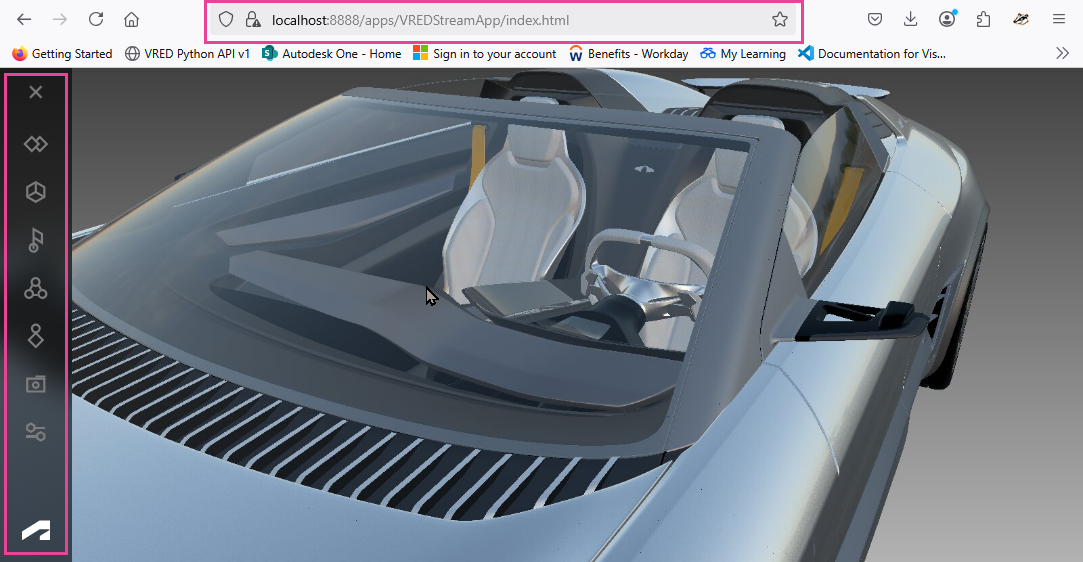
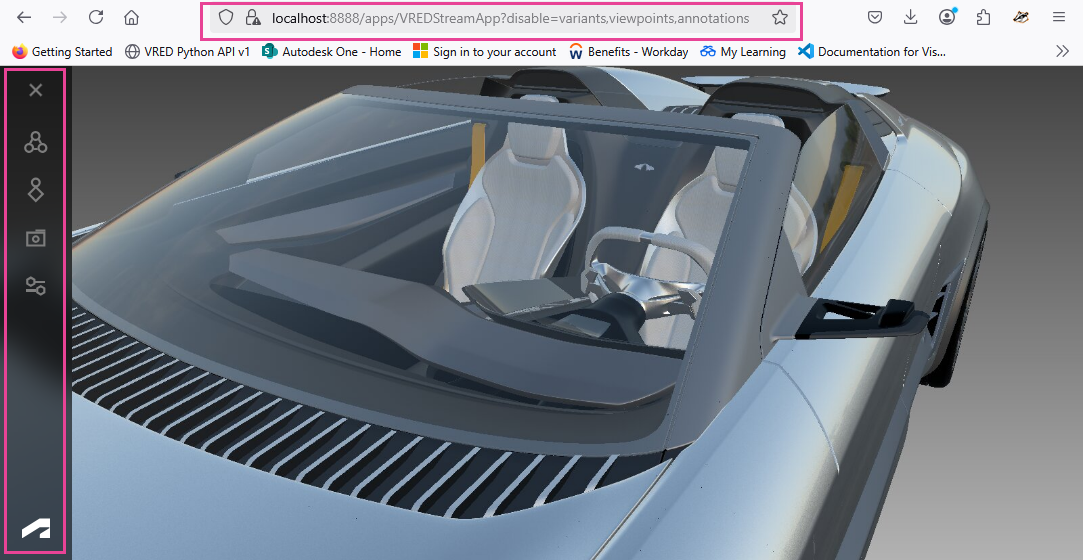
Customizing the Streaming App UI
We've added an option to disable features in the Streaming App.
Use the following new VRED Streaming App search parameter:
disable- Enter a comma-separated list of UI features to disable. Notice there is no space between the comma and the next parameter. This is an example value:collaboration,presenter.
Here is an example of a VRED Streaming App URL with a disable parameter set:
https://localhost:8888/apps/VREDStreamApp?disable=variants,viewpoints,annotations,collaboration,presenter,snapshot,settings
| Default Streaming App | Customized Streaming App |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Here is a list of features that can be disabled:
- annotations
- collaboration
- presenter
- settings
- snapshot
- variants
- viewpoints
The left navigation bar becomes invisible when all features are deactivated.
Keyboard Use for the Streaming App
We've added the preference option, Enable Key Events, for using A-Z and 0-9 keyboard events in the Streaming App. Find it in the Preferences > General Settings > Web Interface > Base section. Enable Web Server must be enabled to access this option. This makes it possible to enter keyboard shortcuts for such things as switching camera modes.
This can also be done through Python, using only Key_A to Key_Z and Key_0 to Key_9. For a list of these keys, see the vrController section of Python v1 Variables.
The following script demonstrates how you can bind these keys in a Python script.
keyA = vrKey(Key_A)
keyA.connect("print(\"Key_A pressed\")")
keyF = vrKey(Key_F)
keyF.connect("toggleFullscreen(0, 0)")XR Improvements
Find video passthrough, Python implementation for XR actions, and Vive Focus Vision support in 2026.
Video Passthrough for OpenXR
In OpenXR, we implemented the Meta XR_FB_passthrough extention, which enables users to see their physical environment when wearing a VR headset that blocks light. However, this is a Beta feature and must be unlocked and enabled in the Meta Quest Link runtime and requires a Meta developer account. We recommend reaching out to Meta if you require assistance in activating this feature.
Trigger XR Actions via Python
We have implemented Python commands to trigger XR actions. vrdDeviceAction can now be manually executed with vrdDeviceAction.execute(device) and vrdDeviceAction.executeOnTrackedHand(trackedHand).
Here are some simple examples for how to manually activate the teleport tool on the left controller.
To get an interaction:
teleport = vrDeviceService.getInteraction("Teleport")To get an action you want to trigger:
teleportPrepare = teleport.getControllerAction("prepare")To execute an action on left controller:
leftController = vrDeviceService.getVRDevice("left-controller") teleportPrepare.execute(leftController)
Vive Focus Vision
Vive Focus Vision is now supported with the same features as XR Elite, such as MR and hand tracking.
Wrist Orientation
We added support for retrieving the wrist orientation of XR devices, using the function vrdVRDevice.getWristOrientationAngle.
Tracked Origin
We added support for setting the tracked origin of XR devices, using the vrDeviceService functions, setTrackingOrigin and getTrackingOrigin.
Tracked Hands
We added support for the vrDeviceService functions, getLeftTrackedHand() → vrdTrackedHand and getRightTrackedHand() → vrdTrackedHand via OpenXR.
XR Options Default Mode Preferences
We moved the Default Mode preference for setting whether to startup in MR or VR mode to Extended Reality > XR Options.
Unified Dialog Behavior
Changes were made to dialogs that weren't aligned in terms of style and usage to others in VRED. Some examples are the Powerwall Settings (View > Display > Powerwall Settings), Texture Manipulator Settings, and Undo/Redo History dialogs.
| In 2025.1 | In 2026 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Scenegraph Tree Behavior
To make the Scenegraph tree more responsive, we have removed the tree expanding/collapsing animation.
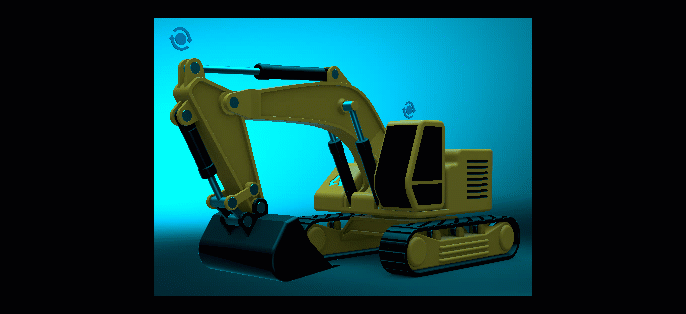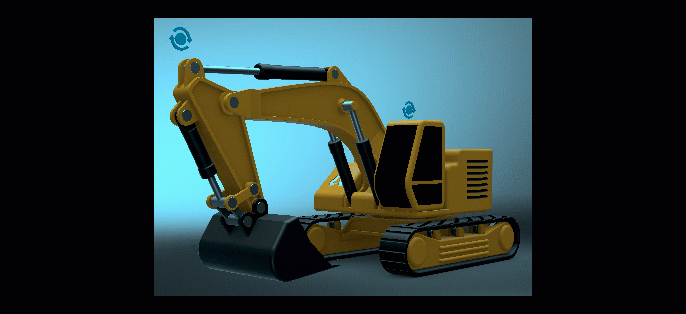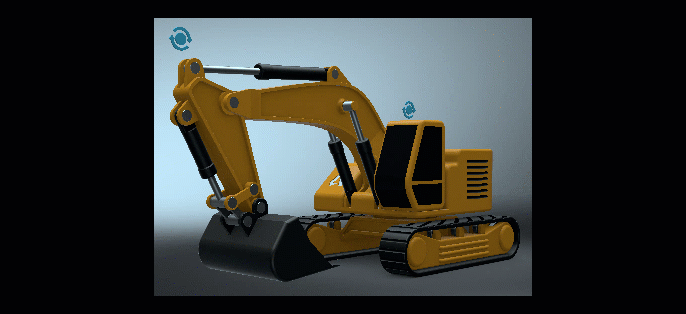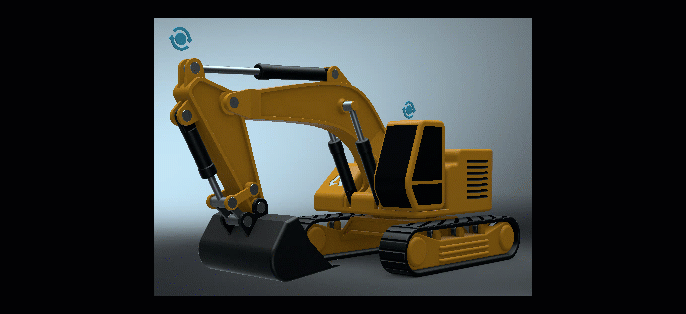
Global Grading Weighting
We added a Weight option for setting the influence of the overall color grading of the image, enabling you to set the mood of an image and convey a visual tone with color. To apply full color grading, enter 1. For no color grading, enter 0. Find this in the Camera Editor > Image Processing tab > Color Grading section.
 |
|---|
| As the Weight value is decreased, so is the color grading's influence on the image's color grading. |
Use Clamping
We increased the clamping limits for Use Clamping, as it was too low for some scenes. Now, when rendering very bright lights using physical camera settings for LEDs, areas that were grey in 2025.3 are now bright.
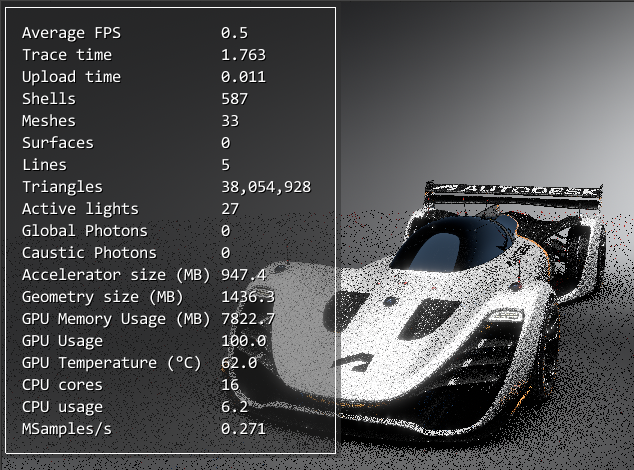
Raytracing Statistics
We added GPU Memory Usage, GPU Usage, and GPU Temperature to the raytracing statistics.
Clones
Deleting objects in the Light, Sceneplate, or Annotation Editor is no longer slow in scenes containing many clones.
Culled Backface
In OpenGL, a selection can now be made through a culled backface in the viewport. Backface culling determines if a polygon should be drawn by checking if it faces away from the camera, optimizing performance by not drawing polygons that aren't visible.
This change also affects the Autofocus when Camera Depth of Field is enabled, setting the focus to the object behind the geometry when viewed through a culled geometry.
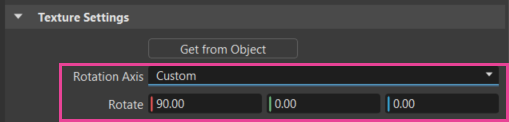
Custom Tire Rotation
We added a Custom tire rotation option to the Tire material's Texture Settings > Rotation Axis option drop-down menu. This displays extra Rotate option for entering X, Y, and Z values.
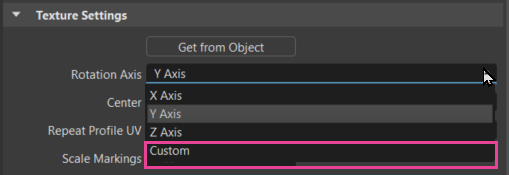
Rotate is only available for a Custom Rotation Axis. It sets a custom rotation of the tire projection. To automatically select a standard projection axis, select an object and click Get from Object.
Toolbar Changes
In 2026, you will find the following addition to the main VRED toolbar:
 DLSS - Enables or disables DLSS. Click
DLSS - Enables or disables DLSS. Click  to set the level of sampling. Choose from Ultra-Performance, Performance, Balanced, and Quality. See How to Enable Deep Learning Supersampling for information DLSS and the differences in settings.
to set the level of sampling. Choose from Ultra-Performance, Performance, Balanced, and Quality. See How to Enable Deep Learning Supersampling for information DLSS and the differences in settings. Render Guide - Opens the Render Guide to help beginner and non-advanced users quickly create a rendered cinematic moody image using its consolidated workflow-driven toolsets.
Render Guide - Opens the Render Guide to help beginner and non-advanced users quickly create a rendered cinematic moody image using its consolidated workflow-driven toolsets. Raytracing - We also include a Vulkan option for the Raytracing tool.
Raytracing - We also include a Vulkan option for the Raytracing tool.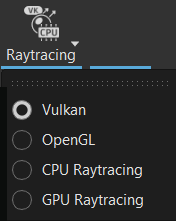
Scripting Updates
We added a new API for Render Settings and new Python classes and functions, along with some other changes.
Find profile information via Python. If you run into a bottleneck when using VRED, there is now a way to get more details for alleviating it. Use the following new Python commands to output profiling information to the console.
setCPUProfiling(true/false)- Enables/disables basic CPU function profiling. The output will only be written to the console.setProfilingInterval(double)- Sets the measuring interval in seconds for the CPU profiling function.setProfilingPruningLimit(double)- Sets a pruning limit in milliseconds for the CPU profiling. Functions requiring less time than the limit will be filtered.
Since the output is only written to the console and not to the internal terminal, VRED needs to be started with -console to get any results.
When using clustering, all render nodes will also output their statistic to their respective console.
See What's New in Python API V1 and V2 for a complete list.
Reference Editor
We improved the File > Unload performance in scenes with deep hierarchies.
Changes to the Help
The Rendering section has been updated to make it easier to find information on the Visualization Menu options like Vulkan, GPU Raytracing, and the new Rasterization Settings.